On this article, we’ll stroll you thru the method of implementing tremendous grained entry management for the info governance framework inside the Cloudera platform. It will permit an information workplace to implement entry insurance policies over metadata administration belongings like tags or classifications, enterprise glossaries, and information catalog entities, laying the inspiration for complete information entry management.
In a superb information governance technique, it is very important outline roles that permit the enterprise to restrict the extent of entry that customers can need to their strategic information belongings. Historically we see three fundamental roles in an information governance workplace:
- Knowledge steward: Defines the enterprise guidelines for information use in accordance with company steering and information governance necessities.
- Knowledge curator: Assigns and enforces information classification in accordance with the principles outlined by the info stewards in order that information belongings are searchable by the info client.
- Knowledge client: Derives insights and worth from information belongings and is eager to grasp the standard and consistency of tags and phrases utilized to the info.
Throughout the Cloudera platform, whether or not deployed on premises or utilizing any of the main public cloud suppliers, the Cloudera Shared Knowledge Expertise (SDX) ensures consistency of all issues information safety and governance. SDX is a elementary a part of any deployment and depends on two key open supply initiatives to offer its information administration performance: Apache Atlas supplies a scalable and extensible set of core governance providers, whereas Apache Ranger allows, screens, and manages complete safety for each information and metadata.
On this article we’ll clarify easy methods to implement a tremendous grained entry management technique utilizing Apache Ranger by creating safety insurance policies over the metadata administration belongings saved in Apache Atlas.
Case Introduction
On this article we’ll take the instance of an information governance workplace that desires to manage entry to metadata objects within the firm’s central information repository. This permits the group to adjust to authorities laws and inner safety insurance policies. For this process, the info governance crew began by wanting on the finance enterprise unit, defining roles and duties for various kinds of customers within the group.
On this instance, there are three totally different customers that can permit us to point out the totally different ranges of permissions that may be assigned to Apache Atlas objects by means of Apache Ranger insurance policies to implement an information governance technique with the Cloudera platform:
- admin is our information steward from the info governance workplace
- etl_user is our information curator from the finance crew
- joe_analyst is our information client from the finance crew
Word that it will be simply as simple to create further roles and ranges of entry, if required. As you will notice as we work by means of the instance, the framework offered by Apache Atlas and Apache Ranger is extraordinarily versatile and customizable.
First, a set of preliminary metadata objects are created by the info steward. These will permit the finance crew to seek for related belongings as a part of their day-to-day actions:
- Classifications (or “tags”) like “PII”, “SENSITIVE”, “EXPIRES_ON”, “DATA QUALITY” and so on.
- Glossaries and phrases created for the three fundamental enterprise models: “Finance,” “Insurance coverage,” and “Automotive.”
- A enterprise metadata assortment referred to as “Venture.”
NOTE: The creation of the enterprise metadata attributes will not be included within the weblog however the steps might be adopted right here.
Then, with a purpose to management the entry to the info belongings associated to the finance enterprise unit, a set of insurance policies should be carried out with the next situations:
The finance information curator <etl_user> ought to solely be allowed to:
- Create/learn classifications that begin with the phrase “finance.”
- Learn/replace entities which can be categorised with any tag that begins with the phrase “finance,” and in addition any entities associated to the “worldwidebank” mission. The person must also have the ability to add labels and enterprise metadata to these entities.
- Add/replace/take away classifications of the entities with the earlier specs.
- Create/learn/replace the glossaries and glossary phrases associated to “finance.”
The finance information client <joe_analyst> ought to solely be allowed to:
- View and entry cClassifications associated to “finance” to look belongings.
- View and entry entities which can be categorised with tags associated to “finance.”
- View and entry the “finance” glossary.
Within the following part, the method for implementing these insurance policies can be defined intimately.
Implementation of fine-grained entry controls (step-by-step)
As a way to meet the enterprise wants outlined above, we’ll display how entry insurance policies in Apache Ranger might be configured to safe and management metadata belongings in Apache Atlas. For this goal we used a public AMI picture to arrange a Cloudera Knowledge Platform setting with all SDX elements. The method of establishing the setting is defined in this text.
1. Authorization for Classification Varieties
Classifications are a part of the core of Apache Atlas. They’re one of many mechanisms offered to assist organizations discover, arrange, and share their understanding of the info belongings that drive enterprise processes. Crucially, classifications can “propagate” between entities in accordance with lineage relationships between information belongings. See this web page for extra particulars on propagation.
1.1 Knowledge Steward – admin person
To manage entry to classifications, our admin person, within the function of information steward, should carry out the next steps:
- Entry the Ranger console.
- Entry Atlas repository to create and handle insurance policies.
- Create the suitable insurance policies for the info curator and the info client of the finance enterprise unit.
