ESET researchers present an evaluation of an assault carried out by a beforehand undisclosed China-aligned menace actor we have now named Blackwood, and that we imagine has been working since at the very least 2018. The attackers ship a complicated implant, which we named NSPX30, by way of adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) assaults hijacking replace requests from respectable software program.
Key factors on this blogpost:
- We found the NSPX30 implant being deployed through the replace mechanisms of respectable software program corresponding to Tencent QQ, WPS Workplace, and Sogou Pinyin.
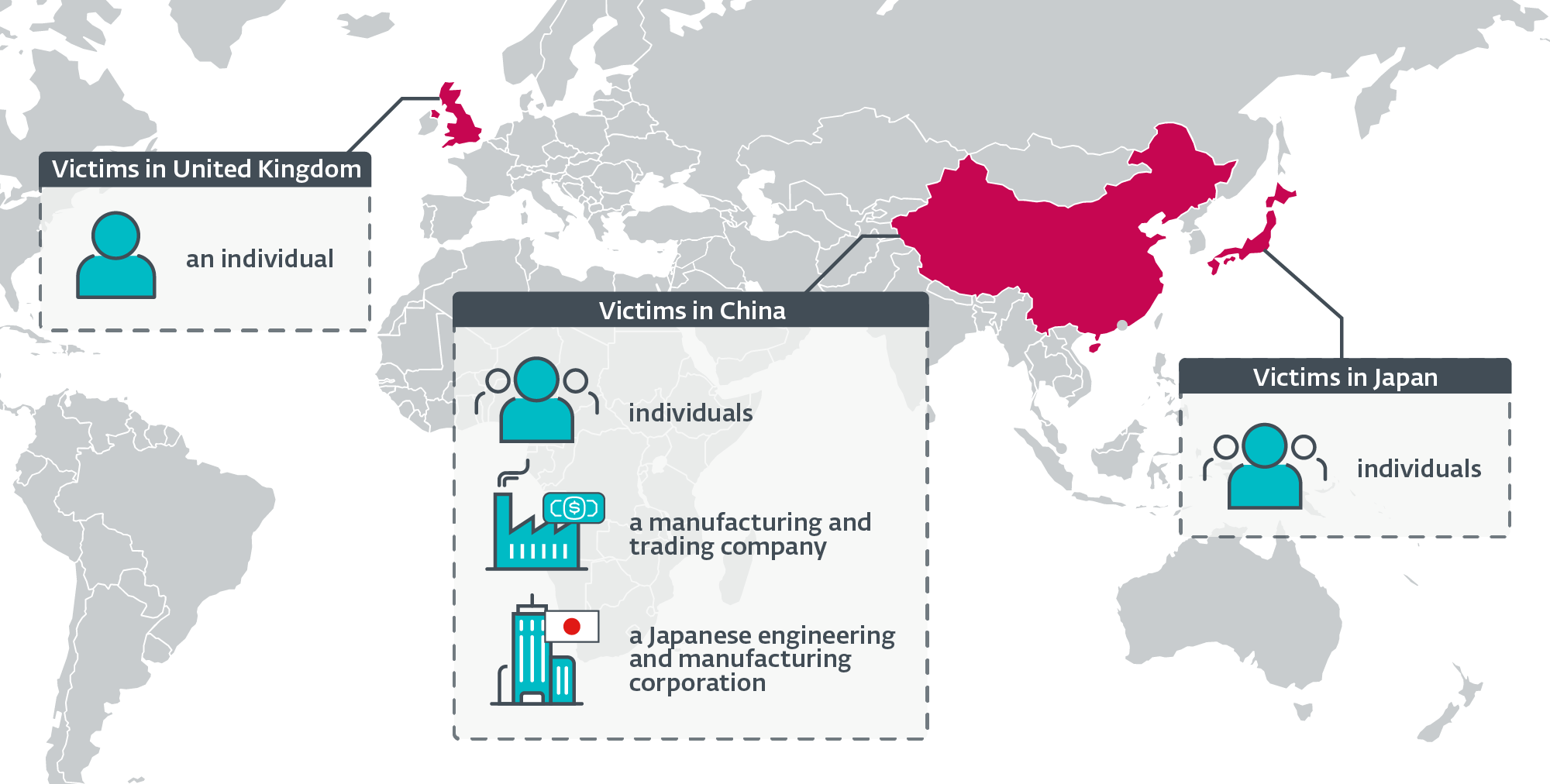
- We’ve got detected the implant in focused assaults towards Chinese language and Japanese firms, in addition to towards people positioned in China, Japan, and the UK.
- Our analysis traced the evolution of NSPX30 again to a small backdoor from 2005 that we have now named Venture Wooden, designed to gather knowledge from its victims.
- NSPX30 is a multistage implant that features a number of parts corresponding to a dropper, an installer, loaders, an orchestrator, and a backdoor. Each of the latter two have their very own units of plugins.
- The implant was designed across the attackers’ functionality to conduct packet interception, enabling NSPX30 operators to cover their infrastructure.
- NSPX30 can also be able to allowlisting itself in a number of Chinese language antimalware options.
- We attribute this exercise to a brand new APT group that we have now named Blackwood.
Blackwood Profile
Blackwood is a China-aligned APT group lively since at the very least 2018, participating in cyberespionage operations towards Chinese language and Japanese people and firms. Blackwood has capabilities to conduct adversary-in-the-middle assaults to ship the implant we named NSPX30 by way of updates of respectable software program, and to cover the situation of its command and management servers by intercepting visitors generated by the implant.
Marketing campaign overview
In 2020, a surge of malicious exercise was detected on a focused system positioned in China. The machine had turn out to be what we generally check with as a “menace magnet”, as we detected makes an attempt by attackers to make use of malware toolkits related to totally different APT teams: Evasive Panda, LuoYu, and a 3rd menace actor we monitor as LittleBear.
On that system we additionally detected suspicious information that didn’t belong to the toolkits of these three teams. This led us to begin an investigation into an implant we named NSPX30; we have been in a position to hint its evolution all the best way again to 2005.
In line with ESET telemetry, the implant was detected on a small variety of methods. The victims embrace:
- unidentified people positioned in China and Japan,
- an unidentified Chinese language-speaking particular person related to the community of a high-profile public analysis college in the UK,
- a big manufacturing and buying and selling firm in China, and
- the workplace in China of a Japanese company within the engineering and manufacturing vertical.
We’ve got additionally noticed that the attackers try and re-compromise methods if entry is misplaced.
Determine 1 is a geographical distribution of Blackwood’s targets, in response to ESET telemetry.
NSPX30 evolution
Throughout our analysis into the NSPX30 implant, we mapped its evolution again to an early ancestor – a easy backdoor we’ve named Venture Wooden. The oldest pattern of Venture Wooden we may discover was compiled in 2005, and it appears to have been used because the codebase to create a number of implants. One such implant, from which NSPX30 developed, was named DCM by its authors in 2008.
