That is the primary publish in a collection by Rockset’s CTO Dhruba Borthakur on Designing the Subsequent Technology of Knowledge Methods for Actual-Time Analytics. We’ll be publishing extra posts within the collection within the close to future, so subscribe to our weblog so you do not miss them!
Posts printed to date within the collection:
- Why Mutability Is Important for Actual-Time Knowledge Analytics
- Dealing with Out-of-Order Knowledge in Actual-Time Analytics Purposes
- Dealing with Bursty Site visitors in Actual-Time Analytics Purposes
- SQL and Complicated Queries Are Wanted for Actual-Time Analytics
- Why Actual-Time Analytics Requires Each the Flexibility of NoSQL and Strict Schemas of SQL Methods
Dhruba Borthakur is CTO and co-founder of Rockset and is accountable for the corporate’s technical course. He was an engineer on the database group at Fb, the place he was the founding engineer of the RocksDB knowledge retailer. Earlier at Yahoo, he was one of many founding engineers of the Hadoop Distributed File System. He was additionally a contributor to the open supply Apache HBase mission.
Profitable data-driven firms like Uber, Fb and Amazon depend on real-time analytics. Personalizing buyer experiences for e-commerce, managing fleets and provide chains, and automating inside operations all require on the spot insights on the freshest knowledge.
To ship real-time analytics, firms want a contemporary expertise infrastructure that features these three issues:
- An actual-time knowledge supply reminiscent of internet clickstreams, IoT occasions produced by sensors, and so on.
- A platform reminiscent of Apache Kafka/Confluent, Spark or Amazon Kinesis for publishing that stream of occasion knowledge.
- An actual-time analytics database able to constantly ingesting massive volumes of real-time occasions and returning question outcomes inside milliseconds.
Occasion streaming/stream processing has been round for nearly a decade. It’s properly understood. Actual-time analytics shouldn’t be. One of many technical necessities for a real-time analytics database is mutability. Mutability is the superpower that allows updates, or mutations, to current information in your knowledge retailer.
Variations Between Mutable and Immutable Knowledge
Earlier than we discuss why mutability is vital to real-time analytics, it’s vital to know what it’s.
Mutable knowledge is knowledge saved in a desk report that may be erased or up to date with newer knowledge. As an illustration, in a database of worker addresses, let’s say that every report has the identify of the particular person and their present residential deal with. The present deal with info could be overwritten if the worker strikes residences from one place to a different.
Historically, this info could be saved in transactional databases — Oracle Database, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and so on. — as a result of they permit for mutability: Any area saved in these transactional databases is updatable. For in the present day’s real-time analytics, there are a lot of further the reason why we want mutability, together with knowledge enrichment and backfilling knowledge.
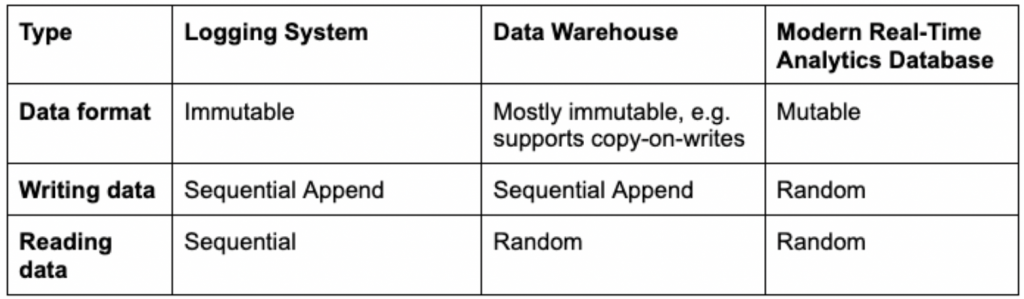
Immutable knowledge is the other — it can’t be deleted or modified. Fairly than writing over current information, updates are append-only. Which means that updates are inserted into a special location otherwise you’re compelled to rewrite previous and new knowledge to retailer it correctly. Extra on the downsides of this later. Immutable knowledge shops have been helpful in sure analytics situations.
