The USA shouldn’t be constructing sufficient transmission traces to attach regional energy networks. The deficit is driving up electrical energy costs, decreasing grid reliability, and hobbling renewable-energy deployment.
On the coronary heart of the issue are utility corporations that refuse to pursue interregional transmission tasks, and typically even impede them, as a result of new tasks threaten their income and disrupt their {industry} alliances. Utilities can stall transmission growth as a result of out-of-date legal guidelines sanction these corporations’ sweeping management over transmission growth.
As we more and more electrify our houses, transportation, and factories, utility corporations’ decisions about transmission may have large penalties for the nation’s financial system and well-being. About 40 companies, valued at a trillion {dollars}, personal the overwhelming majority of transmission traces in america. Their grip over the spine of U.S. grids calls for public scrutiny and accountability.
Many Strains, Steady Energy
Excessive-voltage transmission traces transfer massive quantities of vitality over lengthy distances, linking energy era to consumption. A transmission community accommodates webs of connections, which create a dependable, redundant power-supply system of huge scale.
At any given time, hundreds of energy vegetation provide simply sufficient vitality to transmission networks to fulfill demand. The foundations that orchestrate the motion of electrical energy via this community decide who generates energy, and the way a lot. The purpose is to maintain the lights on at a low value by using an environment friendly mixture of energy vegetation.
Constructing extra transmission will increase the capability and connectivity of the system, permitting new energy vegetation to attach and extra energy to movement between transmission networks. That is
why utility corporations usually are not embracing transmission growth. They don’t need their energy vegetation to face competitors or their regional alliances to lose management over their networks.
Growth can open alternatives for brand new power-plant and transmission builders to undercut utility corporations’ income and take management over the foundations that form the {industry}’s future. Utility corporations are prioritizing their shareholders over the general public’s want for cleaner, cheaper, and extra dependable vitality.
Previous Alliances, Previous Expertise
Transmission networks in america, which transfer alternating present, have been constructed over the past century largely by for-profit utility corporations, and to a lesser extent by nonprofit utilities operated by governments and native communities. The traces are usually concentrated round fossil-fuel reserves and inhabitants facilities however are additionally formed by historic utility alliances.
The place utilities agreed to commerce vitality, they constructed ample transmission to maneuver energy between their native service territories. As utility alliances expanded, transmission networks grew to incorporate new members, however connections to nonallied utilities tended to be weaker.
The results of these generations-old alliances is a U.S. system fragmented into
a few dozen areas with restricted connectivity between them. The areas are distributed throughout three separate and largely remoted networks, known as “interconnections”–Japanese, Western, and most of Texas.
An October 2023
report from the U.S. Division of Vitality reveals the severity of the issue. Primarily based on research carried out by nationwide labs and tutorial researchers, the DoE calculated that interregional transmission in america should broaden as a lot as fivefold to take care of reliability and enhance resilience to excessive climate and supply entry to low-cost clear vitality.
The worth of linking regional networks
is broadly accepted globally. The European Fee in 2018 set a goal for every member nation to transmit throughout its borders at the very least 15 p.c of the electrical energy produced in its territories. By the tip of 2022, 23 gigawatts of cross-border connections in Europe have been below building or in superior levels of allowing, with rather more on the best way.
Huge Advantages
One of many most important values of connecting regional networks is that it allows—and is the truth is
essential for—incorporating renewable vitality. For example, 4 proposed high-voltage traces totaling 600 kilometers alongside the seam of regional networks within the higher Midwest may join at the very least 28 gigawatts of wind and photo voltaic. These traces have been on the drafting board for years, however utilities within the neighboring areas haven’t moved them ahead. The price of the mission, estimated at US $1.9 billion, could seem to be a significant funding, however it’s a fraction of what U.S. utilities spend every year rebuilding getting older transmission infrastructure.
Plus, including interregional transmission for renewables can
considerably cut back prices for customers. Such connections permit extra wind and solar energy to movement to neighboring areas when climate situations are favorable and permit the import of vitality from elsewhere when renewables are much less productive.