Determine 2 illustrates a timeline of those developments, primarily based on our evaluation of samples in our assortment and ESET telemetry, in addition to public documentation. Nonetheless, the occasions and knowledge documented listed below are nonetheless an incomplete image of just about 20 years of improvement and malicious exercise by an unknown variety of menace actors.
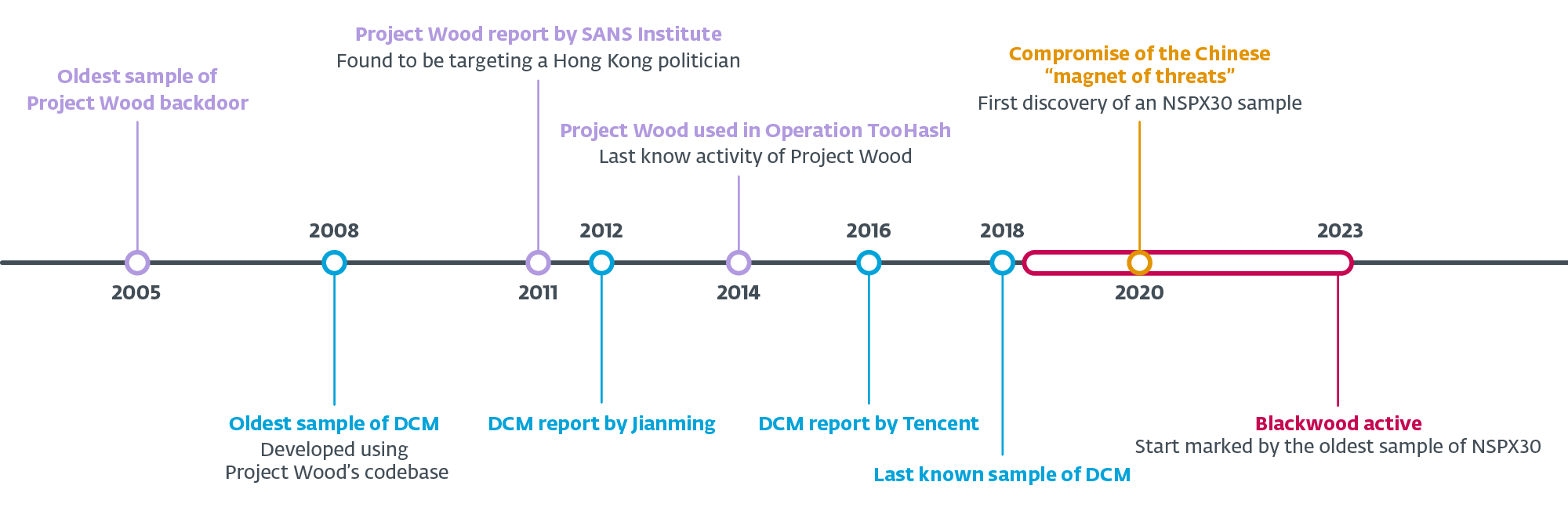
Within the following sections we describe a few of our findings relating to Venture Wooden, DCM, and NSPX30.
Venture Wooden
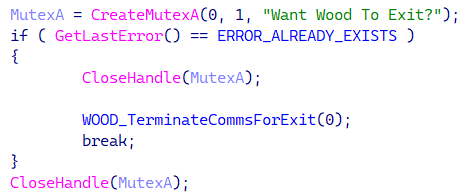
The place to begin within the evolution of those implants is a small backdoor compiled on January 9th, 2005, in response to the timestamps current within the PE header of its two parts – the loader and the backdoor. The latter has capabilities to gather system and community info, in addition to to report keystrokes and take screenshots.
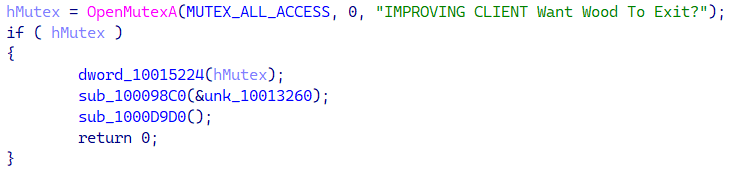
We named the backdoor Venture Wooden, primarily based on a recurring mutex title, as proven in Determine 3.
Compilation timestamps are unreliable indicators, as they are often tampered by attackers; due to this fact, on this particular case, we thought of extra knowledge factors. First, the timestamps from the PE header of the loader and backdoor samples; see Desk 1. There’s solely a distinction of 17 seconds within the compilation time of each parts.
Desk 1. PE compilation timestamps in parts from the 2005 pattern
|
SHA-1 |
Filename |
PE compilation timestamp |
Description |
|
9A1B575BCA0DC969B134 |
MainFuncOften.dll |
2005-01-09 08:21:22 |
Venture Wooden backdoor. The timestamp from the Export Desk matches the PE compilation timestamp. |
|
834EAB42383E171DD6A4 |
N/A |
2005-01-09 08:21:39 |
The Venture Wooden loader accommodates the backdoor embedded as a useful resource. |
The second knowledge level comes from the dropper pattern that was compressed utilizing UPX. This software inserts its model (Determine 4) into the ensuing compressed file – on this case, UPX model 1.24, which was launched in 2003, previous to the compilation date of the pattern.
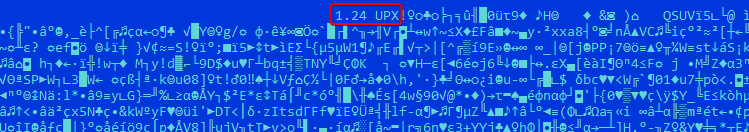
The third knowledge level is the legitimate metadata from the PE Wealthy Headers (Determine 5) which point out that the pattern was compiled utilizing Visible Studio 6.0, launched in 1998, previous to the pattern’s compilation date.
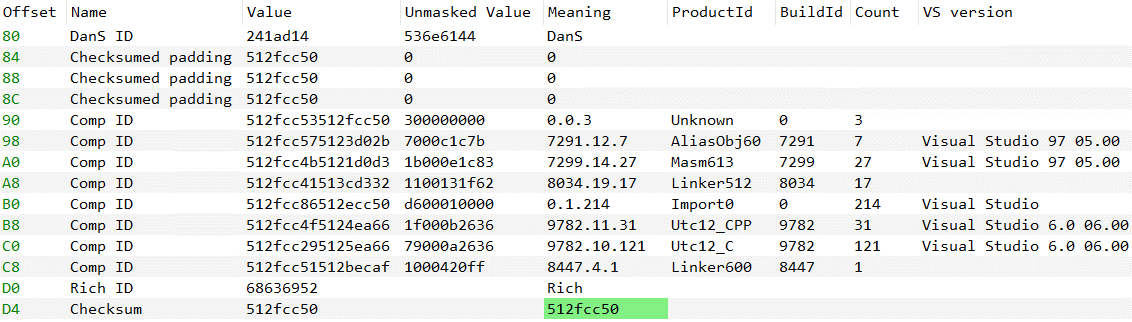
We assess that it’s unlikely that the timestamps, Wealthy Headers metadata, and UPX model have been all manipulated by the attackers.