The Historic Usefulness of Immutability
Knowledge warehouses popularized immutability as a result of it eased scalability, particularly in a distributed system. Analytical queries may very well be accelerated by caching heavily-accessed read-only knowledge in RAM or SSDs. If the cached knowledge was mutable and probably altering, it must be constantly checked towards the unique supply to keep away from turning into stale or inaccurate. This is able to have added to the operational complexity of the information warehouse; immutable knowledge, however, created no such complications.
Immutability additionally reduces the danger of unintentional knowledge deletion, a major profit in sure use circumstances. Take well being care and affected person well being information. One thing like a brand new medical prescription could be added quite than written over current or expired prescriptions so that you simply at all times have a whole medical historical past.
Extra just lately, firms tried to pair stream publishing methods reminiscent of Kafka and Kinesis with immutable knowledge warehouses for analytics. The occasion methods captured IoT and internet occasions and saved them as log information. These streaming log methods are troublesome to question, so one would usually ship all the information from a log to an immutable knowledge system reminiscent of Apache Druid to carry out batch analytics.
The info warehouse would append newly-streamed occasions to current tables. Since previous occasions, in principle, don’t change, storing knowledge immutably appeared to be the fitting technical choice. And whereas an immutable knowledge warehouse may solely write knowledge sequentially, it did assist random knowledge reads. That enabled analytical enterprise purposes to effectively question knowledge every time and wherever it was saved.
The Issues with Immutable Knowledge
After all, customers quickly found that for a lot of causes, knowledge does must be up to date. That is very true for occasion streams as a result of a number of occasions can mirror the true state of a real-life object. Or community issues or software program crashes could cause knowledge to be delivered late. Late-arriving occasions must be reloaded or backfilled.
Corporations additionally started to embrace knowledge enrichment, the place related knowledge is added to current tables. Lastly, firms began having to delete buyer knowledge to satisfy client privateness laws reminiscent of GDPR and its “proper to be forgotten.”
Immutable database makers had been compelled to create workarounds so as to insert updates. One well-liked technique utilized by Apache Druid and others is known as copy-on-write. Knowledge warehouses usually load knowledge right into a staging space earlier than it’s ingested in batches into the information warehouse the place it’s saved, listed and made prepared for queries. If any occasions arrive late, the information warehouse should write the brand new knowledge and rewrite already-written adjoining knowledge so as to retailer every part accurately in the fitting order.
One other poor resolution to take care of updates in an immutable knowledge system is to maintain the unique knowledge in Partition A (above) and write late-arriving knowledge to a special location, Partition B. The appliance, and never the information system, should preserve monitor of the place all linked-but-scattered information are saved, in addition to any ensuing dependencies. This course of is known as referential integrity and must be carried out by the applying software program.

Each workarounds have important issues. Copy-on-write requires knowledge warehouses to expend a major quantity of processing energy and time — tolerable when updates are few, however intolerably pricey and sluggish because the variety of updates rise. That creates important knowledge latency that may rule out real-time analytics. Knowledge engineers should additionally manually supervise copy-on-writes to make sure all of the previous and new knowledge is written and listed precisely.
An software implementing referential integrity has its personal points. Queries should be double-checked that they’re pulling knowledge from the fitting areas or run the danger of information errors. Making an attempt any question optimizations, reminiscent of caching knowledge, additionally turns into way more difficult when updates to the identical report are scattered in a number of locations within the knowledge system. Whereas these could have been tolerable at slower-paced batch analytic methods, they’re enormous issues on the subject of mission-critical real-time analytics.
Mutability Aids Machine Studying
At Fb, we constructed an ML mannequin that scanned all-new calendar occasions as they had been created and saved them within the occasion database. Then, in real-time, an ML algorithm would examine this occasion, and resolve whether or not it’s spam. Whether it is categorized as spam, then the ML mannequin code would insert a brand new area into that current occasion report to mark it as spam. As a result of so many occasions had been flagged and instantly taken down, the information needed to be mutable for effectivity and pace. Many trendy ML-serving methods have emulated our instance and chosen mutable databases.
