Over time, Google has seemingly established a sample in the way it interacts with the net. The search engine supplies structured information codecs and instruments that permit us to provide data to Google. Suppose: meta tags, schema markup, the disavow device and extra.
Google then consumes and learns from this structured information deployed throughout the net. As soon as adequate learnings are extracted, Google then retires or de-emphasizes these structured information codecs, making them much less impactful or out of date.
This cyclical technique of giving structured information capabilities, consuming the data, studying from it after which eradicating or diminishing these capabilities appears to be a core a part of Google’s technique.
It permits the search engine to briefly empower SEOs and types as a way to an finish – extracting information to enhance its algorithms and frequently enhance its understanding of the net.
This text explores this “give and take” sample by a number of examples.
Google’s sample of ‘give and take’
The sample may be divided into 4 levels:
- Construction: Google supplies structural methods to work together with search snippets or its rating algorithms. For instance, previously, meta key phrases may inform Google which key phrases had been related to a given webpage.
- Devour: Google collects information from the net by crawling web sites. This step is necessary. With out consuming information from the net, Google has nothing to study from.
- Be taught: Google then leverages contemporary crawl information, after its beneficial constructions are applied. What had been the reactions to Google’s proposed instruments or snippets of code? Had been these helpful adjustments, or had been they abused? Google can now confidently make adjustments to its rating algorithms.
- Retire: As soon as Google has realized what they will, there’s no motive to depend on us to feed them structured data. Leaving such inbound information pipes intact will invariably result in abuse over time, so the search engine should study to outlive with out them. The instructed construction from Google is retired in lots of (although not all) cases.
The race is for the search engine to study from site owners’ interactions with Google’s instructed construction earlier than they will study to control it. Google normally wins this race.
It doesn’t imply nobody can leverage new structural gadgets earlier than Google discards them. It merely signifies that Google normally discards such gadgets earlier than illegitimate manipulations turn into widespread.
Give and take examples
1. Metadata
Previously, meta key phrases and meta descriptions performed essential roles inside Google’s rating algorithms. The preliminary assist for meta key phrases inside search engines like google truly predates Google’s founding in 1998.
Deploying meta key phrases was a approach for a webpage to inform a search engine the phrases for which the web page must be findable. Nevertheless, such a direct and helpful little bit of code was shortly abused.
Many site owners injected 1000’s of key phrases per web page within the curiosity of getting extra search visitors than was honest. It shortly led to the rise of low-quality web sites crammed with adverts that unfairly transformed acquired visitors into promoting earnings.
In 2009, Google confirmed what many had suspected for years. Google said:
“Not less than for Google’s internet search outcomes presently (September 2009), the reply isn’t any. Google doesn’t use the key phrases meta tag in our internet search rating.”
One other instance is the meta description, a snippet of code that Google supported since its early days. Meta descriptions had been used because the snippet textual content below a hyperlink in Google search outcomes.
As Google improved, it began ignoring meta descriptions in sure conditions. It is because customers may uncover a webpage by varied Google key phrases.
If a webpage discusses a number of subjects and a consumer searches for a time period associated to subject 3, exhibiting a snippet with an outline of subjects 1 or 2 wouldn’t be useful.
Due to this fact, Google started rewriting search snippets primarily based on consumer search intent, typically ignoring a web page’s static meta description.
In latest occasions, Google has shortened search snippets and even confirmed that they principally look at a web page’s main content material when producing descriptive snippets.
2. Schema and structured information
Google launched assist schema (a type of structured information) in 2009.
Initially, it pushed the “microformats” fashion of schema, the place particular person components needed to be marked up throughout the HTML to feed structured or contextual data to Google.
When it comes to idea, this truly isn’t too far faraway from the considering behind HTML meta tags. Surprisingly, a brand new coding syntax was adopted as an alternative of simply utilizing meta tags extra extensively.
For instance, the concept of schema markup was initially (and largely stays) to provide further contextual data regarding information or code that’s already deployed – which has similarities to the definition of metadata:
- “Data that describes different data with a view to aid you perceive or use it.”
Each schema and metadata try to attain this similar objective. Data that describes different current data to assist the consumer leverage such data. Nevertheless, the element and structural hierarchy of schema (ultimately) made it much more scalable and efficient.
As we speak, Google nonetheless makes use of schema for contextual consciousness and element regarding varied internet entities (e.g., webpages, organizations, opinions, movies, merchandise – the checklist goes on).