Public documentation
In line with a technical paper revealed by the SANS Institute on September 2011, an unnamed and unattributed backdoor (Venture Wooden) was used to focus on a political determine from Hong Kong through spearphishing emails.
In October 2014, G DATA revealed a report of a marketing campaign it named Operation TooHash, which has since been attributed to the Gelsemium APT group. The rootkit G DATA named DirectsX masses a variant of the Venture Wooden backdoor (see Determine 6) with some options seen in DCM and later in NSPX30, corresponding to allowlisting itself in cybersecurity merchandise (detailed later, in Desk 4).
DCM aka Darkish Specter
The early Venture Wooden served as a codebase for a number of initiatives; one in every of them is an implant known as DCM (see Determine 7) by its authors.

The report from Tencent in 2016 describes a extra developed DCM variant that depends on the AitM capabilities of the attackers to compromise its victims by delivering the DCM installer as a software program replace, and to exfiltrate knowledge through DNS requests to respectable servers. The final time that we noticed DCM utilized in an assault was in 2018.
Public documentation
DCM was first documented by the Chinese language firm Jiangmin in 2012, though it was left unnamed at that time, and was later named Darkish Specter by Tencent in 2016.
NSPX30
The oldest pattern of NSPX30 that we have now discovered was compiled on June 6th, 2018. NSPX30 has a special element configuration than DCM as a result of its operation has been divided into two phases, relying totally on the attacker’s AitM functionality. DCM’s code was cut up into smaller parts.
We named the implant after PDB paths present in plugin samples:
- Z:Workspacemm32NSPX30Pluginspluginb001.pdb
- Z:WorkspaceCodeMMX30ProtrunkMMPluginshookdllReleasehookdll.pdb
We imagine that NSP refers to its persistence approach: the persistent loader DLL, which on disk is known as msnsp.dll, is internally named mynsp.dll (in response to the Export Desk knowledge), in all probability as a result of it’s put in as a Winsock namestempo provider (NSP).
Lastly, to the most effective of our data, NSPX30 has not been publicly documented previous to this publication.
Technical evaluation
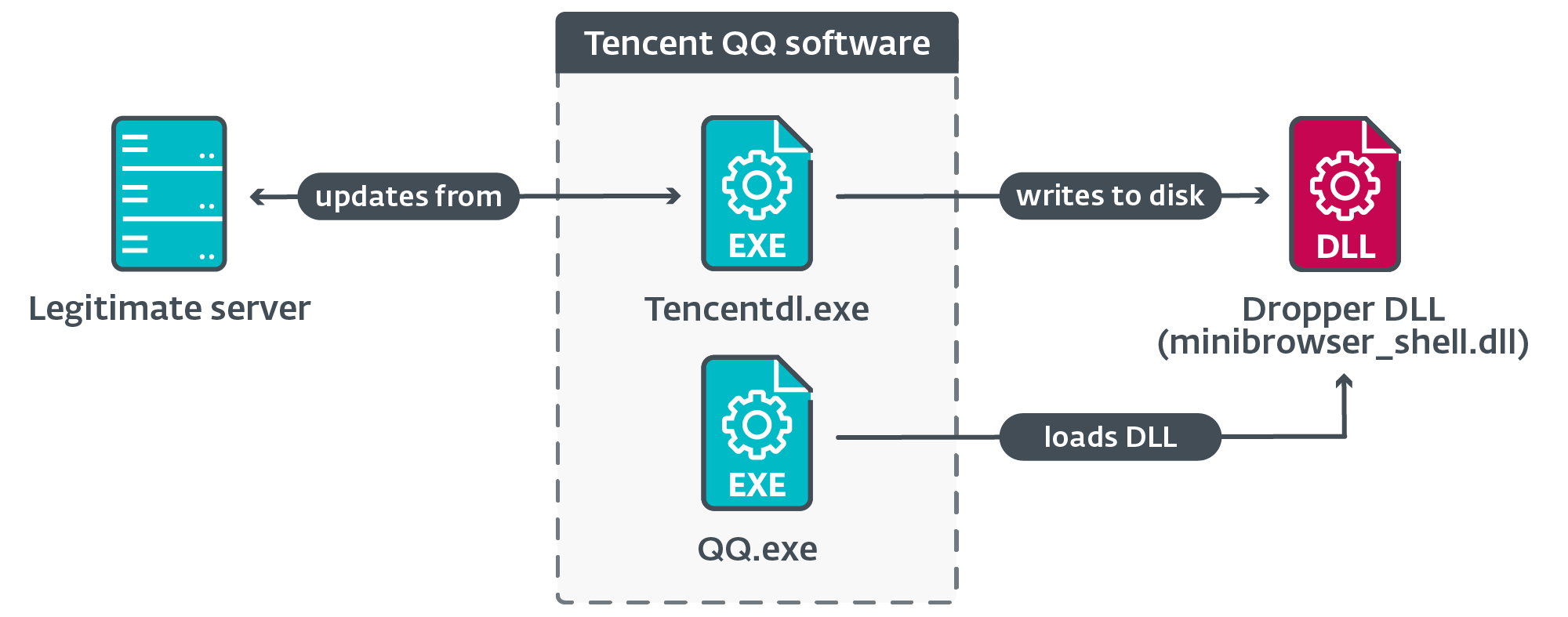
Utilizing ESET telemetry, we decided that machines are compromised when respectable software program makes an attempt to obtain updates from respectable servers utilizing the (unencrypted) HTTP protocol. Hijacked software program updates embrace these for in style Chinese language software program corresponding to Tencent QQ, Sogou Pinyin, and WPS Workplace.
An illustration of the chain of execution as seen in ESET telemetry is proven in Determine 8.
In Desk 2, we offer an instance of a URL and the IP tackle to which the area was resolved on the person’s system on the time the obtain occurred.
Desk 2. An noticed URL, server IP tackle, and course of title of a respectable downloader element
|
URL |
First seen |
IP tackle |
ASN |
Downloader |
|
http://dl_dir.qq[.]com/ |
2021‑10‑17 |
183.134.93[.]171 |
AS58461 (CHINANET) |
Tencentdl.exe |
In line with ESET telemetry and passive DNS info, the IP addresses that noticed on different circumstances, are related to domains from respectable software program firms; we have now registered as much as thousands and thousands of connections on a few of them, and we have now seen respectable software program parts being downloaded from these IP addresses.
Community implant speculation
How precisely the attackers are in a position to ship NSPX30 as malicious updates stays unknown to us, as we have now but to find the software that allows the attackers to compromise their targets initially.
Primarily based on our personal expertise with China-aligned menace actors that exhibit these capabilities (Evasive Panda and TheWizards), in addition to current analysis on router implants attributed to BlackTech and Camaro Dragon (aka Mustang Panda), we speculate that the attackers are deploying a community implant within the networks of the victims, presumably on weak community home equipment corresponding to routers or gateways.
