COMMENTARY
2024 is shaping as much as be a panorama of unparalleled volatility in cybersecurity. With regulatory shifts, third-party service incidents, and looming financial uncertainties, the necessity for board engagement in threat administration packages is essential.
It additionally has {dollars} hooked up to it. Knowledge breaches are two to a few occasions dearer for organizations through which boards aren’t actively concerned in cyber discussions. There’s additionally a rising demand for CISOs to search out progressive methods to speak their firm’s threat setting with stakeholders.
As well as, regulators are imposing new fiduciary necessities. For instance, the US Securities and Trade Fee’s cyber laws mandate the disclosure of “materials” cyber incidents inside 4 days of figuring out an occasion’s materiality in an try and align boards with this rising cyber risk. The rulings additionally require annual disclosure of fabric dangers and the way the corporate manages them.
CISOs are utilizing agreed-upon materiality definitions to speak threat to senior executives and boards. This helps them make clear what materiality means for his or her specific group and consider the probability of cyber incidents. However for a lot of CISOs, materiality stays an ambiguous time period, open for interpretation primarily based on a company’s distinctive cybersecurity setting.
Figuring out Materials Loss With Business Benchmarks
The core of the confusion round materiality is figuring out what constitutes a “materials loss.” It is a difficult, however important, dialogue to provoke. Essentially the most specific business definition revealed to date — by Dr. Jack Freund, chief threat officer of Kovrr and Distinguished ISSA Fellow, and Natalie Jorion, who formulated the Freund-Jorion Cyber Materiality Heuristic — assesses materiality as 0.01% of the prior yr’s income, equating to roughly one foundation level of income. (As we are going to see under, this equates to roughly an hour’s value of income for Fortune 1000 firms.)
By testing completely different thresholds towards business benchmarks, organizations can achieve a clearer understanding of their vulnerability to materials cyberattacks. Kovrr not too long ago modeled the anticipated cyber incidents skilled by the US Fortune 1000 firms. Every group was analyzed in response to a tailor-made assortment of occasions and responses from safety controls, producing a cyber threat quantification (CRQ) evaluation that exposed the probability and value of every occasion in response to business.
The “Fortune 1000 Cyber Danger Report” estimates the likelihood for an organization within the Fortune 1000 to expertise cyber losses totaling greater than a threshold. For example, the mannequin evaluates the likelihood of experiencing cyber losses totaling $50 million, which quantities to roughly 1.2 days of income. Though important, this can be thought of materially low. A $100 million incident equates to 2.4 days of income, and a $500 million incident represents practically two weeks of operations — undoubtedly a fabric loss for the common Fortune 1000 firm.
To place these figures into context, the common annual income of an organization within the Fortune 1000 is roughly $15 billion, and every day income is roughly $41 million. This can be a extra sensible interpretation of the mannequin outcomes, which may help monetary planning.
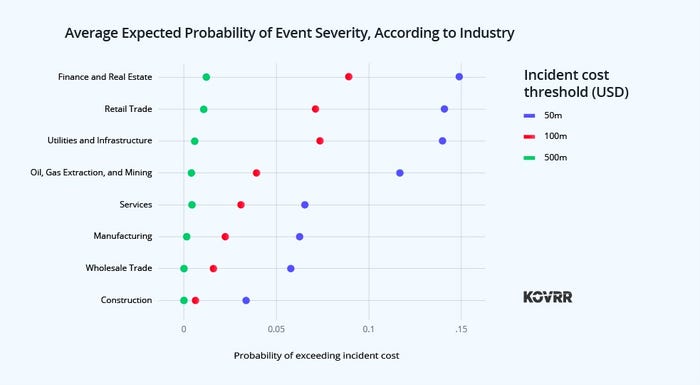
The chart above illustrates the likelihood of organizations inside a selected business experiencing a loss in response to magnitude, which may consequence from a single important occasion or a sequence of smaller incidents pointing to weaknesses in a company’s cybersecurity posture.
Notably, the finance and actual property, retail commerce, utilities, and oil, gasoline extraction, and mining industries all have a better than 10% likelihood (1 in 10) of cyber occasions costing their companies greater than $50 million (inside 12 months) and a greater than 5% likelihood (1 in 20) of costing greater than $100 million.
Whereas a 1 in 10 likelihood of experiencing an occasion that prices a company sooner or later of income feels like a excessive likelihood, if the incident have been decreased to 1 hour, the likelihood can be a lot larger.
Defining Materiality to Defend In opposition to Materials Occasions
CISOs can make use of various methods to find out materiality thresholds, enabling them to make the required investments within the enterprise areas which might be most vulnerable to materials threat. With sharp definitions, executives and cybersecurity leaders can collaborate and make data-driven selections that precisely replicate a company’s risk panorama.
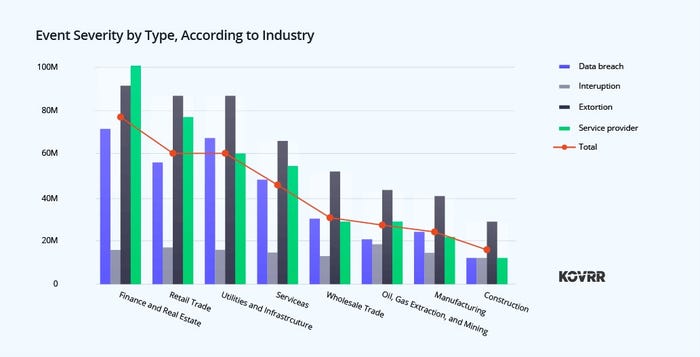
First, CISOs ought to determine which occasion drivers are most definitely to spur a fabric loss inside their given business. Though there are overarching traits, together with the excessive value of information breaches, a extra honed evaluation is important. For instance, the chart under, which exhibits the median (most definitely) value of occasions by kind, reveals that extortion and companies supplier occasions have a better threat for a lot of organizations.
By means of monetary insights supplied by a CRQ answer, CISOs can successfully talk the good thing about enhancing controls, postures, and safety practices with the board, demonstrating the potential discount in materials occasion probability and total value.
Lastly, it is essential to observe organizational threat on an ongoing foundation. The exterior risk setting and value of remediation are topic to common modifications.
Though 2024 is about to be one of the vital difficult years for cybersecurity personnel, implementing a data-driven framework that clearly defines materials loss can facilitate extra simple discussions with the board and promote a tradition of cyber resiliency.