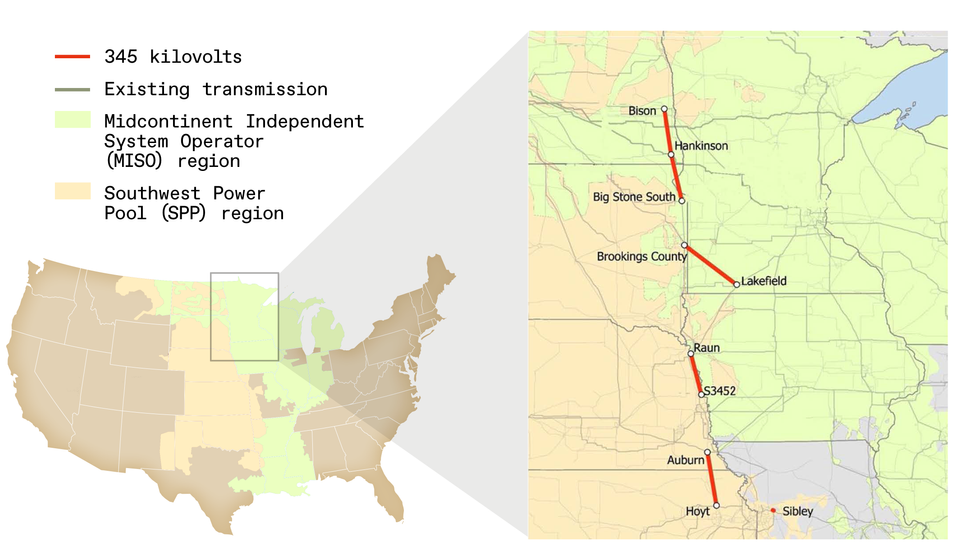 Proposed new transmission traces within the higher Midwest may join at the very least 28 gigawatts of wind and photo voltaic to regional networks.Joint Focused Interconnection Queue Research (JTIQ), MISO, SPP
Proposed new transmission traces within the higher Midwest may join at the very least 28 gigawatts of wind and photo voltaic to regional networks.Joint Focused Interconnection Queue Research (JTIQ), MISO, SPP
Even with out renewables, higher built-in networks usually decrease prices for customers as a result of they cut back the quantity of era capability wanted total and lower vitality market costs. Interregional transmission additionally enhances reliability,notably throughout excessive climate.
In December 2022, Winter Storm Elliott
disabled energy vegetation and pipelines from North Dakota to Georgia, resulting in energy outages within the South and billions of {dollars} in extra vitality expenses throughout the Japanese United States. Restricted interregional connections staved off catastrophe. These hyperlinks moved electrical energy to the place it was most wanted, serving to to keep away from the form of disaster that befell Texas’s remoted electrical grid the 12 months earlier than, when a deep freeze left tens of millions with out energy for days.
Energy, Revenue, and Management
However from the angle of utility corporations, interregional transmission presents a number of drawbacks. First, constructing such connections
opens the door for rivals who could promote lower-priced energy into their area. Second, utilities make far extra money establishing energy vegetation than constructing transmission traces, so they’re reluctant to construct connections that may completely cut back their alternatives for future era investments.
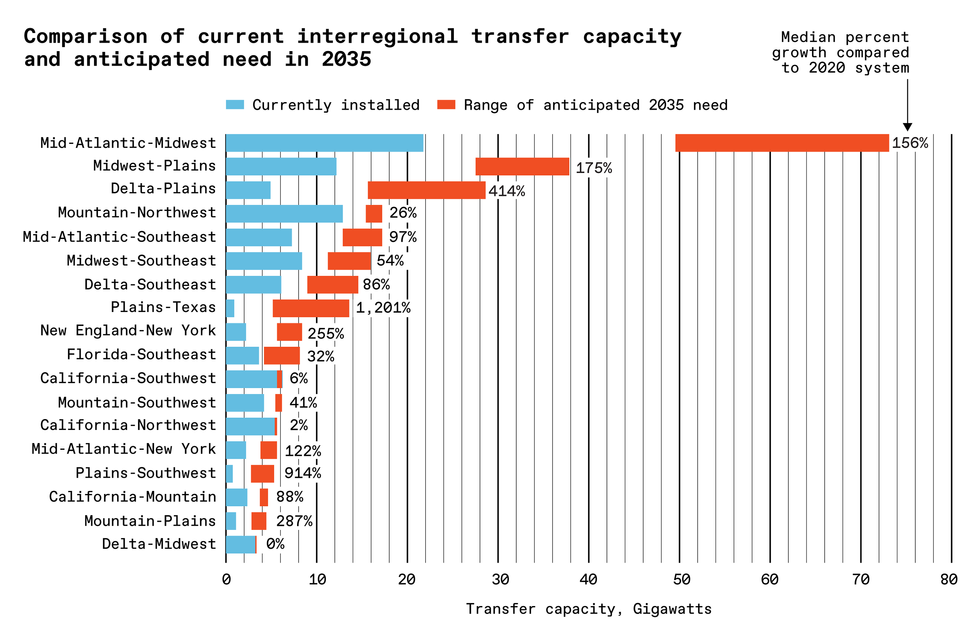 This comparability of present interregional switch capability and anticipated want reveals that areas might want to enhance transmission considerably, assuming average load and excessive clean-energy development.“Nationwide Transmission Wants Research,” U.S. Division of Vitality
This comparability of present interregional switch capability and anticipated want reveals that areas might want to enhance transmission considerably, assuming average load and excessive clean-energy development.“Nationwide Transmission Wants Research,” U.S. Division of Vitality
Third, main interregional transmission tasks are much less financially enticing to utility corporations as compared with smaller ones. For bigger tasks, utilities could need to compete towards different builders for the chance to revenue from building. The utility {industry} sponsors
third-party oversight of such tasks, whereas smaller tasks are much less scrutinized by the {industry}. Smaller tasks are simpler to drag off and extra worthwhile than the bigger ones, as a result of they want fewer building permits, face much less assessment by regulators and {industry}, and are constructed by utilities with out competitors from different builders.