The truth that we discovered no indications of visitors redirection through DNS would possibly point out that when the hypothesized community implant intercepts unencrypted HTTP visitors associated to updates, it replies with the NSPX30 implant’s dropper within the type of a DLL, an executable file, or a ZIP archive containing the DLL.
Beforehand, we talked about that the NSPX30 implant makes use of the packet interception functionality of the attackers to be able to anonymize its C&C infrastructure. Within the following subsections we are going to describe how they do that.
HTTP interception
To obtain the backdoor, the orchestrator performs an HTTP request (Determine 9) to the Baidu’s web site – a respectable Chinese language search engine and software program supplier – with a peculiar Consumer-Agent masquerading as Web Explorer on Home windows 98. The response from the server is saved to a file from which the backdoor element is extracted and loaded into reminiscence.
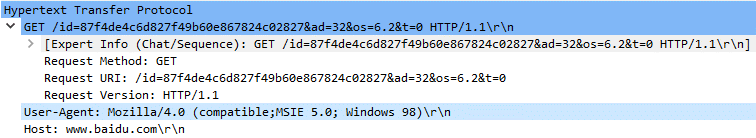
The Request-URI is customized and contains info from the orchestrator and the compromised system. In non-intercepted requests, issuing such a request to the respectable server returns a 404 error code. The same process is utilized by the backdoor to obtain plugins, utilizing a barely totally different Request-URI.
The community implant would merely have to search for HTTP GET requests to www.baidu.com with that individual previous Consumer-Agent and analyze the Request-URI to find out what payload should be despatched.
UDP interception
Throughout its initialization, the backdoor creates a passive UDP listening socket and lets the working system assign the port. There could be issues for attackers utilizing passive backdoors: as an example, if firewalls or routers utilizing NAT forestall incoming communication from outdoors of the community. Moreover, the controller of the implant must know the precise IP tackle and port of the compromised machine to contact the backdoor.
We imagine that the attackers solved the latter downside by utilizing the identical port on which the backdoor listens for instructions to additionally exfiltrate the collected knowledge, so the community implant will know precisely the place to ahead the packets. The info exfiltration process, by default, begins after the socket has been created, and it consists of DNS queries for the microsoft.com area; the collected knowledge is appended to the DNS packet. Determine 10 exhibits a seize of the primary DNS question despatched by the backdoor.
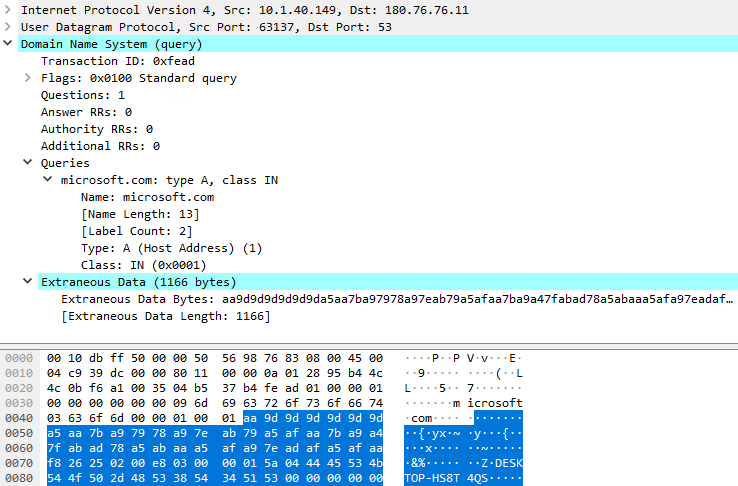
The primary DNS question is shipped to 180.76.76[.]11:53 (a server that, on the time of writing, doesn’t expose any DNS service) and for every of the next queries, the vacation spot IP tackle is modified to the succeeding tackle, as proven in Determine 11.
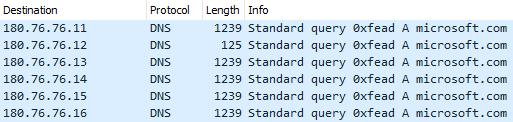
The 180.76.76.0/24 community is owned by Baidu, and apparently, a few of the servers at these IP addresses do expose DNS companies, corresponding to 180.76.76.76, which is Baidu’s public DNS service.
We imagine that when the DNS question packets are intercepted, the community implant forwards them to the attackers’ server. The implant can simply filter the packets by combining a number of values to create a fingerprint, as an example:
- vacation spot IP tackle
- UDP port (we noticed 53, 4499, and 8000),
- transaction ID of the DNS question matching 0xFEAD,
- area title, and,
- DNS question with extraneous knowledge appended.
Ultimate ideas
Utilizing the attackers’ AitM functionality to intercept packets is a intelligent approach to disguise the situation of their C&C infrastructure. We’ve got noticed victims positioned outdoors of China – that’s, in Japan and the UK – towards whom the orchestrator was in a position to deploy the backdoor. The attackers then despatched instructions to the backdoor to obtain plugins; for instance, the sufferer from the UK acquired two plugins designed to gather info and chats from Tencent QQ. Due to this fact, we all know that the AitM system was in place and dealing, and we should assume that the exfiltration mechanism was as effectively.
A few of the servers – as an example, within the 180.76.76.0/24 community – appear to be anycasted, which means that there is likely to be a number of servers geolocated around the globe to answer to (respectable) incoming requests. This means community interception is probably going carried out nearer to the targets moderately than nearer to Baidu’s community. Interception from a Chinese language ISP can also be unlikely as a result of Baidu has a part of its community infrastructure outdoors of China, so victims outdoors China might not undergo any Chinese language ISPs to succeed in Baidu companies.
NSPX30
Within the following sections we are going to describe the main phases of execution of the malware.
Stage 1
Determine 12 illustrates the execution chain when the respectable element masses a malicious dropper DLL that creates a number of information on disk.
