To deploy a ransomware assault, adversaries should first achieve entry to a sufferer’s company atmosphere, units, and information. Risk actors sometimes use two principal approaches to achieve entry: logging in utilizing compromised credentials, i.e., reputable entry information that had beforehand been stolen, and exploiting vulnerabilities in purposes and instruments utilized by the enterprise. Different much less widespread modes of entry embrace brute power assaults, provide chain compromise, malicious emails/paperwork, and adware. Phishing options closely in ransomware assaults however is primarily used to steal the credentials later used to log in to the group.

This report highlights how ransomware outcomes differ relying on the foundation reason behind the assault. It compares the severity, monetary price, and operational impression of assaults that begin with an exploited vulnerability with these the place adversaries use compromised credentials to penetrate the group. It additionally identifies the {industry} sectors most and least generally exploited.
The findings are primarily based on a vendor-agnostic survey commissioned by Sophos of two,974 IT/cybersecurity professionals in small and mid-sized organizations (100-5,000 workers) that had been hit by ransomware within the final yr. The survey was carried out by unbiased analysis company Vanson Bourne in early 2024 and displays respondents’ experiences over the earlier 12 months.
>> Obtain the PDF copy of the report
Govt abstract
Whereas all ransomware assaults have adverse outcomes, those who begin by exploiting unpatched vulnerabilities are significantly brutal for his or her victims. Organizations hit by assaults that started on this method report significantly extra extreme outcomes than these whose assaults began with compromised credentials, together with the next propensity to:
- Have backups compromised (75% success fee vs. 54% for compromised credentials)
- Have information encrypted (67% encryption fee vs. 43% for compromised credentials)
- Pay the ransom (71% cost fee vs. 45% for compromised credentials)
- Cowl the complete price of the ransom in-house (31% funded the complete ransom in-house vs. 2% for compromised credentials)
Additionally they reported:
- 4X greater general assault restoration prices ($3M vs. $750k for compromised credentials)
- Slower restoration time (45% took greater than a month vs. 37% for compromised credentials)
The examine focuses on correlation, and additional exploration is required into causes behind these outcomes. It’s necessary to keep in mind that not all ransomware assaults are equal. Some are executed by refined, well-funded gangs utilizing a spread of revolutionary approaches. On the identical time, using crude, low-cost ransomware by lower-skilled risk actors is on the rise. It could be that adversaries which might be capable of exploit unpatched software program vulnerabilities are extra expert than attackers who purchase stolen credentials from the darkish net (for instance), and subsequently higher ready to reach compromising backups and encrypting information.
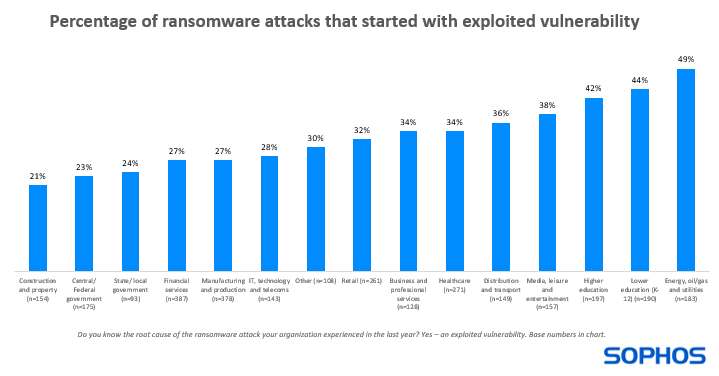
One-third of ransomware assaults begin with an unpatched vulnerability
32% of ransomware assaults skilled by the survey respondents up to now yr began with an exploited vulnerability. Diving deeper, we see that the proportion of ransomware assaults that started on this method varies significantly by {industry}:
- Highest: power, oil/gasoline, and utilities – 49% of assaults
- Lowest: development and property – 21% of assaults
This variation is probably going impacted, partly, by the totally different expertise options used and their related patching challenges. Sectors similar to power, oil/gasoline, and utilities sometimes use the next proportion of older applied sciences extra liable to safety gaps than many different sectors, and patches might not be obtainable for legacy and end-of-life options.