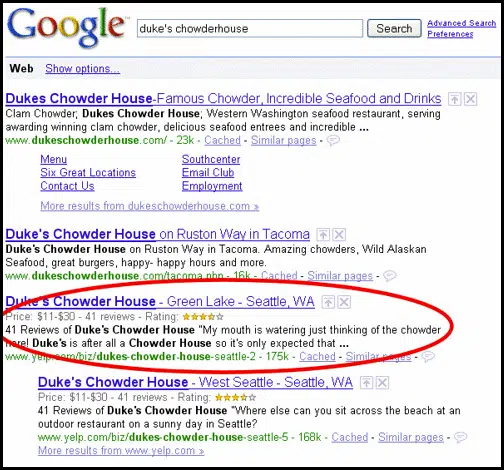
That mentioned, Google initially allowed schema to change the visuals of a web page’s search listings with a fantastic diploma of management. You would simply add star scores to your pages for Google’s search outcomes, making them stand out (visually) towards competing internet outcomes.
As traditional, some started abusing these powers to outperform much less website positioning-aware opponents.
In February 2014, Google began speaking about penalties for wealthy snippet spam. This was when individuals misused schema to make their search outcomes look higher than others, despite the fact that the data behind them was improper. For instance, a website with out opinions purports a 5-star mixture evaluation ranking (clearly false).
Quick-forward to 2024, and whereas nonetheless situationally helpful, schema shouldn’t be as highly effective because it as soon as was. Supply is simpler, because of Google’s JSON-LD choice. Nevertheless, schema now not has absolutely the energy to regulate the visuals of a search itemizing.
Get the every day publication search entrepreneurs depend on.
3. Rel=Prev / Subsequent
Rel=”prev” and rel=”subsequent” had been two HTML attributes Google instructed in 2011. The concept was to assist Google develop extra contextual consciousness of how sure sorts of paginated addresses had been interrelated:
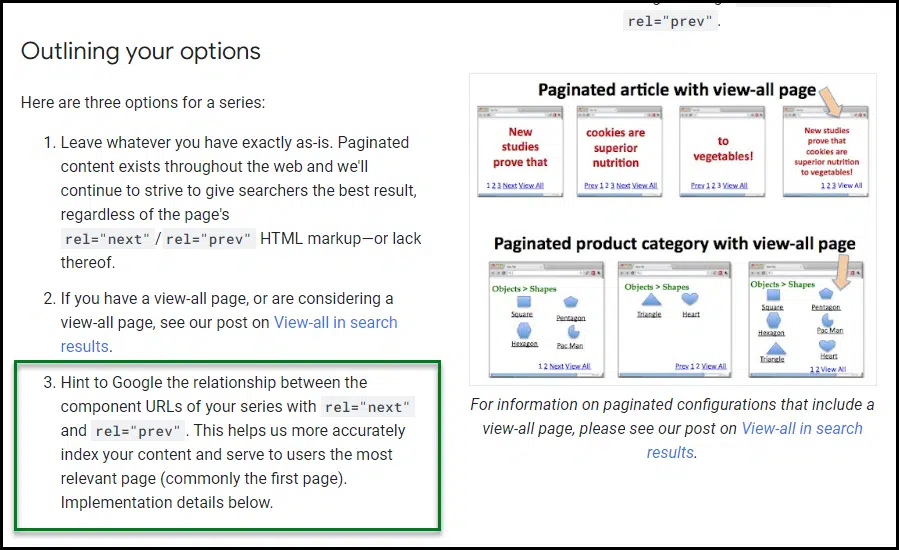
Eight years later, Google introduced they now not supported it. In addition they mentioned they hadn’t supported this type of coding for some time, suggesting assist ended round 2016, simply 5 years after the ideas had been first made.
Many had been understandably aggravated as a result of the tags had been fiddly to implement, typically requiring precise internet builders to re-code elements of web site themes.
More and more, it appeared as if Google would recommend complicated code adjustments in a single second solely to ditch them the subsequent. In actuality, it’s seemingly that Google had merely realized all it wanted from the rel=prev / subsequent experiment.