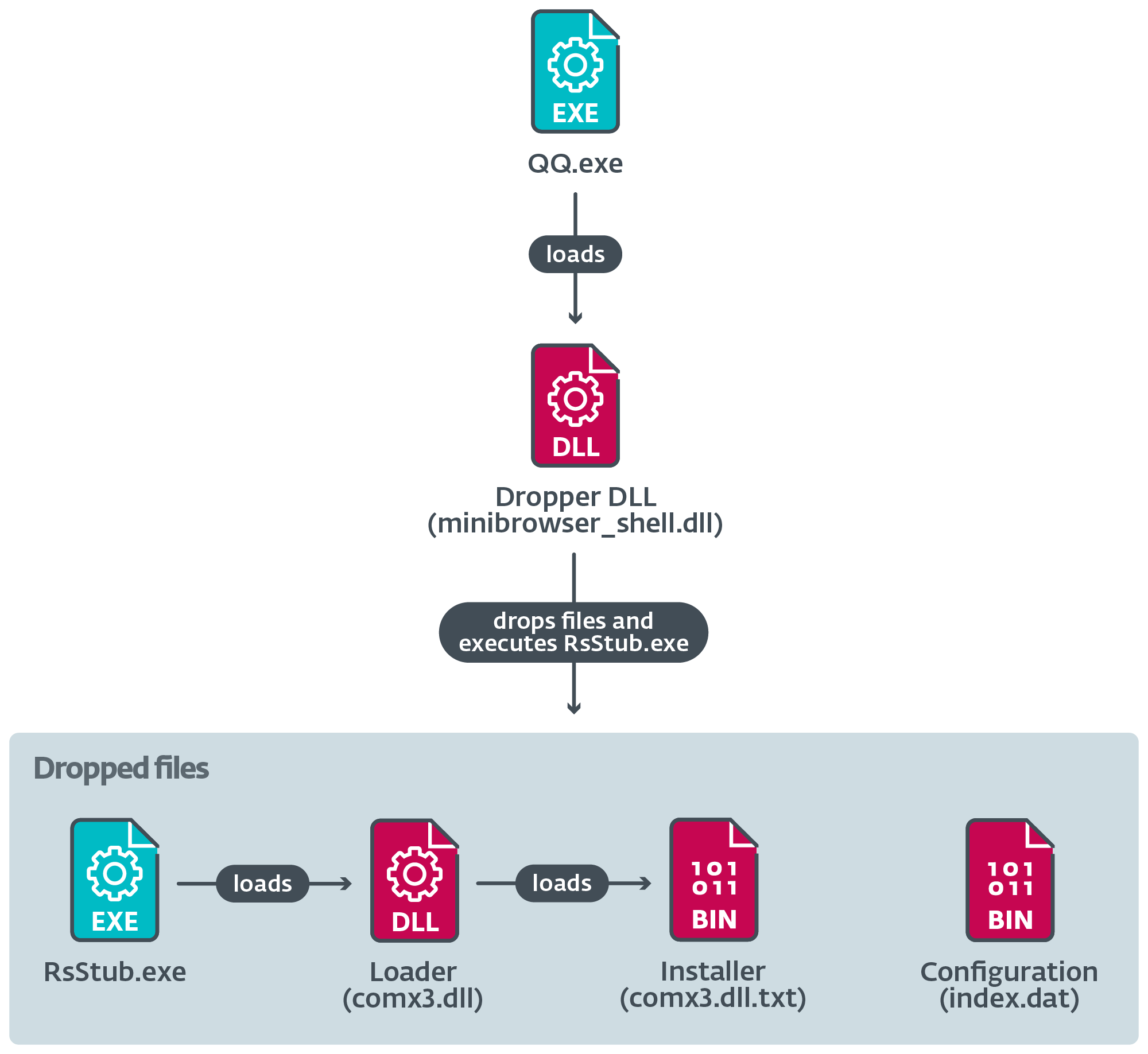
The dropper executes RsStub.exe, a respectable software program element of the Chinese language antimalware product Rising Antivirus, which is abused to side-load the malicious comx3.dll.
Determine 13 illustrates the main steps taken in the course of the execution of this element.
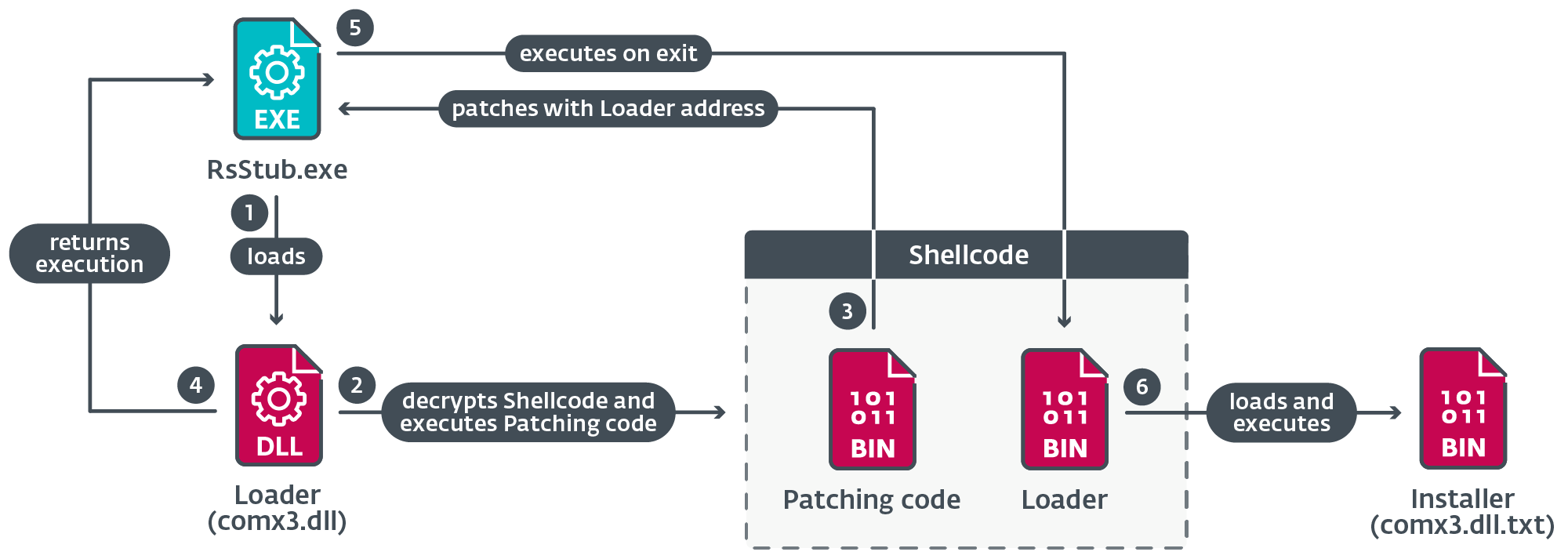
When RsStub.exe calls ExitProcess, the loader perform from the shellcode is executed as an alternative of the respectable API perform code.
The loader decrypts the installer DLL from the file comx3.dll.txt; the shellcode then masses the installer DLL in reminiscence and calls its entry level.
Installer DLL
The installer makes use of UAC bypass strategies taken from open-source implementations to create a brand new elevated course of. Which one it makes use of relies on a number of circumstances, as seen in Desk 3.
Desk 3. Essential situation and respective sub-conditions that should be met to be able to apply a UAC bypass approach
The circumstances confirm the presence of two processes: we imagine that avp.exe is a element of Kaspersky’s antimalware software program, and rstray.exe a element of Rising Antivirus.
The installer makes an attempt to disable the submission of samples by Home windows Defender, and provides an exclusion rule for the loader DLL msnsp.dll. It does this by executing two PowerShell instructions by way of cmd.exe:
- cmd /c powershell -inputformat none -outputformat none -NonInteractive -Command Set-MpPreference -SubmitSamplesConsent 0
- cmd /c powershell -inputformat none -outputformat none -NonInteractive -Command Add-MpPreference -ExclusionPath “C:Program Recordsdata (x86)Widespread Filesmicrosoft sharedTextConvmsnsp.dll”
The installer then drops the persistent loader DLL to C:Program Recordsdata (x86)Widespread Filesmicrosoft sharedTextConvmsnsp.dll and establishes persistence for it utilizing the API WSCInstallNameSpace to put in the DLL as a Winsock namespace supplier named msnsp, as proven in Determine 14.

