A passkey is a particular authentication technique that can be utilized as generally as a password however to supply extra safety. Passkeys differ from passwords as they mix personal and public cryptographic keys to authenticate customers, whereas a password depends on a particular variety of characters.
In accordance with Google, probably the most quick advantages of passkeys are that they’re phishing-resistant and spare folks the headache of remembering numbers and particular characters in passwords.
As passwordless authentication continues to evolve — in response to phishing-related dangers — think about using passkeys to implement an added layer of safety to guard your on-line accounts and information.
This text will outline passkey expertise, discover the way it works and talk about the added safety advantages of utilizing a passkey.
What’s a passkey?
A passkey refers to a code or a collection of characters used to achieve entry to a secured system, system, community or service. Passkeys are sometimes used along with usernames or consumer IDs to create two-factor authentication (2FA).
After you’ve established a passkey, all it’s essential do is log in to finish the authentication course of, sometimes utilizing biometric information equivalent to a fingerprint or facial recognition. For individuals who make the most of a passkey, logging in turns into a easy, almost automated course of; for malicious actors, it turns into almost not possible.
The implementation of passkeys is extremely adaptable since they might be configured to be cloud-synced or hardware-bound, contingent on the consumer’s decisions relating to the actual software, service or system.
How do passkeys work?
When logging in for the primary time, a consumer who needs to entry an app or web site with passkey expertise — equivalent to NordPass — can be requested to generate an unique passkey. This passkey, which can be required for authentication sooner or later, may be accessed utilizing both biometrics or private PINs primarily based on the consumer’s choice and the capabilities of their most popular system.
Determine A
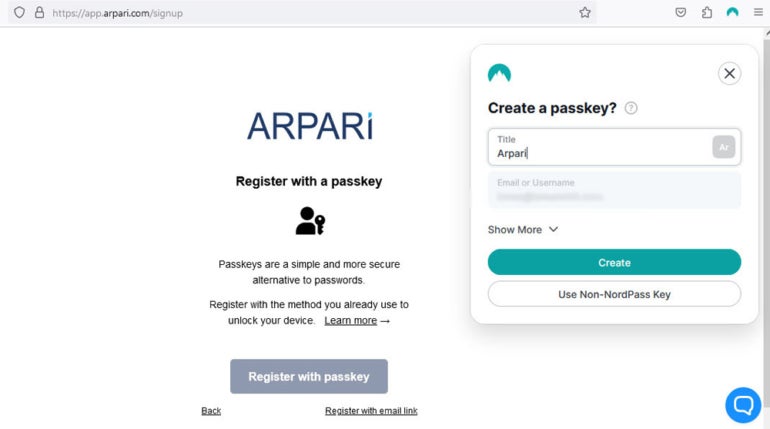
Throughout this stage, two mathematically linked cryptographic keys are generated: a public key that stays with the web site, service or software however is related to the account, and a personal key that stays on the consumer’s {hardware} or cloud account. The service or software will ship a randomly generated “problem” to the consumer’s system throughout successive logins, which the consumer should react to by signing in with the personal key.
The app or web site can affirm the legitimacy of the personal key by using the corresponding public key to substantiate the response. Entry is allowed, and authentication is validated if the consumer’s verified signature connected to the problem’s response agrees with the unique randomly generated problem; if not, entry is denied.
This authentication course of is finished within the background, making login on the consumer’s finish seamless — with simply the press of a button.
Determine B
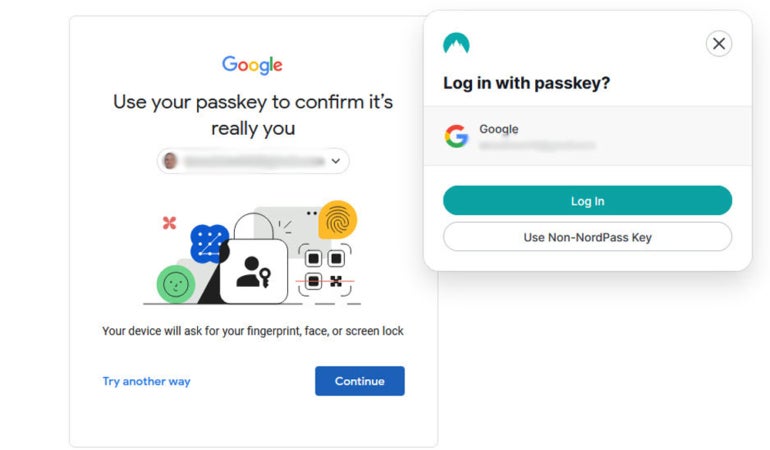
Can passkeys be shared?
The implementation of passkey expertise continues to be growing, however some corporations have talked about the potential for credential sharing amongst customers — so long as the precise passkeys are saved protected within the cloud and out of the fingers of potential hackers. Since sharing account entry with household, pals and coworkers is a quite simple and fast course of, this characteristic might enhance the general consumer expertise. Nevertheless, it’s nonetheless unclear how this perform may be securely managed in a enterprise setting.
One other essential issue to think about is whether or not companies ought to develop into much more depending on cloud suppliers and quit much more possession and management over credential administration, given {that a} breach of these events’ information would, surely, have disastrous penalties.
{Hardware}-bound passkeys, versus cloud-based passkeys, are saved on safety keys, bodily {hardware} authenticators or specialised {hardware} built-in into laptops and desktops. Which means the passkey is neither transferable nor duplicated. {Hardware}-bound passkeys may be another for organizations wanting to stop staff from copying or sharing keys throughout units.
Are passkeys safer than passwords?
Normally, each passkeys and passwords may be safe if managed correctly. Nevertheless, safety will depend on varied elements, together with the complexity of authentication, implementation and the way effectively customers handle and defend their credentials. To be deemed safe by immediately’s requirements, passkeys and passwords ought to have the next traits:
- Complexity: The longer and extra complicated the passkey or password, the tougher it’s for unhealthy actors to compromise.
- 2FA: A second issue of authentication can improve safety for each passkeys and passwords, making it more difficult for unauthorized customers to achieve entry.
- Encryption: Robust encryption strategies are essential for shielding saved credentials.
Finally, the safety of passkeys and passwords isn’t inherently dependent upon the kind of credential however as an alternative how they’re applied and managed.
