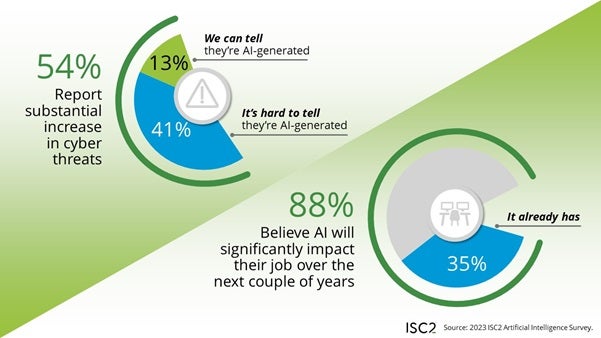
Most cybersecurity professionals (88%) imagine AI will considerably influence their jobs, in keeping with a new survey by the Worldwide Data System Safety Certification Consortium; with solely 35% of the respondents having already witnessed AI’s results on their jobs (Determine A). The influence shouldn’t be essentially a optimistic or unfavorable influence, however relatively an indicator that cybersecurity professionals count on their jobs to vary. As well as, considerations have arisen about deepfakes, misinformation and social engineering assaults. The survey additionally lined insurance policies, entry and regulation.
How AI may have an effect on cybersecurity professionals’ duties
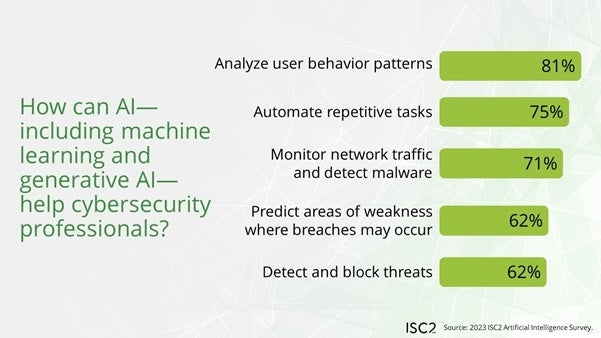
Survey respondents usually imagine that AI will make cybersecurity jobs extra environment friendly (82%) and can unlock time for higher-value duties by caring for different duties (56%). Specifically, AI and machine studying may take over these elements of cybersecurity jobs (Determine B):
- Analyzing consumer conduct patterns (81%).
- Automating repetitive duties (75%).
- Monitoring community visitors and detecting malware (71%).
- Predicting the place breaches may happen (62%).
- Detecting and blocking threats (62%).
The survey doesn’t essentially rank a response of “AI will make some components of my job out of date” as unfavorable; as a substitute, it’s framed as an enchancment in effectivity.
Prime AI cybersecurity considerations and doable results
By way of cybersecurity assaults, the professionals surveyed have been most involved about:
- Deepfakes (76%).
- Disinformation campaigns (70%).
- Social engineering (64%).
- The present lack of regulation (59%).
- Moral considerations (57%).
- Privateness invasion (55%).
- The chance of information poisoning, intentional or unintentional (52%).
The group surveyed was conflicted on whether or not AI can be higher for cyber attackers or defenders. When requested in regards to the assertion “AI and ML profit cybersecurity professionals greater than they do criminals,” 28% agreed, 37% disagreed and 32% have been not sure.
Of the surveyed professionals, 13% mentioned they have been assured they may definitively hyperlink an increase in cyber threats during the last six months to AI; 41% mentioned they couldn’t make a definitive connection between AI and the rise in threats. (Each of those statistics are subsets of the group of 54% who mentioned they’ve seen a considerable improve in cyber threats during the last six months.)
SEE: The UK’s Nationwide Cyber Safety Centre warned generative AI may improve the amount and influence of cyberattacks over the subsequent two years – though it’s somewhat extra difficult than that. (TechRepublic)
Menace actors may reap the benefits of generative AI in an effort to launch assaults at speeds and volumes not doable with even a big crew of people. Nonetheless, it’s nonetheless unclear how generative AI has affected the risk panorama.
In flux: Implementation of AI insurance policies and entry to AI instruments in companies
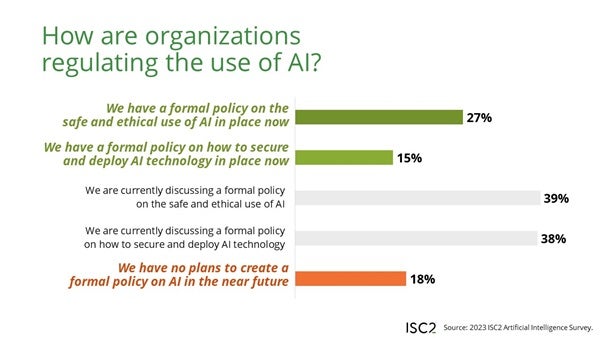
Solely 27% of ISC2 survey respondents mentioned their organizations have formal insurance policies in place for secure and moral use of AI; one other 15% mentioned their organizations have formal insurance policies on learn how to safe and deploy AI expertise (Determine C). Most organizations are nonetheless engaged on drafting an AI use coverage of 1 form or one other:
- 39% of respondents’ corporations are engaged on AI ethics insurance policies.
- 38% of respondents’ corporations are engaged on AI secure and safe deployment insurance policies.
The survey discovered a really large number of approaches to permitting workers entry to AI instruments, together with:
- My group has blocked entry to all generative AI instruments (12%).
- My group has blocked entry to some generative AI instruments (32%).
- My group permits entry to all generative AI instruments (29%).
- My group has not had inside discussions about permitting or disallowing generative AI instruments (17%).
- I don’t know my group’s strategy to generative AI instruments (10%).
The adoption of AI remains to be in flux and can absolutely change much more because the market grows, falls or stabilizes, and cybersecurity professionals could also be on the forefront of consciousness about generative AI points within the office because it impacts each the threats they reply to and the instruments they use for work. A slim majority of cybersecurity professionals (60%) surveyed mentioned they really feel assured they may lead the rollout of AI of their group.
“Cybersecurity professionals anticipate each the alternatives and challenges AI presents, and are involved their organizations lack the experience and consciousness to introduce AI into their operations securely,” mentioned ISC2 CEO Clar Rosso in a press launch. “This creates an amazing alternative for cybersecurity professionals to steer, making use of their experience in safe expertise and guaranteeing its secure and moral use.”
How generative AI needs to be regulated
The methods through which generative AI is regulated will rely so much on the interaction between authorities regulation and main tech organizations. 4 out of 5 survey respondents mentioned they “see a transparent want for complete and particular laws” over generative AI. How that regulation could also be finished is a sophisticated matter: 72% of respondents agreed with the assertion that several types of AI will want completely different laws.
- 63% mentioned regulation of AI ought to come from collaborative authorities efforts (guaranteeing standardization throughout borders).
- 54% mentioned regulation of AI ought to come from nationwide governments.
- 61% (polled in a separate query) want to see AI specialists come collectively to assist the regulation effort.
- 28% favor personal sector self-regulation.
- 3% need to retain the present unregulated setting.
ISC2’s methodology
The survey was distributed to a world group of 1,123 cybersecurity professionals who’re ISC2 members between November and December 2023.
The definition of “AI” can typically be unsure immediately. Whereas the report makes use of the final phrases “AI” and machine studying all through, the subject material is described as “public-facing massive language fashions” like ChatGPT, Google Gemini or Meta’s Llama, often generally known as generative AI.
