Posted by Ben Trengrove, Android Developer Relations Engineer
In the present day, as a part of the Compose January ‘24 Invoice of Supplies, we’re releasing model 1.6 of Jetpack Compose, Android’s trendy, native UI toolkit that’s utilized by apps akin to Threads, Reddit, and Dropbox. This launch largely focuses on efficiency enhancements, as we proceed emigrate modifiers and enhance the effectivity of main components of our API.
To make use of at the moment’s launch, improve your Compose BOM model to 2024.01.00
Efficiency
Efficiency continues to be our high precedence, and this launch of Compose has main efficiency enhancements throughout the board. We’re seeing an extra ~20% enchancment in scroll efficiency and ~12% enchancment to startup time in our benchmarks, and that is on high of the enhancements from the August ‘23 launch. As with that launch, most apps will see these advantages simply by upgrading to the newest model, with no different code adjustments wanted.
The development to scroll efficiency and startup time comes from our continued deal with reminiscence allocations and lazy initialization, to make sure the framework is just doing work when it has to. These enhancements may be seen throughout all APIs in Compose, particularly in textual content, clickable, Lazy lists, and graphics APIs, together with vectors, and had been made attainable partially by the Modifier.Node refactor work that has been ongoing for a number of releases.
There’s additionally new steerage so that you can create your personal customized modifiers with Modifier.Node.
Configuring the soundness of exterior lessons
Compose compiler 1.5.5 introduces a brand new compiler choice to offer a configuration file for what your app considers secure. This selection permits you to mark any class as secure, together with your personal modules, exterior library lessons, and customary library lessons, with out having to change these modules or wrap them in a secure wrapper class. Notice that the usual stability contract applies; that is simply one other handy technique to let the Compose compiler know what your app ought to think about secure. For extra info on use stability configuration, see our documentation.
Generated code efficiency
The code generated by the Compose compiler plugin has additionally been improved. Small tweaks on this code can result in massive efficiency enhancements as a result of reality the code is generated in each composable perform. The Compose compiler tracks Compose state objects to know which composables to recompose when there’s a change of worth; nevertheless, many state values are solely learn as soon as, and a few state values are by no means learn in any respect however nonetheless change incessantly! This replace permits the compiler to skip the monitoring when it isn’t wanted.
Compose compiler 1.5.6 additionally permits “intrinsic bear in mind” by default. This mode transforms bear in mind at compile time to bear in mind info we have already got about any parameters of a composable which might be used as a key to bear in mind. This hastens the calculation of figuring out if a remembered expression wants reevaluating, but additionally means in the event you place a breakpoint contained in the bear in mind perform throughout debugging, it might not be known as, because the compiler has eliminated the utilization of bear in mind and changed it with totally different code.
Composables not being skipped
We’re additionally investing in making the code you write extra performant, routinely. We need to optimize for the code you intuitively write, eradicating the necessity to dive deep into Compose internals to know why your composable is recomposing when it shouldn’t.
This launch of Compose provides assist for an experimental mode we’re calling “robust skipping mode”. Robust skipping mode relaxes a few of the guidelines about which adjustments can skip recomposition, transferring the steadiness in direction of what builders count on. With robust skipping mode enabled, composables with unstable parameters may skip recomposition if the identical cases of objects are handed in to its parameters. Moreover, robust skipping mode routinely remembers lambdas in composition that seize unstable values, along with the present default conduct of remembering lambdas with solely secure captures. Robust skipping mode is presently experimental and disabled by default as we don’t think about it prepared for manufacturing utilization but. We’re evaluating its results earlier than aiming to show it on by default in Compose 1.7. See our steerage to experiment with robust skipping mode and assist us discover any points.
Textual content
Adjustments to default font padding
This launch now makes the includeFontPadding setting false by default. includeFontPadding is a legacy property that provides additional padding primarily based on font metrics on the high of the primary line and backside of the final line of a textual content. Making this setting default to false brings the default textual content structure extra consistent with widespread design instruments, making it simpler to match the design specs generated. Upon upgrading to the January ‘24 launch, you might even see small adjustments in your textual content structure and screenshot checks. For extra details about this setting, see the Fixing Font Padding in Compose Textual content weblog put up and the developer documentation.

Help for nonlinear font scaling
The January ‘24 launch makes use of nonlinear font scaling for higher textual content readability and accessibility. Nonlinear font scaling prevents massive textual content parts on display from scaling too massive by making use of a nonlinear scaling curve. This scaling technique signifies that massive textual content would not scale on the similar charge as smaller textual content.