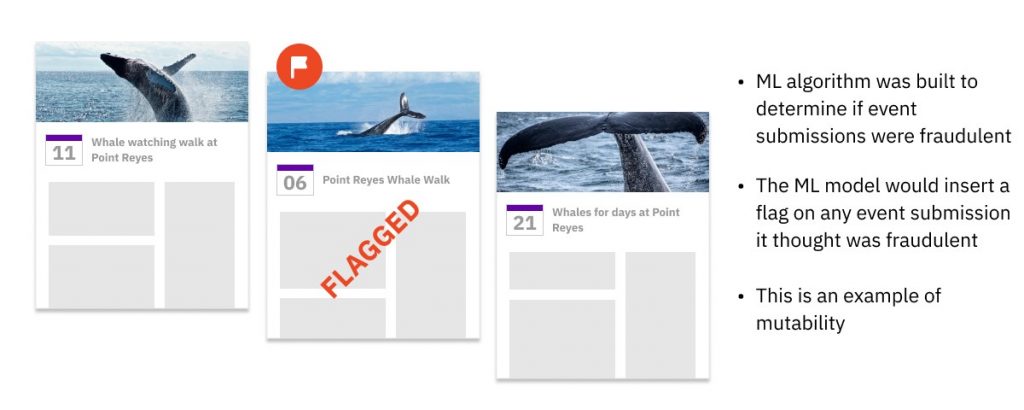
This degree of efficiency would have been inconceivable with immutable knowledge. A database utilizing copy-on-write would rapidly get slowed down by the variety of flagged occasions it must replace. If the database saved the unique occasions in Partition A and appended flagged occasions to Partition B, this may require further question logic and processing energy, as each question must merge related information from each partitions. Each workarounds would have created an insupportable delay for our Fb customers, heightened the danger of information errors and created extra work for builders and/or knowledge engineers.
How Mutability Allows Actual-Time Analytics
At Fb, I helped design mutable analytics methods that delivered real-time pace, effectivity and reliability.
One of many applied sciences I based was open supply RocksDB, the high-performance key-value engine utilized by MySQL, Apache Kafka and CockroachDB. RocksDB’s knowledge format is a mutable knowledge format, which implies that you could replace, overwrite or delete particular person fields in a report. It’s additionally the embedded storage engine at Rockset, a real-time analytics database I based with totally mutable indexes.
By tuning open supply RocksDB, it’s doable to allow SQL queries on occasions and updates arriving mere seconds earlier than. These queries might be returned within the low tons of of milliseconds, even when complicated, advert hoc and excessive concurrency. RocksDB’s compaction algorithms additionally robotically merge previous and up to date knowledge information to make sure that queries entry the most recent, right model, in addition to stop knowledge bloat that may hamper storage effectivity and question speeds.
By selecting RocksDB, you possibly can keep away from the clumsy, costly and error-creating workarounds of immutable knowledge warehouses reminiscent of copy-on-writes and scattering updates throughout completely different partitions.
To sum up, mutability is vital for in the present day’s real-time analytics as a result of occasion streams might be incomplete or out of order. When that occurs, a database might want to right and backfill lacking and inaccurate knowledge. To make sure excessive efficiency, low price, error-free queries and developer effectivity, your database should assist mutability.
If you wish to see all the key necessities of real-time analytics databases, watch my latest discuss on the Hive on Designing the Subsequent Technology of Knowledge Methods for Actual-Time Analytics, obtainable beneath.
Embedded content material: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NOuxW_SXj5M
The second publish on this collection is now obtainable at Dealing with Out-of-Order Knowledge in Actual-Time Analytics Purposes
Rockset is the real-time analytics database within the cloud for contemporary knowledge groups. Get quicker analytics on brisker knowledge, at decrease prices, by exploiting indexing over brute-force scanning.
