For cybersecurity professionals in electronic mail safety and anti-phishing, the start of 2024 marked the beginning of an evolution.
In January, adoption of the e-mail commonplace for shielding domains from spoofing by fraudsters — Area-based Messaging Authentication, Reporting and Conformance, or DMARC — turned a necessity as firms ready for the enforcement of mandates by electronic mail giants Google and Yahoo. DMARC makes use of a website file and different email-focused safety applied sciences to find out whether or not an electronic mail comes from a server approved to ship messages on behalf of a specific group.
But three months later, DMARC adoption is already beginning to taper off, and lots of firms have accomplished solely essentially the most minimal configuration of their domains, equivalent to setting DMARC to flag points fairly than quarantine and even reject messages.
Sadly, many organizations stay involved that DMARC is simply one other safety management that, if completed fallacious, may break vital electronic mail companies, says Rahul Powar, CEO of Pink Sift, a risk intelligence supplier.
“Many organizations are rightly involved that in the event that they go they usually do a DMARC coverage and it is not appropriate, that they might block one thing that is actually materials to the enterprise, equivalent to a large advertising and marketing marketing campaign, or that the CEO’s electronic mail will not land in the fitting inbox,” he says. “There is a concern about getting it fallacious.”
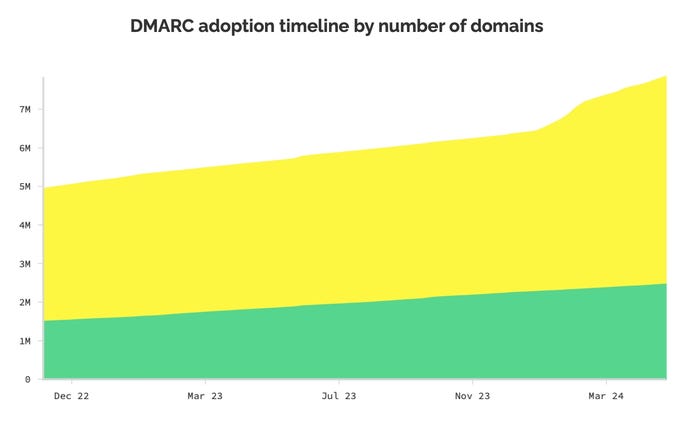
As of the top of April, about 7.9 million domains have some form of DMARC file (yellow), however solely 32% are BIMI prepared (inexperienced). Supply: BIMIRadar.com
Nevertheless, DMARC — and the underlying applied sciences of Sender Coverage Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Recognized Mail (DKIM) — are usually not tough to arrange for small or midsize companies which have easy electronic mail infrastructure by a third-party service, equivalent to Google Workspace or Microsoft 365. Nevertheless, if there are older techniques or some segmentation utilizing subdomains, the configuration can get complicated — quick, says Gerasim Hovhannisyan, co-founder and CEO at service supplier EasyDMARC.
“The issue comes when you might have legacy techniques and a number of sending sources and infrastructure,” he says. “Not solely enterprises, however the midmarket can have big issues throughout electronic mail authentication deployment. It is easy or simple to do at first look, however for those who do one thing fallacious, completely legitimate emails can be rejected.”
Here’s what to bear in mind when organising DMARC on your group.
1. SPF Alerts Recipients to Emails From Nonapproved Sources
The primary DNS file that a corporation must arrange is SPF, a string that lists the IP addresses and domains of the mail servers approved to ship electronic mail on behalf of the area. This file is often arrange by your area supplier or electronic mail internet hosting supplier.
A typical SPF file is a DNS TXT file and appears like:
v=spf1 ip4:192.168.1.1 ip4:192.168.2.1 embody:instance.com -all
The “v=spf1” designates the string as an SPF file and is required for all SPF data. The “ip4” fields record the IP addresses which can be allowed to ship electronic mail on behalf of the area and may embody community addresses utilizing the slash notation. The “embody” tag lists the third-party domains which can be approved to ship electronic mail for the area, whereas the “-all” flag specifies that each different area is just not allowed. Different variants, equivalent to “~all,” are attainable and specify that mail from different domains are allowed however marked insecure, whereas “+all” permits any server to ship electronic mail on behalf of the area.
Whereas the SPF file is an efficient first step, spammers may exploit the truth that different organizations utilizing a standard third-party server, equivalent to Google’s, could be approved to ship electronic mail on behalf of each different group utilizing that server.