In consequence, the DLL will likely be loaded routinely at any time when a course of makes use of Winsock.
Lastly, the installer drops the loader DLL mshlp.dll and the encrypted orchestrator DLL WIN.cfg to C:ProgramDataWindows.
Stage 2
This stage begins with the execution of msnsp.dll. Determine 15 illustrates the loading chain in Stage 2.
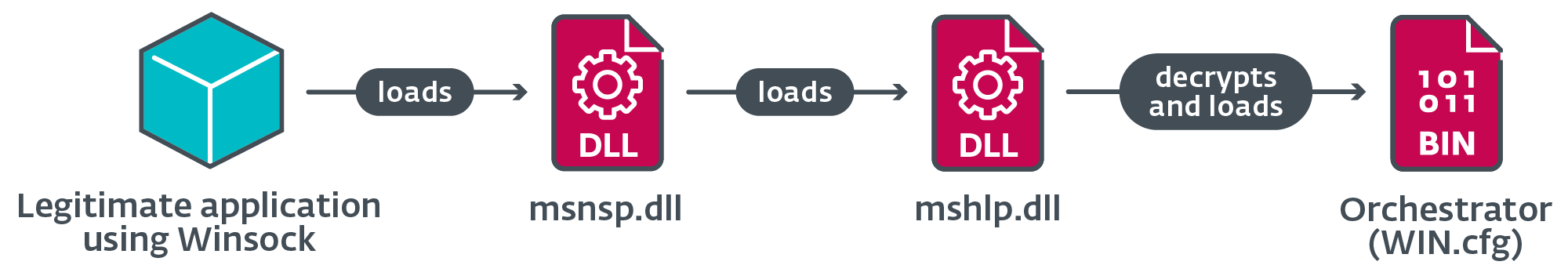
Orchestrator
Determine 16 illustrates the main duties carried out by the orchestrator, which incorporates acquiring the backdoor and loading plugins.
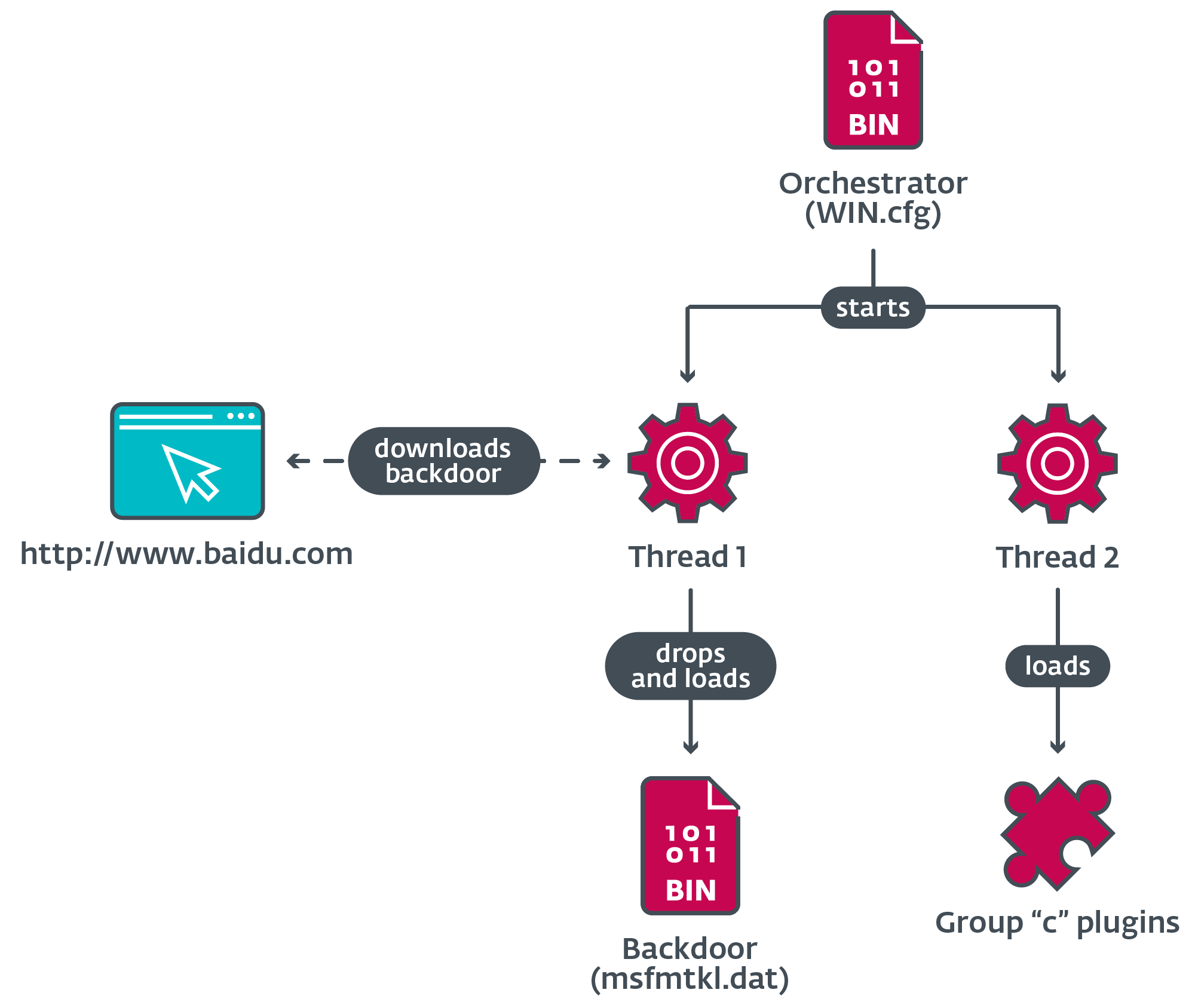
When loaded, the orchestrator creates two threads to carry out its duties.
Orchestrator thread 1
The orchestrator deletes the unique dropper file from disk, and tries to load the backdoor from msfmtkl.dat. If the file doesn’t exist or fails to open, the orchestrator makes use of Home windows Web APIs to open a connection to the respectable web site of the Chinese language firm Baidu as defined beforehand.
The response from the server is saved to a brief file topic to a validation process; if all circumstances are met, the encrypted payload that’s contained in the file is written to a brand new file and renamed as msfmtkl.dat.
After the brand new file is created with the encrypted payload, the orchestrator reads its contents and decrypts the payload utilizing RC4. The ensuing PE is loaded into reminiscence and its entry level is executed.
Orchestrator thread 2
Relying on the title of the present course of, the orchestrator performs a number of actions, together with the loading of plugins, and addition of exclusions to allowlist the loader DLLs within the native databases of three antimalware software program merchandise of Chinese language origin.
Desk 4 describes the actions taken when the method title matches that of a safety software program suite by which the orchestrator can allowlist its loaders.
