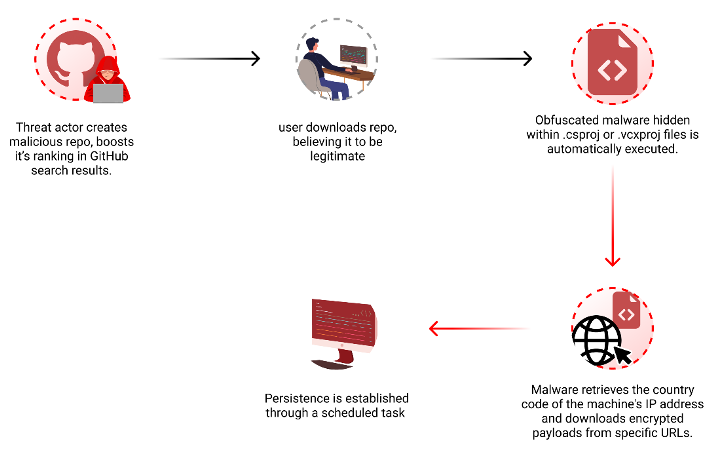
Risk actors at the moment are profiting from GitHub’s search performance to trick unsuspecting customers searching for standard repositories into downloading spurious counterparts that serve malware.
The newest assault on the open-source software program provide chain includes concealing malicious code inside Microsoft Visible Code challenge information that is designed to obtain next-stage payloads from a distant URL, Checkmarx mentioned in a report shared with The Hacker Information.
“Attackers create malicious repositories with standard names and matters, utilizing strategies like automated updates and faux stars to spice up search rankings and deceive customers,” safety researcher Yehuda Gelb mentioned.
The thought is to control the search rankings in GitHub to convey menace actor-controlled repositories to the highest when customers filter and type their outcomes based mostly on the newest updates and enhance the recognition by way of bogus stars added by way of pretend accounts.
In doing so, the assault lends a veneer of legitimacy and belief to the fraudulent repositories, successfully deceiving builders into downloading them.
“In distinction to previous incidents the place attackers had been discovered so as to add a whole bunch or hundreds of stars to their repos, it seems that in these circumstances, the attackers opted for a extra modest variety of stars, most likely to keep away from elevating suspicion with an exaggerated quantity,” Gelb mentioned.
It is value stating that earlier analysis from Checkmarx late final yr uncovered a black market comprising on-line shops and discussion groups which might be promoting GitHub stars to artificially increase a repository’s reputation, a way known as star inflation.
What’s extra, a majority of those repositories are disguised as legit tasks associated to standard video games, cheats, and instruments, including one other layer of sophistication to make it more durable to tell apart them from benign code.
Some repositories have been noticed downloading an encrypted .7z file containing an executable named “feedbackAPI.exe” that has been inflated to 750 MB in a probable try to evade antivirus scanning and finally launch malware that shares similarities with Keyzetsu clipper.
The Home windows malware, which got here to gentle early final yr, is usually distributed via pirated software program comparable to Evernote. It is able to diverting cryptocurrency transactions to attacker-owned wallets by substituting the pockets handle copied within the clipboard.
The findings underscore the due diligence that builders should observe when downloading supply code from open-source repositories, to not point out the hazards of solely counting on fame as a metric to guage trustworthiness.
“Using malicious GitHub repositories to distribute malware is an ongoing pattern that poses a major menace to the open-source ecosystem,” Gelb mentioned.
“By exploiting GitHub’s search performance and manipulating repository properties, attackers can lure unsuspecting customers into downloading and executing malicious code.”
The event comes as Phylum mentioned it found an uptick within the variety of spam (i.e., non-malicious) packages being printed to the npm registry by a consumer named ylmin to orchestrate a “large automated crypto farming marketing campaign” that abuses the Tea protocol.
“The Tea protocol is a web3 platform whose said aim is compensating open supply package deal maintainers, however as a substitute of money rewards, they’re rewarded with TEA tokens, a cryptocurrency,” the corporate’s analysis crew mentioned.
“The Tea protocol is just not even reside but. These customers are farming factors from the ‘Incentivized Testnet,’ apparently with the expectation that having extra factors within the Testnet will enhance their odds of receiving a later airdrop.”