4. Disavow device
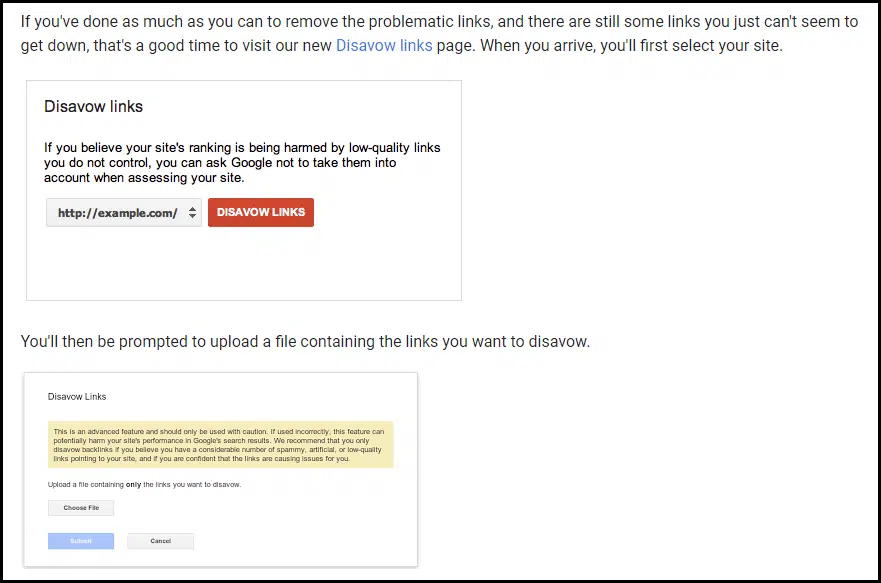
In October 2012, the net buzzed with information of Google’s new Disavow hyperlinks device.
In April 2012, Google launched the Penguin replace, which induced the net to be in turmoil. The replace focused spammy off-site exercise (hyperlink constructing) closely, and lots of web sites noticed guide motion notices seem throughout the Search Console (then named Webmaster Instruments).
Utilizing the Disavow device, you may add lists of linking pages or domains they want to exclude from Google’s rating algorithms. If these uploaded hyperlinks largely agreed with Google’s personal inner evaluation of the backlink profile, the lively guide penalty might then have been lifted.
This is able to give again a “honest” quantity of Google visitors to their website, although clearly, with a part of their backlink profile now “disavowed” – post-penalty visitors was normally decrease than pre-penalty visitors.
As such, the website positioning group had a comparatively low opinion of the device. Often, an entire backlink removing or disavow venture was obligatory. Having much less visitors after the penalty was higher than having no visitors in any respect.
Disavow tasks haven’t been obligatory for years. Google now says that anybody nonetheless providing this service is utilizing outdated practices.
In recent times, Google’s John Mueller has been extraordinarily important of these promoting “disavow” or “poisonous hyperlinks” work. It appears as if Google now not needs us to make use of this device; actually, they don’t advise us on its utilization (and haven’t in a few years).
Dig deeper. Poisonous hyperlinks and disavows: A complete website positioning information
Unraveling Google’s give-and-take relationship with the net
Google supplies instruments or code snippets for SEOs to control its search leads to minor methods. As soon as Google positive aspects insights from these deployments, such options are often phased out. Google grants us a restricted quantity of non permanent management to facilitate its long-term studying and adaptation.
Does this make these small, non permanent releases from Google ineffective? There are two methods of taking a look at this:
- Some individuals will say, “Don’t soar on the bandwagon! These non permanent deployments aren’t definitely worth the effort they require.”
- Others will say, “Google provides us non permanent alternatives for management, so you have to take benefit earlier than they vanish.”
In fact, there isn’t any proper or improper reply. It depends upon your potential to adapt to internet adjustments effectively.
If you happen to’re comfy with fast adjustments, implement what you may and react quick. In case your group lacks the experience or sources for fast adjustments, it’s not price following developments blindly.
I feel this ebb and move of give and take doesn’t essentially make Google evil or dangerous. Any enterprise will leverage its distinctive belongings to drive additional studying and industrial exercise.
On this occasion, we’re considered one of Google’s belongings. Whether or not you would like for this relationship (between your self and Google) to proceed is as much as you.
You would select to not cooperate with Google’s non permanent energy, long-term studying commerce offers. Nevertheless, this may increasingly depart you at a aggressive drawback.
Opinions expressed on this article are these of the visitor writer and never essentially Search Engine Land. Employees authors are listed right here.