On the identical time, most of the time, patches are obtainable – they only haven’t been utilized. Of the assaults that Sophos incident responders have been introduced in to remediate in 2022 that began with exploited vulnerabilities, over half (55%) have been brought on by ProxyShell and Log4Shell — each of which had present patches on the time of compromise. Sophos continues to see ProxyShell being exploited 30 months after the discharge of the patch. Be taught extra.
The evaluation additionally revealed that the propensity to expertise an exploit-led assault varies by group dimension:
- 26% of ransomware assaults in small companies (sub $50M annual income)
- 30% of ransomware assaults in mid-sized companies ($50M-$1B)
- 37% of ransomware assaults in giant companies ($1B+)
As organizations develop, their IT infrastructures are likely to develop with them. The bigger the atmosphere, the higher the problem in understanding the assault floor and the extra instruments and applied sciences that should be maintained.
Ransomware impacts are extra extreme when the assault begins with an exploited vulnerability
The ultimate objective for a ransomware actor is to encrypt a company’s information and extract a ransom cost in return for the decryption key. On the best way, they nearly all the time try to compromise their sufferer’s backups to scale back their means to revive information with out paying.
The evaluation reveals that throughout all three factors – backup compromise, information encryption, and ransom cost – the impacts are most extreme when the assault begins with an exploited vulnerability.
Backup compromise
There is no such thing as a distinction in attackers’ propensity to try to compromise backups primarily based on the foundation trigger. Adversaries tried to compromise them in 96% of assaults that began with exploited vulnerabilities and compromised credentials. Nevertheless, there’s a appreciable distinction of their success fee:
- 75% of makes an attempt have been profitable when the assault began with an exploited vulnerability
- 54% of makes an attempt have been profitable when the assault began with compromised credentials
This can be as a result of adversaries who leverage unpatched vulnerabilities are extra expert at breaching backups. It could additionally mirror that organizations with an uncovered assault floor have weaker backup safety. Regardless of the trigger, having your backups compromised reduces resilience in opposition to the complete impression of the assault.
Knowledge encryption
Organizations are greater than 50% extra more likely to have their information encrypted when an assault begins with an exploited vulnerability fairly than compromised credentials:
- 67% of assaults resulted in information encryption when the assault began with an exploited vulnerability
- 43% of assaults resulted in information encryption when the assault began with compromised credentials
As with backup compromise, the distinction in final result by root trigger could mirror differing ability ranges in adversary teams and variations within the general power of a company’s cyber defenses.
Ransom cost fee
Given the upper fee of backup compromise reported when the assault began with an exploited vulnerability, it’s maybe no shock that this group reported the next propensity to pay the ransom:
- 71% of organizations that had information encrypted paid the ransom when the assault began with an exploited vulnerability
- 45% of organizations that had information encrypted paid the ransom when the assault began with compromised credentials
With out backups to recuperate from, the stress on ransomware victims to entry the decryption key will increase, seemingly driving organizations to work with the attackers to revive information.
Unpatched vulnerabilities have business-critical penalties
Ransomware assaults that begin with an exploited vulnerability have significantly higher monetary and operational impression than those who start with compromised credentials.
Ransom cost
Whereas the assault root trigger has an nearly negligible impression on the ransom cost sum, with the median quantity coming in at $1.988M (exploited vulnerabilities) and $2M (compromised credentials), it does have a substantial impression on the funding of the ransom cost:
- 31% of organizations funded the complete ransom in-house when the assault began with an exploited vulnerability
- 2% of organizations funded the complete ransom in-house when the assault began with compromised credentials
Father or mother firms and cyber insurance coverage suppliers usually tend to contribute to the ransom when the assault begins with compromised credentials fairly than an exploited vulnerability.
