Menace actors are actively exploiting vital vulnerabilities in OpenMetadata to achieve unauthorized entry to Kubernetes workloads and leverage them for cryptocurrency mining exercise.
That is in keeping with the Microsoft Menace Intelligence staff, which mentioned the failings have been weaponized because the begin of April 2024.
OpenMetadata is an open-source platform that operates as a metadata administration instrument, providing a unified resolution for information asset discovery, observability, and governance.
The issues in query – all found and credited to safety researcher Alvaro Muñoz – are listed beneath –
- CVE-2024-28847 (CVSS rating: 8.8) – A Spring Expression Language (SpEL) injection vulnerability in PUT /api/v1/occasions/subscriptions (fastened in model 1.2.4)
- CVE-2024-28848 (CVSS rating: 8.8) – A SpEL injection vulnerability in GET /api/v1/insurance policies/validation/situation/<expr> (fastened in model 1.2.4)
- CVE-2024-28253 (CVSS rating: 8.8) – A SpEL injection vulnerability in PUT /api/v1/insurance policies (fastened in model 1.3.1)
- CVE-2024-28254 (CVSS rating: 8.8) – A SpEL injection vulnerability in GET /api/v1/occasions/subscriptions/validation/situation/<expr> (fastened in model 1.2.4)
- CVE-2024-28255 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – An authentication bypass vulnerability (fastened in model 1.2.4)
Profitable exploitation of the vulnerabilities may enable a risk actor to bypass authentication and obtain distant code execution.
The modus operandi uncovered by Microsoft entails the focusing on of internet-exposed OpenMetadata workloads which have been left unpatched to achieve code execution on the container operating the OpenMetadata picture.
Upon gaining an preliminary foothold, the risk actors have been noticed finishing up reconnaissance actions to find out their degree of entry to the compromised atmosphere and collect particulars in regards to the community and {hardware} configuration, working system model, the variety of lively customers, and the atmosphere variables.
“This reconnaissance step usually entails contacting a publicly accessible service,” safety researchers Hagai Ran Kestenberg and Yossi Weizman mentioned.
“On this particular assault, the attackers ship ping requests to domains that finish with oast[.]me and oast[.]professional, that are related to Interactsh, an open-source instrument for detecting out-of-band interactions.”
In doing so, the thought is to validate community connectivity from the infiltrated system to attacker-controlled infrastructure with out elevating any crimson flags, thereby giving risk actors the boldness to ascertain command-and-control (C2) communications and deploy extra payloads.
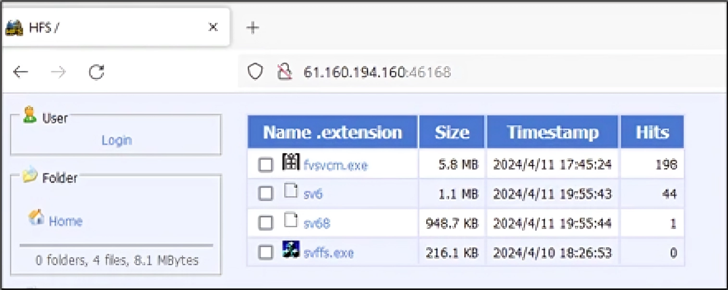
The tip aim of the assaults is to retrieve and deploy a Home windows or Linux variant of the crypto-mining malware from a distant server positioned in China, relying on the working system.
As soon as the miner is launched, the preliminary payloads are faraway from the workload, and the attackers provoke a reverse shell for his or her distant server utilizing the Netcat instrument, letting them commandeer the system. Persistence is achieved by setting cron jobs to run the malicious code at predefined intervals.
Apparently, the risk actor additionally leaves behind a private word telling that they’re poor and that they want the cash to purchase a automotive and a set. “I do not wish to do something unlawful,” the word reads.
OpenMetadata customers are suggested to change to sturdy authentication strategies, keep away from utilizing default credentials, and replace their pictures to the most recent model.
“This assault serves as a invaluable reminder of why it is essential to remain compliant and run totally patched workloads in containerized environments,” the researchers mentioned.
The event comes as publicly accessible Redis servers which have the authentication characteristic disabled or have unpatched flaws are being focused to put in Metasploit Meterpreter payloads for post-exploitation.
“When Metasploit is put in, the risk actor can take management of the contaminated system and likewise dominate the inner community of a corporation utilizing the varied options supplied by the malware,” the AhnLab Safety Intelligence Middle (ASEC) mentioned.
It additionally follows a report from WithSecure that detailed how search permissions on Docker directories may very well be abused to attain privilege escalation. It is value declaring that the difficulty (CVE-2021-41091, CVSS rating: 6.3) was beforehand flagged by CyberArk in February 2022, and addressed by Docker in model 20.10.9.
“The setting of the searchable bit for different customers on /var/lib/docker/ and youngster directories can enable for a low-privileged attacker to achieve entry to varied containers’ filesystems,” WithSecure mentioned.