Desk 4. Orchestrator actions when executing in a course of with the title of particular safety software program
|
Course of title |
Focused software program |
Motion |
|
qqpcmgr.exe qqpctray.exe qqpcrtp.exe |
Makes an attempt to load the respectable DLL <CURRENT_DIRECTORY>TAVinterface.dll to make use of the exported perform CreateTaveInstance to acquire an interface. When calling a second perform from the interface, it passes a file path as a parameter. |
|
|
360safe.exe 360tray.exe |
Makes an attempt to load the respectable DLL <CURRENT_DIRECTORY>deepscancloudcom2.dll to make use of the exported capabilities XDOpen, XDAddRecordsEx, and XDClose, it provides a brand new entry within the SQL database file speedmem2.hg. |
|
|
360sd.exe |
Makes an attempt to open the file <CURRENT_DIRECTORY>sl2.db to provides a base64-encoded binary construction that accommodates the trail to the loader DLL. |
|
|
kxescore.exe kxetray.exe |
Makes an attempt to load the respectable DLL <CURRENT_DIRECTORY>securitykxescankhistory.dll to make use of the exported perform KSDllGetClassObject to acquire an interface. When it calls one of many capabilities from the vtable, it passes a file path as a parameter. |
Desk 5 describes the actions taken when the method title matches that of chosen instant-messaging software program. In these circumstances, the orchestrator masses plugins from disk.
Desk 5. Ochestrator actions when executing in a course of with the title of particular instant-messaging software program
|
Course of title |
Focused software program |
Motion |
|
qq.exe |
Makes an attempt to create a mutex named GET QQ MESSAGE LOCK <PROCESS_ID>. If the mutex doesn’t exist already, it masses the plugins c001.dat, c002.dat, and c003.dat from disk. |
|
|
wechat.exe |
Masses plugin c006.dat. |
|
|
telegram.exe |
Masses plugin c007.dat. |
|
|
skype.exe |
Masses plugin c003.dat. |
|
|
cc.exe |
Unknown; presumably CloudChat. |
|
|
raidcall.exe |
||
|
yy.exe |
Unknown; presumably an utility from YY social community. |
|
|
aliim.exe |
Masses plugin c005.dat. |
After finishing the corresponding actions, the thread returns.
Plugins group “c”
From our evaluation of the orchestrator code, we perceive that at the very least six plugins of the “c” group would possibly exist, of which solely three are recognized to us at the moment.
Desk 6 describes the fundamental performance of the recognized plugins.
Desk 6. Description of the plugins from group “c”
|
Plugin title |
Description |
|
c001.dat |
Steals info from QQ databases, together with credentials, chat logs, contact lists, and extra. |
|
c002.dat |
Hooks a number of capabilities from Tencent QQ’s KernelUtil.dll and Widespread.dll within the reminiscence of the QQ.exe course of, enabling interception of direct and group messages, and SQL queries to databases. |
|
c003.dat |
Hooks a number of APIs: – CoCreateInstance – waveInOpen – waveInClose – waveInAddBuffer – waveOutOpen – waveOutWrite – waveOutClose This allows the plugin to intercept audio conversations in a number of processes. |
Backdoor
We’ve got already shared a number of particulars on the fundamental goal of the backdoor: to speak with its controller and exfiltrate collected knowledge. Communication with the controller is generally primarily based round writing plugin configuration knowledge into an unencrypted file named license.dat, and invoking performance from loaded plugins. Desk 7 describes probably the most related instructions dealt with by the backdoor.
Desk 7. Description of a few of the instructions dealt with by the backdoor
|
Command ID |
Description |
|
0x04 |
Creates or closes a reverse shell and handles enter and output. |
|
0x17 |
Strikes a file with paths supplied by the controller. |
|
0x1C |
Uninstalls the implant. |
|
0x1E |
Collects file info from a specified listing, or collects drive’s info. |
|
0x28 |
Terminates a course of with a PID given by the controller. |
Plugin teams “a” and “b”
The backdoor element accommodates its personal embedded plugin DLLs (see Desk 8) which might be written to disk and provides the backdoor its fundamental spying and information-collecting capabilities.
Desk 8. Descriptions of plugin teams “a” and “b” embedded within the backdoor
|
Plugin title |
Description |
|
a010.dat |
Collects put in software program info from the registry. |
|
b010.dat |
Takes screenshots. |
|
b011.dat |
Fundamental keylogger. |
Conclusion
We’ve got analyzed assaults and capabilities from a menace actor that we have now named Blackwood, which has carried out cyberespionage operations towards people and firms from China, Japan, and the UK. We mapped the evolution of NSPX30, the customized implant deployed by Blackwood, all the best way again to 2005 to a small backdoor we’ve named Venture Wooden.
Apparently, the Venture Wooden implant from 2005 seems to be the work of builders with expertise in malware improvement, given the strategies carried out, main us to imagine that we’re but to find extra in regards to the historical past of the primordial backdoor.
For any inquiries about our analysis revealed on WeLiveSecurity, please contact us at threatintel@eset.com.
ESET Analysis gives personal APT intelligence experiences and knowledge feeds. For any inquiries about this service, go to the ESET Risk Intelligence web page.