First, entry the Atlas Ranger insurance policies repository from the Ranger admin UI
Picture 1 – Ranger fundamental web page
Within the Atlas coverage repository:
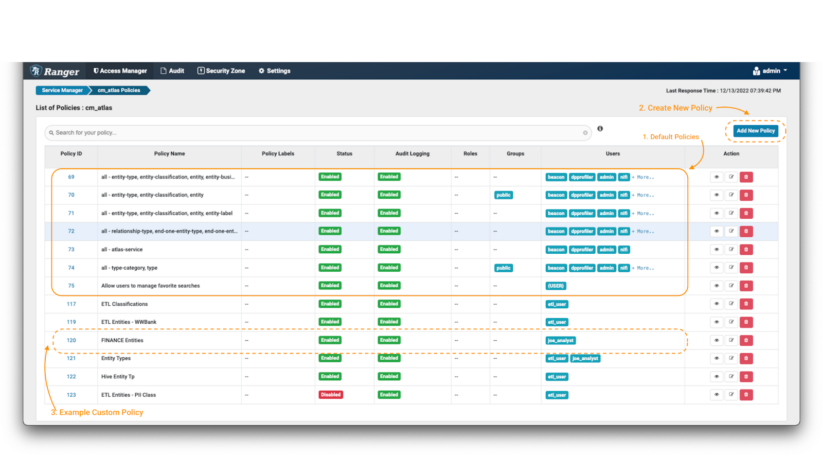
Picture 2 – Atlas insurance policies
The very first thing you will notice are the default Atlas insurance policies (notice 1). Apache Ranger permits specification of entry insurance policies as each “permit” guidelines and “deny” guidelines. Nonetheless, it’s a really useful good observe in all safety contexts to use the “precept of least privilege”: i.e., deny entry by default, and solely permit entry on a selective foundation. It is a far more safe strategy than permitting entry to everybody, and solely denying or excluding entry selectively. Subsequently, as a primary step, it is best to confirm that the default insurance policies don’t grant blanket entry to the customers we’re in search of to limit on this instance state of affairs.
Then, you possibly can create the brand new insurance policies (eg. take away the general public entry of the default insurance policies by making a deny coverage; notice 2) and eventually you will notice that the newly created insurance policies will seem on the backside of the part (notice 3).
After clicking the “Add New Coverage” button:
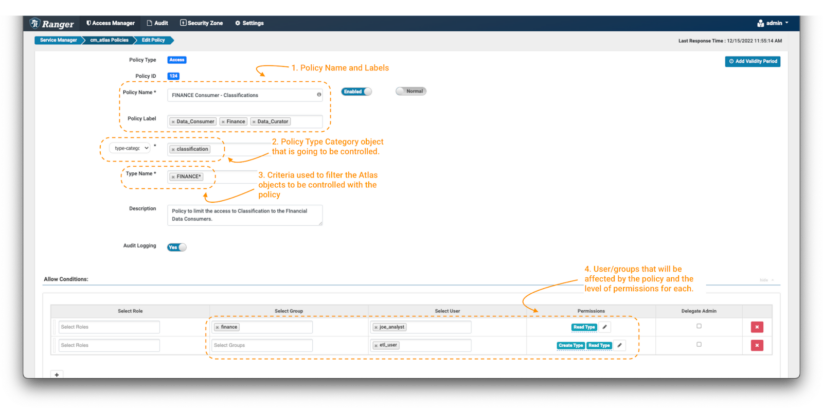
Picture 3 – Create coverage over finance classification
- First, outline a coverage identify and, if desired, some coverage labels (notice 1). These should not have a “purposeful” impact on the coverage, however are an essential a part of conserving your safety insurance policies manageable as your setting grows over time. It’s regular to undertake a naming conference to your insurance policies, which can embrace short-hand descriptions of the person teams and/or belongings to which the coverage applies, and a sign of its intent. On this case we have now chosen the coverage identify “FINANCE Client – Classifications,” and used the labels “Finance.” “Knowledge Governance,” and “Knowledge Curator.”
- Subsequent, outline the kind of object on which you wish to apply the coverage. On this case we’ll choose “type-category” and fill with “Classifications” (notice 2).
- Now, it’s worthwhile to outline the factors used to filter the Apache Atlas objects to be affected by the coverage. You should utilize wildcard notations like “*”. To restrict the info client to solely seek for classifications beginning with the work finance, use FINANCE* (notice 3).
- Lastly, it’s worthwhile to outline the permissions that you simply wish to grant on the coverage and the teams and customers which can be going to be managed by the coverage. On this case, apply the Learn Kind permission to group: finance and person: joe_analyst and Create Kind & Learn Kind permission to person: etl_user. (notice 4)
Now, as a result of they’ve the Create Kind permission for classifications matching FINANCE*, the info curator etl_user can create a brand new classification tag referred to as “FINANCE_WW” and apply this tag to different entities. This could be helpful if a tag-based entry coverage has been outlined elsewhere to offer entry to sure information belongings.
1.2 Knowledge Curator – etl_user person
We will now display how the classification coverage is being enforced over etl_user. This person is barely allowed to see classifications that begin with the phrase finance, however he may also create some further ones for the totally different groups beneath that division.
etl_user can create a brand new classification tag referred to as FINANCE_WW beneath a guardian classification tag FINANCE_BU.
