Think about a slime-like robotic that may seamlessly change its form to squeeze by means of slender areas, which might be deployed contained in the human physique to take away an undesirable merchandise.
Whereas such a robotic doesn’t but exist outdoors a laboratory, researchers are working to develop reconfigurable comfortable robots for purposes in well being care, wearable units, and industrial techniques.
However how can one management a squishy robotic that doesn’t have joints, limbs, or fingers that may be manipulated, and as a substitute can drastically alter its complete form at will? MIT researchers are working to reply that query.
They developed a management algorithm that may autonomously learn to transfer, stretch, and form a reconfigurable robotic to finish a selected activity, even when that activity requires the robotic to vary its morphology a number of occasions. The workforce additionally constructed a simulator to check management algorithms for deformable comfortable robots on a collection of difficult, shape-changing duties.
Their technique accomplished every of the eight duties they evaluated whereas outperforming different algorithms. The approach labored particularly properly on multifaceted duties. As an illustration, in a single check, the robotic needed to cut back its top whereas rising two tiny legs to squeeze by means of a slender pipe, after which un-grow these legs and prolong its torso to open the pipe’s lid.
Whereas reconfigurable comfortable robots are nonetheless of their infancy, such a method may sometime allow general-purpose robots that may adapt their shapes to perform numerous duties.
“When folks take into consideration comfortable robots, they have a tendency to consider robots which are elastic, however return to their unique form. Our robotic is like slime and may really change its morphology. It is vitally hanging that our technique labored so properly as a result of we’re coping with one thing very new,” says Boyuan Chen, {an electrical} engineering and laptop science (EECS) graduate scholar and co-author of a paper on this strategy.
Chen’s co-authors embody lead writer Suning Huang, an undergraduate scholar at Tsinghua College in China who accomplished this work whereas a visiting scholar at MIT; Huazhe Xu, an assistant professor at Tsinghua College; and senior writer Vincent Sitzmann, an assistant professor of EECS at MIT who leads the Scene Illustration Group within the Laptop Science and Synthetic Intelligence Laboratory. The analysis might be offered on the Worldwide Convention on Studying Representations.
Controlling dynamic movement
Scientists usually educate robots to finish duties utilizing a machine-learning strategy referred to as reinforcement studying, which is a trial-and-error course of through which the robotic is rewarded for actions that transfer it nearer to a aim.
This may be efficient when the robotic’s shifting components are constant and well-defined, like a gripper with three fingers. With a robotic gripper, a reinforcement studying algorithm may transfer one finger barely, studying by trial and error whether or not that movement earns it a reward. Then it might transfer on to the following finger, and so forth.
