Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered an up to date model of a backdoor known as LODEINFO that is distributed by way of spear-phishing assaults.
The findings come from Japanese firm ITOCHU Cyber & Intelligence, which stated the malware “has been up to date with new options, in addition to modifications to the anti-analysis (evaluation avoidance) strategies.”
LODEINFO (variations 0.6.6 and 0.6.7) was first documented by Kaspersky in November 2022, detailing its capabilities to execute arbitrary shellcode, take screenshots, and exfiltrate information again to an actor-controlled server.
A month later, ESET disclosed assaults concentrating on Japanese political institutions that led to the deployment of LODEINFO.
The backdoor is the work of a Chinese language nation-state actor often called Stone Panda (aka APT10, Bronze Riverside, Cicada, Earth Tengshe, MirrorFace, and Potassium), which has a historical past of orchestrating assaults concentrating on Japan since 2021.
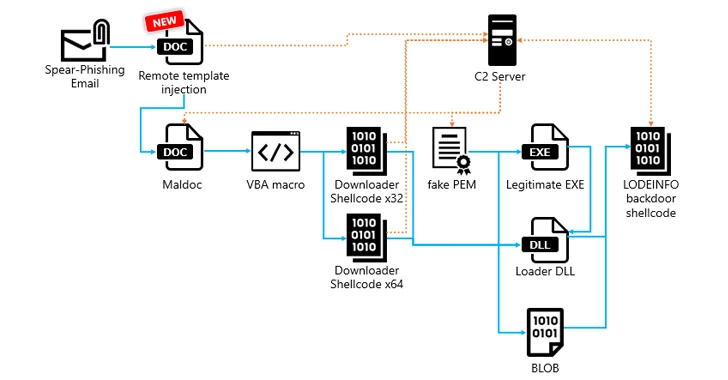
Assault chains start with phishing emails bearing malicious Microsoft Phrase paperwork that, when opened, execute VBA macros to launch downloader shellcode able to in the end executing the LODEINFO implant.
LODEINFO an infection paths in 2023 have additionally been noticed making use of distant template injection strategies to retrieve and execute malicious macros hosted on the adversary’s infrastructure each time the sufferer opens a lure Phrase doc containing the template.
What’s extra, checks are stated to have been added someday round June 2023 to confirm the language settings of Microsoft Workplace to find out if it is Japanese, just for it to be eliminated a month later in assaults leveraging LODEINFO model 0.7.1.
“As well as, the filename of the maldoc itself has been modified from Japanese to English,” ITOCHU famous. “From this, we imagine that v0.7.1 was possible used to assault environments in languages apart from Japanese.”
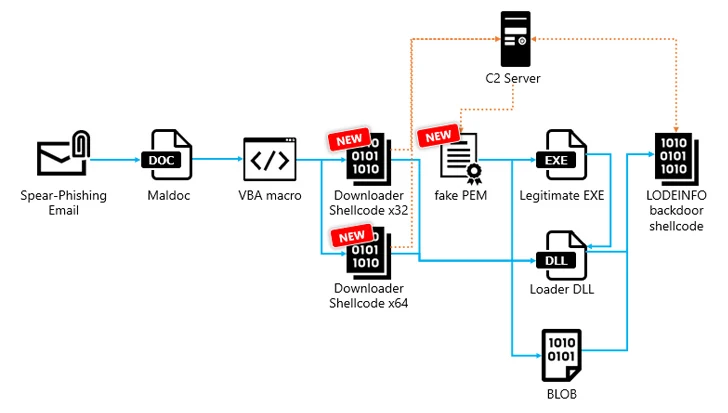
One other notable change in assaults delivering LODEINFO model 0.7.1 is the introduction of a brand new intermediate stage that entails the shellcode downloader fetching a file that masquerades as a Privateness-Enhanced Mail (PEM) from a C2 server, which, in flip, hundreds the backdoor instantly in reminiscence.
The downloader shares similarities with a recognized fileless downloader dubbed DOWNIISSA based mostly on the self-patching mechanism to hide malicious code, encoding technique for command-and-control (C2) server info, and the construction of the information decrypted from the pretend PEM file.
“LODEINFO backdoor shellcode is a fileless malware that enables attackers to remotely entry and function contaminated hosts,” the corporate stated, with samples present in 2023 and 2024 incorporating additional instructions. The newest model of LODEINFO is 0.7.3.
“As a countermeasure, since each the downloader shellcode and the backdoor shellcode of LODEINFO are fileless malware, it’s important to introduce a product that may scan and detect malware in reminiscence with the intention to detect it,” it added.