Fourth, interregional traces threaten utility corporations’ dominance over the nation’s energy provide. Within the energy {industry},
asset possession offers management over guidelines that govern vitality markets and transmission service and growth. When upstart entities construct energy vegetation and transmission traces, they can dilute utility corporations’ management over power-industry guidelines and forestall utilities from dictating selections about transmission growth.
Assistance on the Hill
Addressing the transmission scarcity is on the agenda in Washington, however utility corporations are lobbying towards reforms. In September, Senator John Hickenlooper (D-Colo.) and Consultant Scott Peters (D-Calif.) launched the
BIG WIRES Act to drive utilities or competing builders to construct extra interregional hyperlinks. In 2022, Senator Joe Manchin (D-W.Va.) proposed an method wherein transmission builders suggest tasks to the DoE. If the company deems a mission to be within the nationwide curiosity, federal regulators may allow the mission’s building and drive utilities to pay for it.
In the meantime, the Federal Vitality Regulatory Fee (FERC) is presently reevaluating how utilities develop and function transmission networks and
could problem new guidelines within the coming months. In response, utilities are making ready litigation that might strip FERC of authority to impose any transmission guidelines in any respect. Their purpose is to guard their income and management, even when it comes on the shopper’s expense.
The U.S. Division of Vitality is pitching in too. On 6 February, the division introduced it might award $1.2 billion to assist new high-voltage transmission traces, on prime of the $1.3 billion it offered final fall to 3 interstate tasks. Later this 12 months, it plans to unveil its long-awaited
nationwide plan for a large-scale transmission build-out. However with out {industry} assist or tens of billions in further funding from Congress to construct these tasks, the company’s imaginative and prescient is not going to be realized.
Main With Expertise
New enterprise fashions and applied sciences provide hope. Buyers and entrepreneurs are growing long-distance
direct-current traces, that are extra environment friendly at transferring massive quantities of vitality over lengthy distances, in contrast with AC. These DC tasks sidestep the utility-dominated transmission-expansion planning processes.
Many high-voltage DC (HVDC) transmission traces are already in operation, particularly in
China and Europe. In truth, DC traces are actually the most well-liked alternative in Europe’s plans to unite the continent.
The USA lacks a coordinated nationwide planning effort to attach regional networks, however builders could make progress mission by mission. For instance, future DC traces will join mills in
Kansas to a neighboring community in Illinois, stretch from Wyoming to California, and transfer wind and photo voltaic vitality throughout the Southwest. Every of those tasks will transfer renewable vitality from the place it may be generated cheaply to bigger markets the place energy costs are greater, and in doing so they’ll assist bolster the nation’s regional transmission networks.
These pioneering tasks present that utility corporations in america don’t need to construct interregional traces, however they do have to get out of the best way. Transmission guidelines written by utilities and their {industry} allies can
hinder, delay, and add prices to those new tasks. Streamlining federal and state allowing processes can encourage extra funding, however slicing authorities purple tape is not going to neutralize utility corporations’ objections to interregional transmission.
U.S. regulators and Congress should press ahead. Promising proposals that promote new enterprise fashions and restrict utility management are on the desk. Our vitality future is on the road.
From Your Website Articles
Associated Articles Across the Internet