IOCs
Recordsdata
|
SHA-1 |
Filename |
ESET detection title |
Description |
|
625BEF5BD68F75624887D732538B7B01E3507234 |
minibrowser_shell.dll |
Win32/Agent.AFYI |
NSPX30 preliminary dropper. |
|
43622B9573413E17985B3A95CBE18CFE01FADF42 |
comx3.dll |
Win32/Agent.AFYH |
Loader for the installer. |
|
240055AA125BD31BF5BA23D6C30133C5121147A5 |
msnsp.dll |
Win32/Agent.AFYH |
Persistent loader. |
|
308616371B9FF5830DFFC740318FD6BA4260D032 |
mshlp.dll |
Win32/Agent.AFYH |
Loader for the orchestrator. |
|
796D05F299F11F1D78FBBB3F6E1F497BC3325164 |
comx3.dll.txt |
Win32/TrojanDropper.Agent.SWR |
Decrypted installer. |
|
82295E138E89F37DD0E51B1723775CBE33D26475 |
WIN.cfg |
Win32/Agent.AFYI |
Decrypted orchestrator. |
|
44F50A81DEBF68F4183EAEBC08A2A4CD6033DD91 |
msfmtkl.dat |
Win32/Agent.VKT |
Decrypted backdoor. |
|
DB6AEC90367203CAAC9D9321FDE2A7F2FE2A0FB6 |
c001.dat |
Win32/Agent.AFYI |
Credentials and knowledge stealer plugin. |
|
9D74FE1862AABAE67F9F2127E32B6EFA1BC592E9 |
c002.dat |
Win32/Agent.AFYI |
Tencent QQ message interception plugin. |
|
8296A8E41272767D80DF694152B9C26B607D26EE |
c003.dat |
Win32/Agent.AFYI |
Audio seize plugin. |
|
8936BD9A615DD859E868448CABCD2C6A72888952 |
a010.dat |
Win32/Agent.VKT |
Info collector plugin. |
|
AF85D79BC16B691F842964938C9619FFD1810C30 |
b011.dat |
Win32/Agent.VKT |
Keylogger plugin. |
|
ACD6CD486A260F84584C9FF7409331C65D4A2F4A |
b010.dat |
Win32/Agent.VKT |
Display screen seize plugin. |
Community
|
IP |
Area |
Internet hosting supplier |
First seen |
Particulars |
|
104.193.88[.]123 |
www.baidu[.]com |
Beijing Baidu Netcom Science and Know-how Co., Ltd. |
2017‑08‑04 |
Legit web site contacted by the orchestrator and backdoor parts to obtain payloads. The HTTP GET request is intercepted by AitM. |
|
183.134.93[.]171 |
dl_dir.qq[.]com |
IRT‑CHINANET‑ZJ |
2021‑10‑17 |
A part of the URL from the place the dropper was downloaded by respectable software program. |
MITRE ATT&CK strategies
This desk was constructed utilizing model 14 of the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
|
Tactic |
ID |
Title |
Description |
|
Useful resource Growth |
Develop Capabilities: Malware |
Blackwood used a customized implant known as NSPX30. |
|
|
Preliminary Entry |
Provide Chain Compromise |
NSPX30’s dropper element is delivered when respectable software program replace requests are intercepted through AitM. |
|
|
Execution |
Command and Scripting Interpreter: PowerShell |
NSPX30’s installer element makes use of PowerShell to disable Home windows Defender’s pattern submission, and provides an exclusion for a loader element. |
|
|
Command and Scripting Interpreter: Home windows Command Shell |
NSPX30’s installer can use cmd.exe when making an attempt to bypass UAC. NSPX30’s backdoor can create a reverse shell. |
||
|
Command and Scripting Interpreter: Visible Fundamental |
NSPX30’s installer can use VBScript when making an attempt to bypass UAC. |
||
|
Native API |
NSPX30’s installer and backdoor use CreateProcessA/W APIs to execute parts. |
||
|
Persistence |
Hijack Execution Movement |
NSPX30’s loader is routinely loaded right into a course of when Winsock is began. |
|
|
Privilege Escalation |
Occasion Triggered Execution |
NSPX30’s installer modifies the registry to alter a media button key worth (APPCOMMAND_LAUNCH_APP2) to level to its loader executable. |
|
|
Abuse Elevation Management Mechanism: Bypass Consumer Account Management |
NSPX30’s installer makes use of three strategies to aim UAC bypasses. |
||
|
Protection Evasion |
Deobfuscate/Decode Recordsdata or Info |
NSPX30’s installer, orchestrator, backdoor, and configuration information are decrypted with RC4, or mixtures of bitwise and arithmetic directions. |
|
|
Impair Defenses: Disable or Modify Instruments |
NSPX30’s installer disables Home windows Defender’s pattern submission, and provides an exclusion for a loader element. NSPX30’s orchestrator can alter the databases of safety software program to allowlist its loader parts. Focused software program contains: Tencent PC Supervisor, 360 Safeguard, 360 Antivirus, and Kingsoft AntiVirus. |
||
|
Indicator Elimination: File Deletion |
NSPX30 can take away its information. |
||
|
Indicator Elimination: Clear Persistence |
NSPX30 can take away its persistence. |
||
|
Oblique Command Execution |
NSPX30’s installer executes PowerShell by way of Home windows’ Command Shell. |
||
|
Masquerading: Match Legit Title or Location |
NSPX30’s parts are saved within the respectable folder %PROGRAMDATApercentIntel. |
||
|
Modify Registry |
NSPX30’s installer can modify the registry when making an attempt to bypass UAC. |
||
|
Obfuscated Recordsdata or Info |
NSPX30’s parts are saved encrypted on disk. |
||
|
Obfuscated Recordsdata or Info: Embedded Payloads |
NSPX30’s dropper accommodates embedded parts. NSPX30’s loader accommodates embedded shellcode. |
||
|
System Binary Proxy Execution: Rundll32 |
NSPX30’s installer could be loaded by way of rundll32.exe. |
||
|
Credential Entry |
Adversary-in-the-Center |
The NSPX30 implant is delivered to victims by way of AitM assaults. |
|
|
Credentials from Password Shops |
NSPX30 plugin c001.dat can steal credentials from Tencent QQ databases. |
||
|
Discovery |
File and Listing Discovery |
NSPX30’s backdoor and plugins can listing information. |
|
|
Question Registry |
NSPX30 a010.dat plugin collects varied info of put in software program from the registry. |
||
|
Software program Discovery |
NSPX30 a010.dat plugin collects info from the registry. |
||
|
System Info Discovery |
NSPX30’s backdoor collects system info. |
||
|
System Community Configuration Discovery |
NSPX30’s backdoor collects varied community adapter info. |
||
|
System Community Connections Discovery |
NSPX30’s backdoor collects community adapter info. |
||
|
System Proprietor/Consumer Discovery |
NSPX30’s backdoor collects system and person info. |
||
|
Assortment |
Enter Seize: Keylogging |
NSPX30 plugin b011.dat is a fundamental keylogger. |
|
|
Archive Collected Knowledge: Archive through Library |
NSPX30 plugins compress collected info utilizing zlib. |
||
|
Audio Seize |
NSPX30 plugin c003.dat information enter and output audio streams. |
||
|
Automated Assortment |
NSPX30’s orchestrator and backdoor routinely launch plugins to gather info. |
||
|
Knowledge Staged: Native Knowledge Staging |
NSPX30’s plugins retailer knowledge in native information earlier than exfiltration. |
||
|
Display screen Seize |
NSPX30 plugin b010.dat takes screenshots. |
||
|
Command and Management |
Software Layer Protocol: Net Protocols |
NSPX30’s orchestrator and backdoor parts obtain payloads utilizing HTTP. |
|
|
Software Layer Protocol: DNS |
NSPX30’s backdoor exfiltrates the collected info utilizing DNS. |
||
|
Knowledge Encoding: Customary Encoding |
Collected knowledge for exfiltration is compressed with zlib. |
||
|
Knowledge Obfuscation |
NSPX30’s backdoor encrypts its C&C communications. |
||
|
Non-Software Layer Protocol |
NSPX30’s backdoor makes use of UDP for its C&C communications. |
||
|
Proxy |
NSPX30’s communications with its C&C server are proxied by an unidentified element. |
||
|
Exfiltration |
Automated Exfiltration |
When accessible, NSPX30’s backdoor routinely exfiltrates any collected info. |
|
|
Knowledge Switch Measurement Limits |
NSPX30’s backdoor exfiltrates collected knowledge through DNS queries with a hard and fast packet measurement. |
||
|
Exfiltration Over Various Protocol: Exfiltration Over Unencrypted Non-C2 Protocol |
NSPX30’s backdoor exfiltrates the collected info utilizing DNS. |

