Artists who convey to life heroes and villains in animated motion pictures and video video games might have extra management over their animations, because of a brand new method launched by MIT researchers.
Their technique generates mathematical features often called barycentric coordinates, which outline how 2D and 3D shapes can bend, stretch, and transfer by way of area. For instance, an artist utilizing their instrument might select features that make the motions of a 3D cat’s tail match their imaginative and prescient for the “look” of the animated feline.
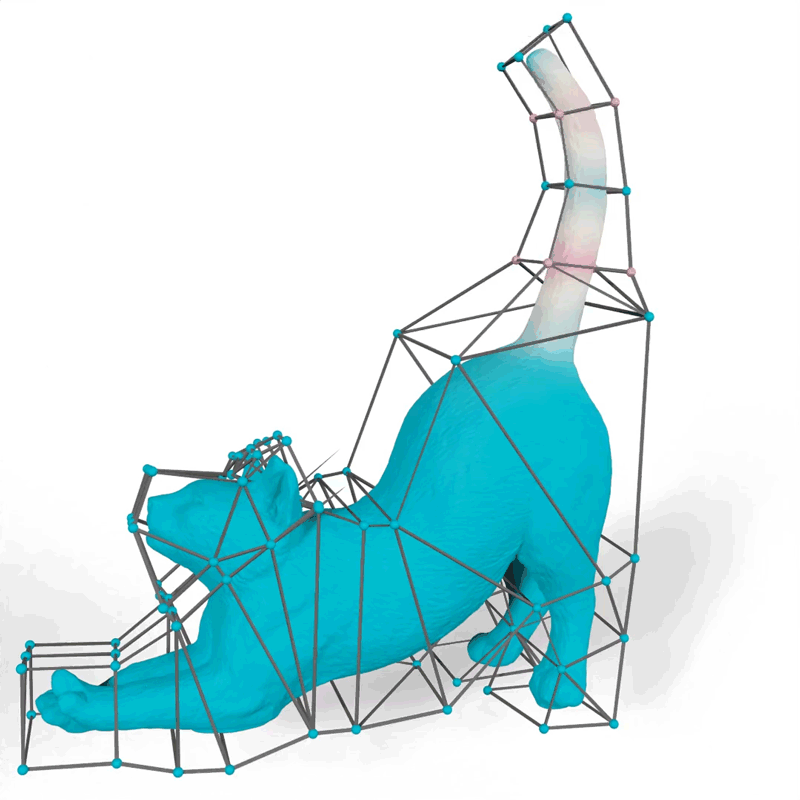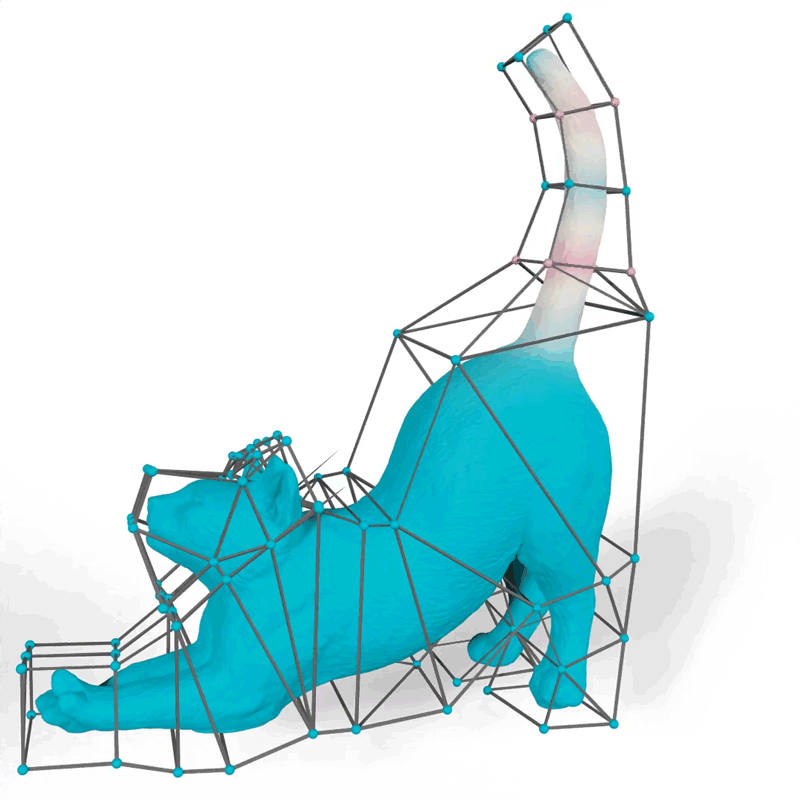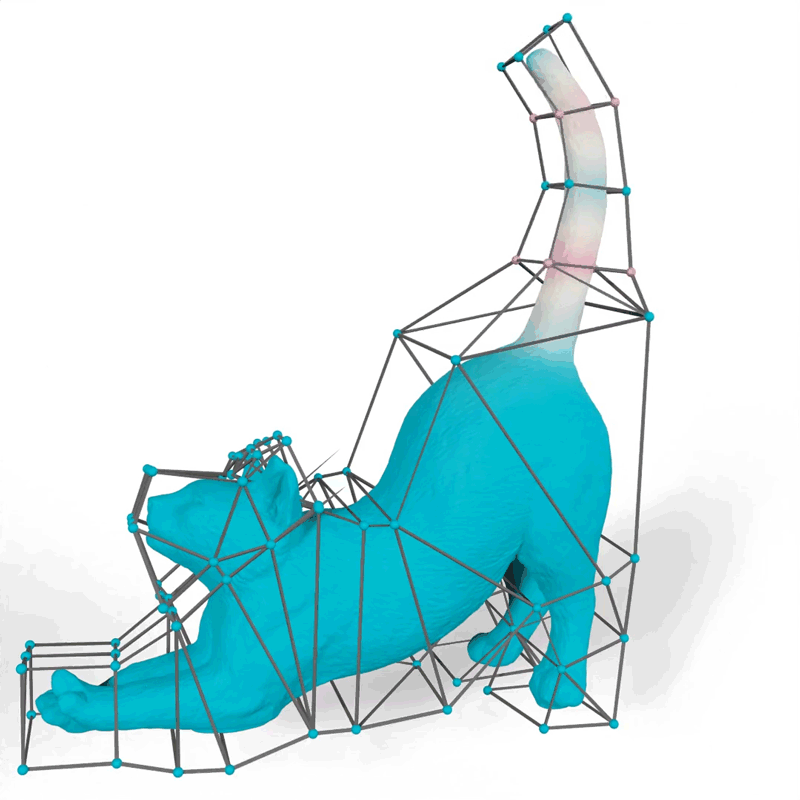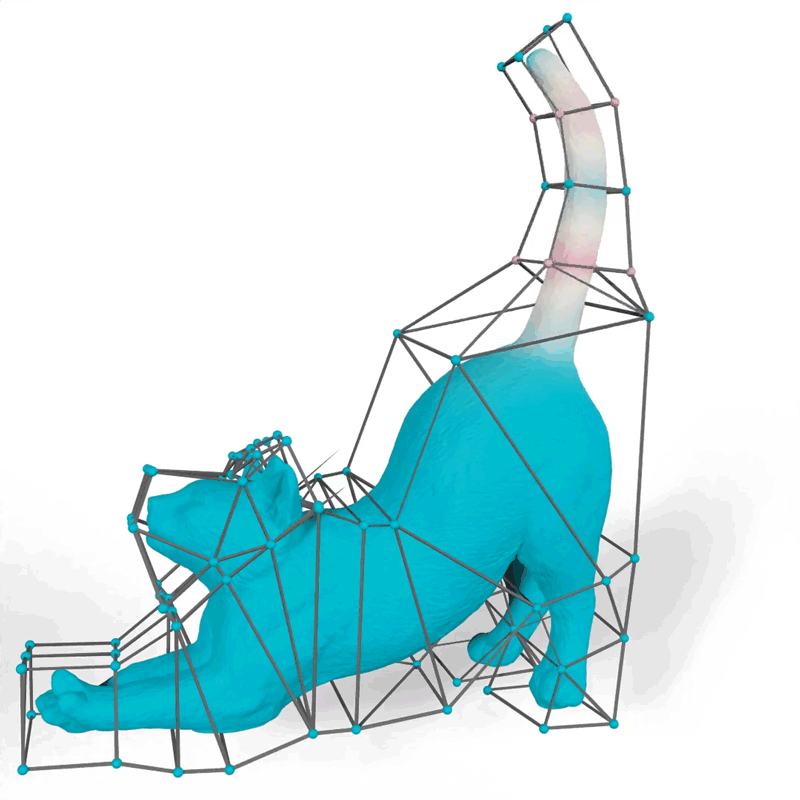
Picture: Courtesy of the researchers
Many different strategies for this drawback are rigid, offering solely a single possibility for the barycentric coordinate features for a sure animated character. Every perform could or is probably not the very best one for a selected animation. The artist must begin from scratch with a brand new strategy every time they need to attempt for a barely completely different look.
“As researchers, we will typically get caught in a loop of fixing inventive issues with out consulting with artists. What artists care about is flexibility and the ‘look’ of their last product. They don’t care concerning the partial differential equations your algorithm solves behind the scenes,” says Ana Dodik, lead writer of a paper on this method.