Trying extra broadly on the propensity of insurance coverage carriers to honor claims we see that one quarter (25%) of denied claims by organizations that skilled an exploited vulnerability have been resulting from not having the required cyber defenses for the declare to be honored, in comparison with 12% of claims the place adversaries used compromised credentials.
Restoration price
The ransom is only one component that contributes to the general restoration price from a ransomware assault. Leaving apart any ransom paid, the median general restoration price for ransomware assaults that begin with an exploited vulnerability ($3M) is 4 instances higher than for those who start with compromised credentials ($750K).
Restoration time
Recovering from an assault that begins with an exploited vulnerability is usually a lot slower than when the foundation trigger is compromised credentials.
- 45% took greater than a month to recuperate when the assault began with an exploited vulnerability
- 37% took greater than a month to recuperate when the assault began with compromised credentials
This discovering seemingly displays the totally different remediation actions that victims must undertake relying on the foundation trigger, and their respective operational overheads. Patching a system or upgrading from an end-of-life product to a supported model could be extra time-consuming than resetting credentials. It could even be a results of the higher injury brought on by exploited vulnerability assaults, together with a higher chance of backup compromise and information encryption.
Suggestions
Patching is a crucial first step in lowering the danger of falling sufferer to a ransomware assault (or some other breach) that begins with an exploited vulnerability. For those who repair the safety hole, adversaries can’t exploit it. It ought to ideally be a part of a broader exploit-prevention threat administration technique:
Reduce your assault floor
- Preserve full visibility of all of your external-facing property to know what you’re coping with and keep away from blind spots.
- Patch utilizing risk-based prioritization. With new exploits found quicker than most organizations can repair them, focus your efforts the place they are going to have essentially the most impression. This implies figuring out and prioritizing the patching of high-risk exposures.
- Replace often. Utilizing the most recent model of an software or software ensures you profit from the distributors’ most up-to-date safety fixes.
Deploy anti-exploit protections
- Whereas the variety of exploitable vulnerabilities continues to develop quickly, attackers can solely leverage a restricted variety of methods to take advantage of. Constructed-in anti-exploitation capabilities in endpoint safety options cease the behaviors utilized in these assaults – together with with zero-day vulnerabilities for which no patch has but been launched.
Detect and reply to suspicious actions
- Expertise alone can not cease each assault. Adversaries are expert at leveraging reputable IT instruments and stolen credentials, adapting their strategy on the fly to keep away from detection. Stopping superior, human-led ransomware assaults and breaches requires 24/7 detection and response throughout your atmosphere, delivered by a specialist supplier or highly-skilled in-house staff.
How Sophos may help
Sophos Managed Threat
Sophos Managed Threat is a vulnerability and assault floor administration service powered by industry-leading Tenable expertise and delivered by a devoted staff of Sophos risk publicity and remediation consultants. It addresses 4 crucial use instances: assault floor visibility, steady threat monitoring, vulnerability prioritization, and quick identification of latest dangers.
Sophos Managed Threat is accessible with Sophos MDR, a totally managed cybersecurity service delivered 24/7 by Sophos risk consultants. A devoted staff of Sophos Managed Threat operators – extremely expert in vulnerabilities and risk exposures – works carefully with Sophos MDR analysts across the clock.
Sophos Endpoint
Sophos Endpoint contains greater than 60 anti-exploitation capabilities that block the behaviors adversaries use to take advantage of an unpatched vulnerability, stopping each identified vulnerabilities and zero-day threats. The anti-exploit capabilities deploy routinely from day one with no configuration or want for wonderful tuning.
Sophos Endpoint takes a complete strategy to safety with out counting on one safety method. Internet, software, and peripheral controls scale back your risk floor and block widespread assault vectors. AI, behavioral evaluation, anti-ransomware, and different state-of-the-art applied sciences cease threats quick earlier than they escalate.