Supply — Nikkei Asia.
Main gamers within the chip business and the street thus far
There are at present three main producers within the chip business and people are Intel (U.S.), TSMC (Taiwan), and Samsung (South Korea). There may be additionally the Chinese language firm SMIC, however it’s lagging behind the remainder of the pack and is about two generations behind for the second.
The three main producers talked about above have all been pushing strongly to advance chips with the extra vital leaps beginning within the 2000s. Right here’s a fast overview beginning with 2013 up till now, the yr we’re in in the mean time, and what to look ahead to within the close to future.
High row has the yr, with the corresponding transistor gate width measured in nanometers under. The empty areas signify no newly launched technology for that yr.
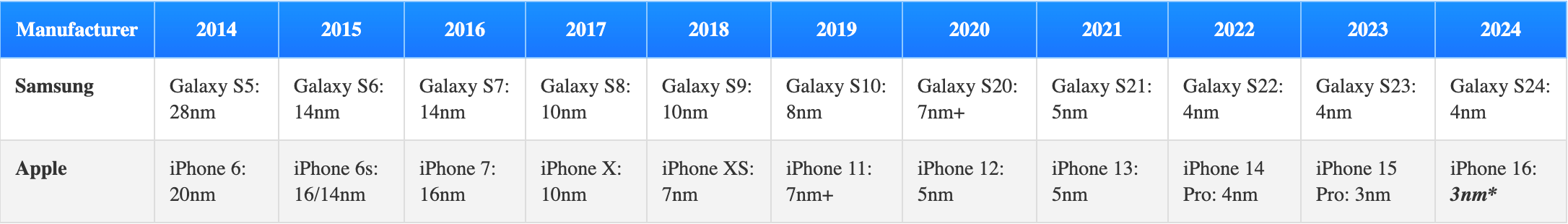
“*” stands for “anticipated” as the data is but to turn into official.
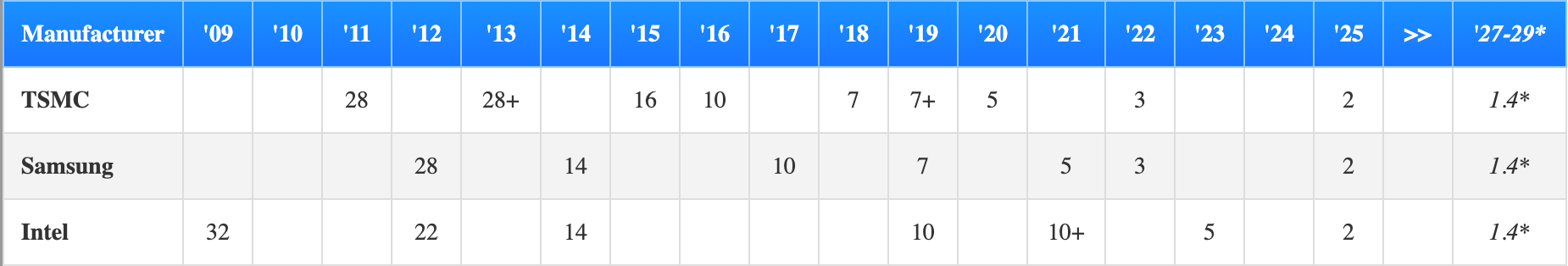
“*” stands for “anticipated” as the data is but to turn into official.
You’ll be able to most likely inform for your self that all through the years, the nanometers have been steadily reducing by about half of the earlier technology’s measurement. In different phrases, the variety of transistors included in a chip has been doubling, and a more in-depth inspection reveals that it has persistently taken the business roughly a few years to go to the following stage.
Moore’s Regulation: A deceptive time period
The persistently related period of time it takes producers to leap from one technology to the following in a chip’s evolution isn’t any coincidence. In reality, Intel co-founder Gordon Moore himself said as early as 1965 that each eighteen months the variety of transistors inside chips will double, which these days is called Moore’s Regulation.This tendency in chip evolution has remained true for therefore lengthy now, that it nearly looks like we’re speaking a couple of pure regulation, one which doesn’t change irrespective of the circumstances. However the reality is totally different. Moore offered his ideas on the topic as a mere statement and never a “regulation”. In reality, he didn’t foresee his prediction to proceed any greater than a single decade.
It’s nothing wanting spectacular that Moore’s statement has continued to be true all through all of those years, however there are bodily limitations to how lengthy this could proceed.
Present transistors are made out of silicon, and a silicon atom is 0.2nm in measurement. In different phrases, even when we do handle to proceed shrinking transistors, we can not make them any smaller than that.
Visible assist for nanometer measurement
Earlier than we proceed speaking about nanometer this and nanometer that, it’s most likely finest if we first perceive how huge a nanometer really is. Now, identical to it’s troublesome for a human mind to understand the dimensions of the universe, so it’s to grasp the dimensions of 1 nanometer, however the next examples ought to put issues into perspective (and can seemingly blow your thoughts).
Are we nearing the top of chipset evolution?
So the pure query to ask ourselves is whether or not chip innovation will come to a halt, or if there are different avenues the chip business can flip to. Properly, fortunately, there’s at all times a method to develop and make a product higher. Listed below are just a few glimpses into the way forward for computing.
Superior chip packaging
Superior chip packaging refers to stacking a number of chips onto wafers, which can assist obtain ranges of efficiency mentioned to be similar to chips made on the 5 and even the 3nm course of.
This technique can also be inexpensive, because it doesn’t require the identical quantity of precision and delicate tools vital for shrinking transistors.
Standard firms reminiscent of Intel and Nvidia have already applied this technique into their newest chipsets.
Making transistors out of a special aspect
So, as we’ve already established, transistors are made out of silicon. There’s a purpose we’ve the so-called Silicon Valley in California. However as we said earlier, silicon can solely take us thus far earlier than we attain its limitations.One instance is gallium. Now, gallium’s atomic radius is just not smaller than that of silicon so you can not match extra transistors made out of it. Gallium Nitride, nonetheless, produces much less warmth, which suggests there’s much less cooling required to maintain them at most efficiency.
This is only one instance although. There are different supplies producers can experiment with to realize higher outcomes from a chip.
Quantum computing
One other street we will take to proceed growing our technological horsepower is quantum computing. Quantum computer systems have the potential to assist us delve into utterly new territories, however the possibilities that they may energy our telephones anytime sooner or later are extraordinarily slim as they require excessive cooling (15 millikelvin to be actual, which is colder than outer area), which in itself requires very advanced and enormous elements.So, in different phrases, quantum computing is an choice, simply not one that might have an effect on cell tech in a significant means. Not less than not for the foreseeable future.