However shape-shifting robots, that are managed by magnetic fields, can dynamically squish, bend, or elongate their complete our bodies.
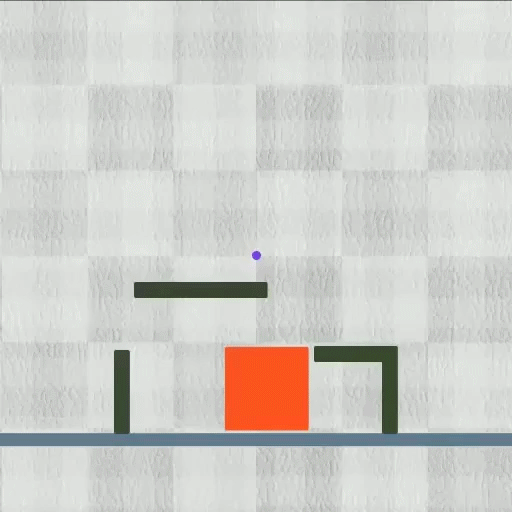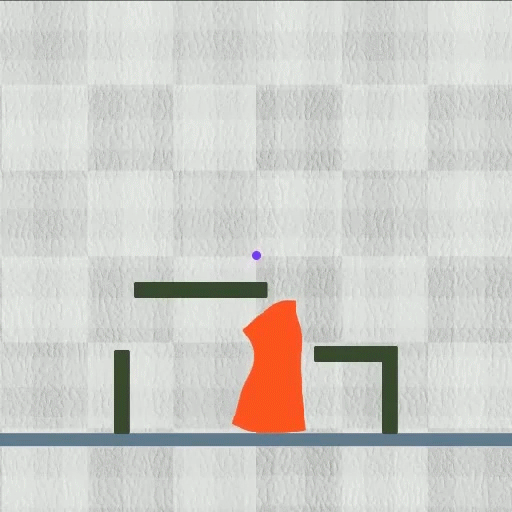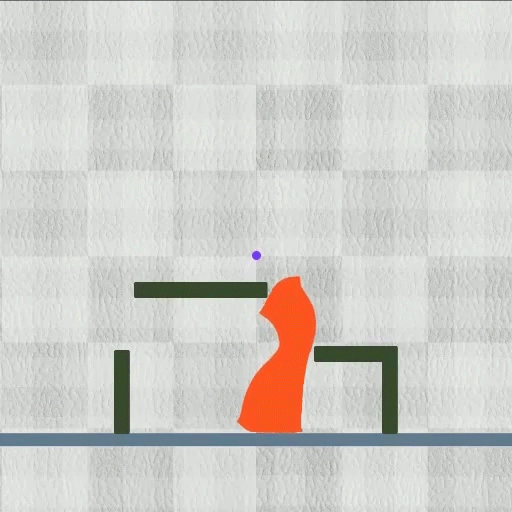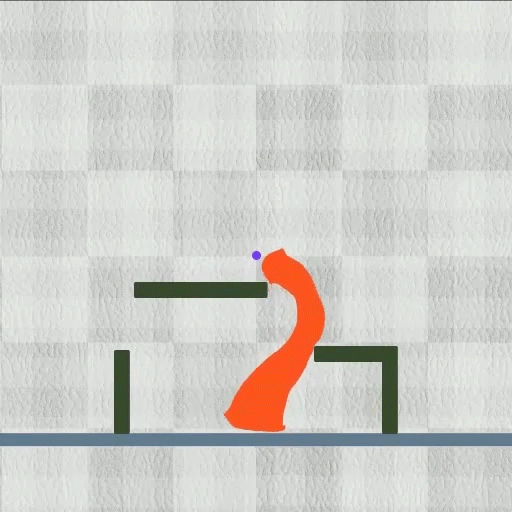
Picture: Courtesy of the researchers
“Such a robotic may have hundreds of small items of muscle to manage, so it is vitally exhausting to study in a standard approach,” says Chen.
To unravel this drawback, he and his collaborators had to consider it in another way. Somewhat than shifting every tiny muscle individually, their reinforcement studying algorithm begins by studying to manage teams of adjoining muscle tissues that work collectively.
Then, after the algorithm has explored the house of attainable actions by specializing in teams of muscle tissues, it drills down into finer element to optimize the coverage, or motion plan, it has discovered. On this approach, the management algorithm follows a coarse-to-fine methodology.
“Coarse-to-fine signifies that while you take a random motion, that random motion is more likely to make a distinction. The change within the final result is probably going very important since you coarsely management a number of muscle tissues on the identical time,” Sitzmann says.
To allow this, the researchers deal with a robotic’s motion house, or the way it can transfer in a sure space, like a picture.
Their machine-learning mannequin makes use of photos of the robotic’s surroundings to generate a 2D motion house, which incorporates the robotic and the world round it. They simulate robotic movement utilizing what is called the material-point-method, the place the motion house is roofed by factors, like picture pixels, and overlayed with a grid.
The identical approach close by pixels in a picture are associated (just like the pixels that type a tree in a photograph), they constructed their algorithm to grasp that close by motion factors have stronger correlations. Factors across the robotic’s “shoulder” will transfer equally when it adjustments form, whereas factors on the robotic’s “leg” will even transfer equally, however another way than these on the “shoulder.”
As well as, the researchers use the identical machine-learning mannequin to take a look at the surroundings and predict the actions the robotic ought to take, which makes it extra environment friendly.
Constructing a simulator
After growing this strategy, the researchers wanted a option to check it, in order that they created a simulation surroundings known as DittoGym.
DittoGym options eight duties that consider a reconfigurable robotic’s capability to dynamically change form. In a single, the robotic should elongate and curve its physique so it may well weave round obstacles to succeed in a goal level. In one other, it should change its form to imitate letters of the alphabet.