2. DKIM Makes use of PKI to Confirm Electronic mail Messages
DKIM solves the issue of a number of tenants on the identical electronic mail server and provides electronic mail verification as properly. The DKIM selector and secret is generated by your electronic mail supplier after which registered as a TXT file in your DNS service supplier.
A typical DKIM file is a DNS TXT file with a selector — a reputation — equivalent to “[third party]._domainkey” and a price of:
v=DKIM1; okay=rsa; p={public key string}
The “v=DKIM1” designates the TXT string as a DKIM file and is required for all DKIM data. The “okay=rsa” designates the kind of encryption used for the public-key information, with RSA because the default and different values, equivalent to Edwards-curve Digital Signature Algorithm (EdDSA), allowed as properly. The “p=” tag incorporates the public-key information generated by the e-mail service supplier.
As with every public-key encryption infrastructure, organizations ought to ensure that to recurrently rotate the keys for his or her area infrastructure, says EasyDMARC’s Hovannisyan.
“We have now password administration techniques or rotating passwords for different [types of] keys, however we do not try this with DKIM keys,” he says. “That is one thing that needs to be in place and every time one thing could be damaged, you should have alerting.”
3. DMARC Establishes Insurance policies for Electronic mail Recipients
DMARC makes use of the already-established controls of SPF and DKIM and specifies a corporation’s electronic mail coverage — not for emails coming into the group, however for emails claiming to be despatched on behalf of the group. Organizations that specify a DMARC file achieve two advantages: They will inform a receiving server what to do with an electronic mail that fails authentication — equivalent to enable supply, quarantine the message, or reject it — they usually direct the receiving server to generate experiences about any messages despatched to the area.
The result’s that a corporation utilizing DMARC positive aspects visibility into how its area title and model is being utilized by unauthorized events.
A typical DMARC file is a DNS TXT file with a “_DMARC” and a price that may be a string with quite a lot of fields, equivalent to:
v=DMARC1; p=reject; adkim=s; aspf=s; rua=mailto:[email protected]
On this instance, the “v=DMARC1” is the required identifier, the authentication insurance policies for each SPF and DKIM at set to strict — as designated by the “aspf=s” and “adkim=s” tags — and the DMARC experiences are despatched to an organization-specific electronic mail at a third-party supplier. On this case, the coverage is about to reject, however firms can begin with a coverage of “none” to realize entry to the reporting and transfer to a coverage of “quarantine.”
4. Examine Your DMARC Reviews Recurrently and Preserve Information
Establishing a DMARC coverage is pretty easy, however utilizing the added info as a part of an email-security and brand-protection program requires an alerting mechanism and common oversight. Usually firms will simply insert a sound DMARC file of their DNS with a coverage of “none” after which overlook in regards to the added risk intelligence, Hovannisyan says.
“One of many largest errors with DMARCs is [a company saying] that when it is completed, I needn’t do something extra,” he says.
As a substitute, firms ought to advance by the completely different insurance policies, beginning with “none” however rapidly transferring to “quarantine” after which lastly “strict.”
Whereas DMARC could be simple to handle for small firms, giant enterprises will doubtless wish to undertake a service to handle the configuration of its electronic mail infrastructure and make use of the added capabilities.
“For a small deployment, the place you mainly simply have a Google or an Workplace 365 in your area, it is fairly easy,” says Pink Sift’s Powar. “I imply, the spec is sort of easy, however as quickly as you add somewhat little bit of complexity — when you begin together with a advertising and marketing division, an HR division, or perhaps a procurement division — you are going to discover plenty of senders abruptly begin to seem out of your infrastructure.”
5. Think about BIMI to Enhance Belief
Lastly, firms have a fourth commonplace that may assist add extra belief to their electronic mail messages. The Model Indicators for Message Identification, or BIMI, commonplace permits firms to register their logos to be used in electronic mail shoppers, however solely after they’ve adopted the utmost degree of strictness for his or her DMARC insurance policies.
Whereas virtually three-quarters of enormous organizations (73%) have adopted essentially the most primary model of DMARC, the share of these organizations that may cross essentially the most stringent requirements range considerably by nation: Within the US, 77% of firms have a strict coverage, whereas solely 40% in Germany and 15% in Japan do, in response to information from Pink Sift. Of all domains, solely 3% are thought-about prepared for BIMI, however 32% of the 7.9 million DMARC-enabled domains have strict sufficient insurance policies to undertake BIMI, in response to the BIMIRadar monitoring web site.