Past its inventive purposes, this method might be utilized in areas similar to medical imaging, structure, digital actuality, and even in pc imaginative and prescient as a instrument to assist robots work out how objects transfer in the true world.
Dodik, {an electrical} engineering and pc science (EECS) graduate pupil, wrote the paper with Oded Stein, assistant professor on the College of Southern California’s Viterbi Faculty of Engineering; Vincent Sitzmann, assistant professor of EECS who leads the Scene Illustration Group within the MIT Pc Science and Synthetic Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL); and senior writer Justin Solomon, an affiliate professor of EECS and chief of the CSAIL Geometric Information Processing Group. The analysis was just lately introduced at SIGGRAPH Asia.
A generalized strategy
When an artist animates a 2D or 3D character, one frequent method is to encompass the advanced form of the character with an easier set of factors related by line segments or triangles, referred to as a cage. The animator drags these factors to maneuver and deform the character contained in the cage. The important thing technical drawback is to find out how the character strikes when the cage is modified; this movement is decided by the design of a selected barycentric coordinate perform.
Conventional approaches use difficult equations to seek out cage-based motions which might be extraordinarily easy, avoiding kinks that might develop in a form when it’s stretched or bent to the intense. However there are various notions of how the inventive thought of “smoothness” interprets into math, every of which results in a special set of barycentric coordinate features.
The MIT researchers sought a normal strategy that enables artists to have a say in designing or selecting amongst smoothness energies for any form. Then the artist might preview the deformation and select the smoothness vitality that appears the very best to their style.
Though versatile design of barycentric coordinates is a contemporary thought, the essential mathematical development of barycentric coordinates dates again centuries. Launched by the German mathematician August Möbius in 1827, barycentric coordinates dictate how every nook of a form exerts affect over the form’s inside.
In a triangle, which is the form Möbius utilized in his calculations, barycentric coordinates are simple to design — however when the cage isn’t a triangle, the calculations turn out to be messy. Making barycentric coordinates for an advanced cage is particularly tough as a result of, for advanced shapes, every barycentric coordinate should meet a set of constraints whereas being as easy as potential.
Diverging from previous work, the workforce used a particular kind of neural community to mannequin the unknown barycentric coordinate features. A neural community, loosely based mostly on the human mind, processes an enter utilizing many layers of interconnected nodes.
Whereas neural networks are sometimes utilized in AI purposes that mimic human thought, on this venture neural networks are used for a mathematical purpose. The researchers’ community structure is aware of find out how to output barycentric coordinate features that fulfill all of the constraints precisely. They construct the constraints straight into the community, so when it generates options, they’re at all times legitimate. This development helps artists design attention-grabbing barycentric coordinates with out having to fret about mathematical facets of the issue.
“The difficult half was constructing within the constraints. Customary instruments didn’t get us all the way in which there, so we actually needed to assume exterior the field,” Dodik says.
Digital triangles
The researchers drew on the triangular barycentric coordinates Möbius launched almost 200 years in the past. These triangular coordinates are easy to compute and fulfill all the mandatory constraints, however trendy cages are rather more advanced than triangles.
To bridge the hole, the researchers’ technique covers a form with overlapping digital triangles that join triplets of factors on the surface of the cage.
“Every digital triangle defines a sound barycentric coordinate perform. We simply want a manner of mixing them,” she says.
That’s the place the neural community is available in. It predicts find out how to mix the digital triangles’ barycentric coordinates to make a extra difficult, however easy perform.
Utilizing their technique, an artist might attempt one perform, take a look at the ultimate animation, after which tweak the coordinates to generate completely different motions till they arrive at an animation that appears the way in which they need.
“From a sensible perspective, I believe the most important affect is that neural networks offer you a variety of flexibility that you just didn’t beforehand have,” Dodik says.
The researchers demonstrated how their technique might generate extra natural-looking animations than different approaches, like a cat’s tail that curves easily when it strikes as a substitute of folding rigidly close to the vertices of the cage.
Sooner or later, they need to attempt completely different methods to speed up the neural community. Additionally they need to construct this technique into an interactive interface that may allow an artist to simply iterate on animations in actual time.
This analysis was funded, partially, by the U.S. Military Analysis Workplace, the U.S. Air Pressure Workplace of Scientific Analysis, the U.S. Nationwide Science Basis, the CSAIL Techniques that Be taught Program, the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab, the Toyota-CSAIL Joint Analysis Heart, Adobe Techniques, a Google Analysis Award, the Singapore Protection Science and Expertise Company, and the Amazon Science Hub.