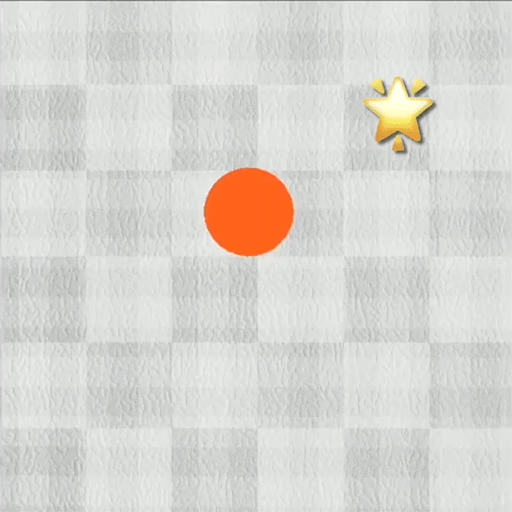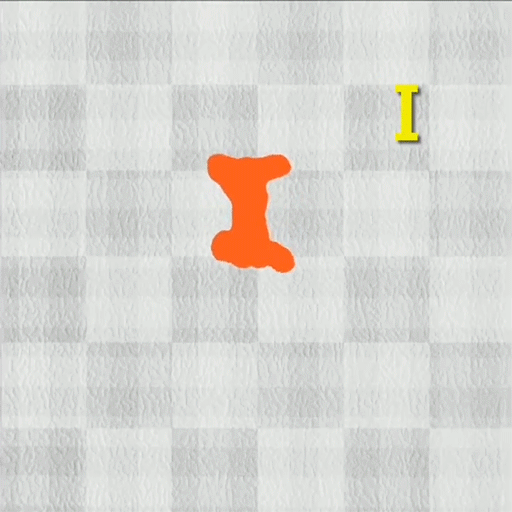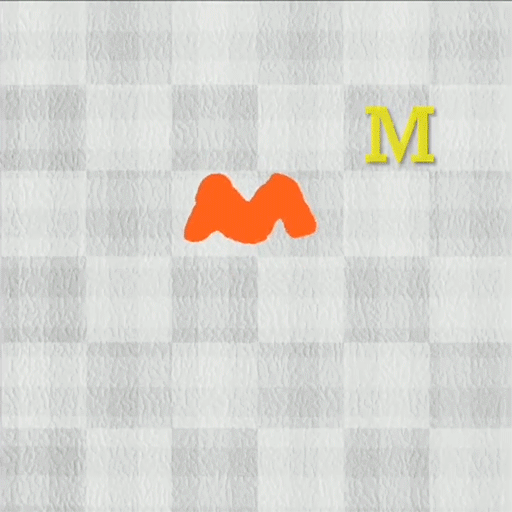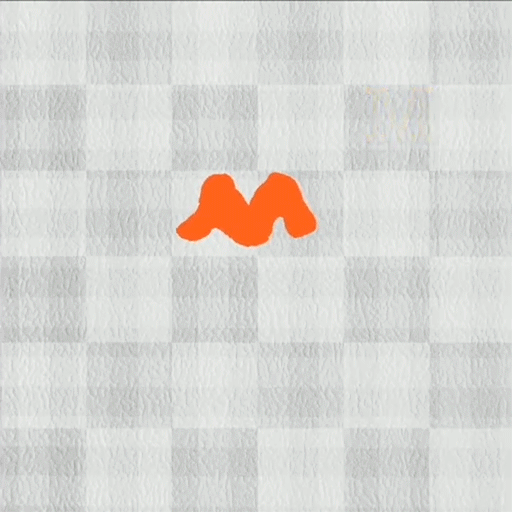
Picture: Courtesy of the researchers
“Our activity choice in DittoGym follows each generic reinforcement studying benchmark design rules and the particular wants of reconfigurable robots. Every activity is designed to symbolize sure properties that we deem vital, resembling the aptitude to navigate by means of long-horizon explorations, the power to investigate the surroundings, and work together with exterior objects,” Huang says. “We imagine they collectively may give customers a complete understanding of the pliability of reconfigurable robots and the effectiveness of our reinforcement studying scheme.”
Their algorithm outperformed baseline strategies and was the one approach appropriate for finishing multistage duties that required a number of form adjustments.
“We have now a stronger correlation between motion factors which are nearer to one another, and I believe that’s key to creating this work so properly,” says Chen.
Whereas it could be a few years earlier than shape-shifting robots are deployed in the true world, Chen and his collaborators hope their work evokes different scientists not solely to review reconfigurable comfortable robots but additionally to consider leveraging 2D motion areas for different complicated management issues.