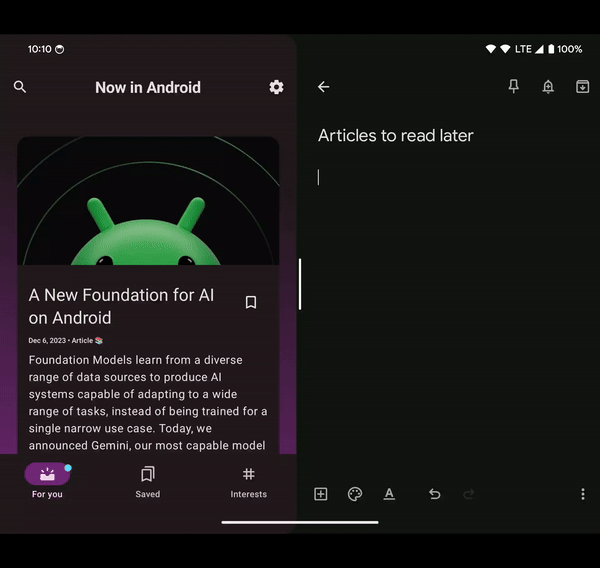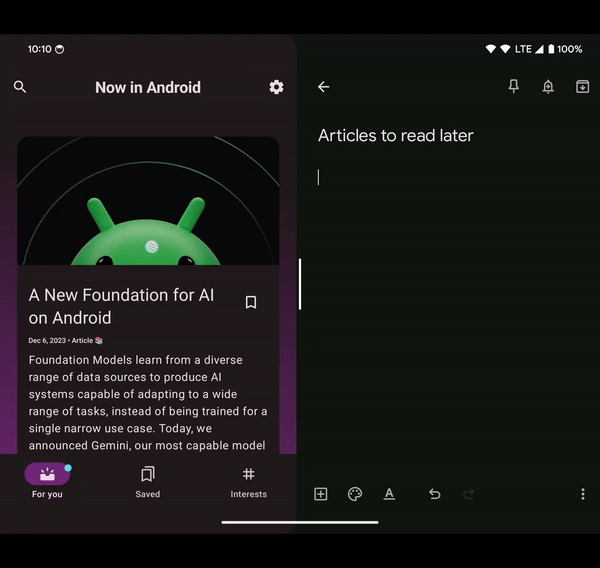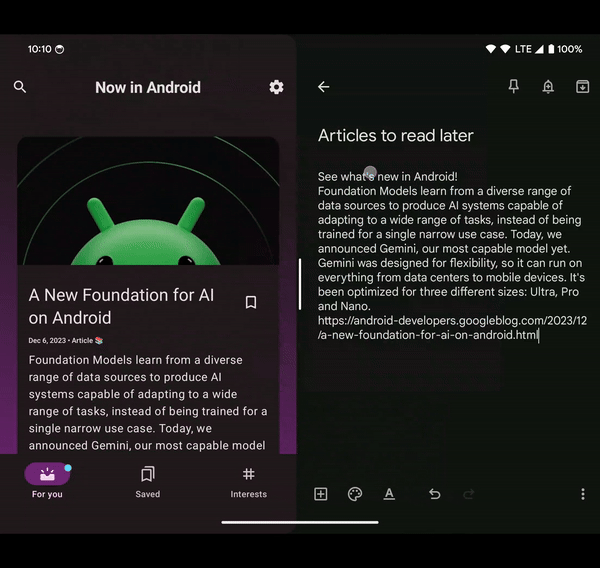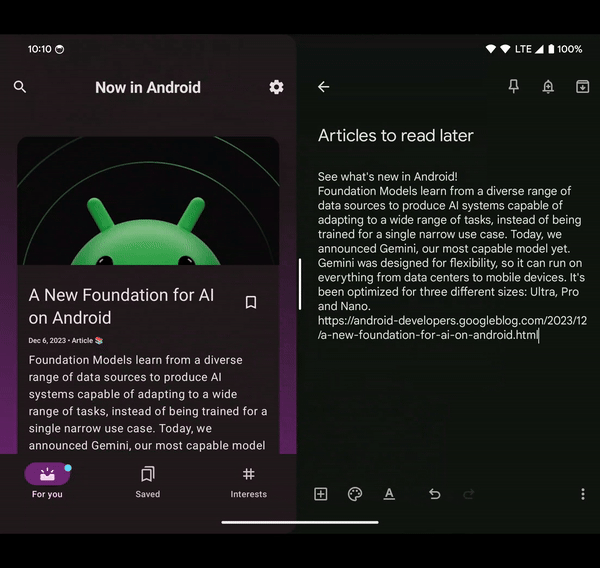
Drag and drop
Compose Basis provides assist for platform-level drag and drop, which permits for content material to be dragged between apps on a tool working in multi-window mode. The API is 100% appropriate with the View APIs, which suggests a drag and drop began from a View may be dragged into Compose and vice versa. To make use of this API, see the code pattern.
Extra options
Different options landed on this launch embody:
- Help for LookaheadScope in Lazy lists.
- Fastened composables which have been deactivated however saved alive for reuse in a Lazy listing not being filtered by default from semantics bushes.
- Spline-based keyframes in animations.
- Added assist for choice by mouse, together with textual content.
Get began!
We’re grateful for all the bug stories and have requests submitted to our subject tracker — they assist us to enhance Compose and construct the APIs you want. Proceed offering your suggestions, and assist us make Compose higher!
Questioning what’s subsequent? Try our roadmap to see the options we’re presently interested by and dealing on. We will’t wait to see what you construct subsequent!
Comfortable composing!