To create a classification in Atlas:
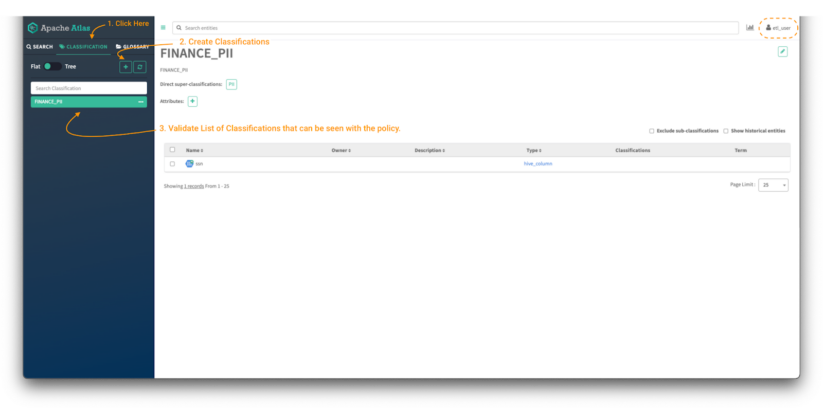
Picture 4 – Atlas classifications tab
- First, click on on the classification panel button (notice 1) to have the ability to see the present tags that the person has entry to. It is possible for you to to see the belongings which can be tagged with the chosen classification. (notice 3)
- Then, click on on the “+” button to create a brand new classification. (notice 2)
A brand new window open, requiring varied particulars to create the brand new classification.
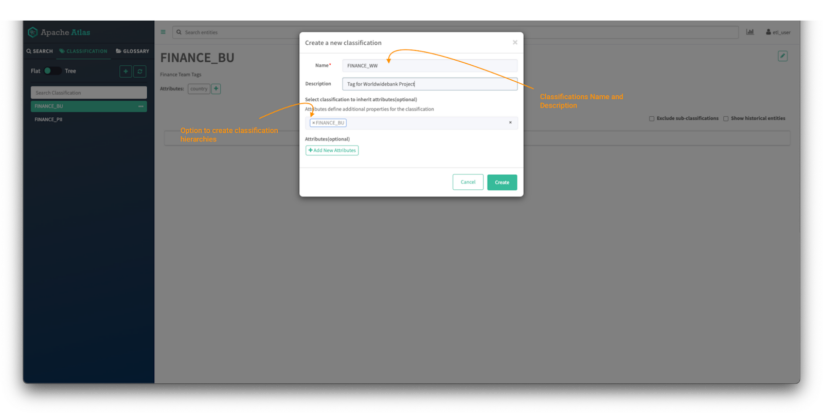
Picture 5 – Atlas classifications creation tab
- First, present the identify of the classification, on this case FINANCE_WW, and supply an outline, in order that colleagues will perceive the way it must be used.
- Classifications can have hierarchies and people inherit attributes from the guardian classification. To create a hierarchy, kind the identify of the guardian tag, on this case FINANCE_BU.
- Extra customized attributes may also be added to later be used on attribute-based entry management (ABAC) insurance policies. This falls exterior of the scope of this weblog put up however a tutorial on the topic might be discovered right here.
- (Non-obligatory) For this instance, you possibly can create an attribute referred to as “nation,” which can merely assist to prepare belongings. For comfort you may make this attribute a “string” (a free textual content) kind, though in a stay system you’ll in all probability wish to outline an enumeration in order that customers’ inputs are restricted to a legitimate set of values.
After clicking the button “create” the newly created classification is proven within the panel:
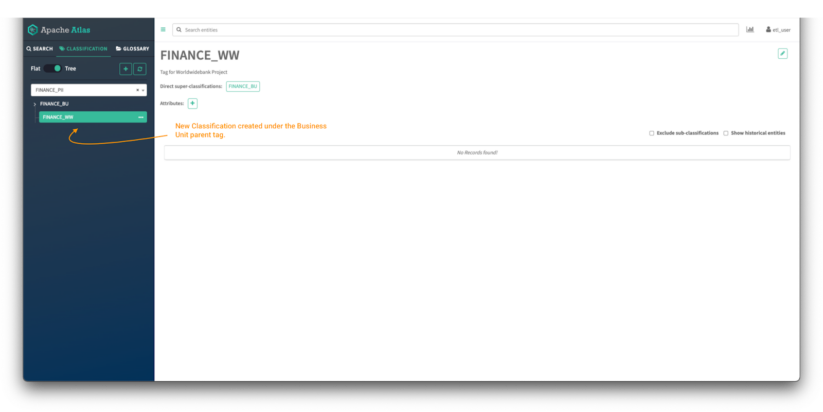
Picture 6 – Atlas classifications tree
Now you possibly can click on on the toggle button to see the tags in tree mode and it is possible for you to to see the guardian/youngster relationship between each tags.
Click on on the classification to view all its particulars: guardian tags, attributes, and belongings at the moment tagged with the classification.
1.3 Knowledge Client – joe_analyst person
The final step on the Classification authorization course of is to validate from the info client function that the controls are in place and the insurance policies are utilized accurately.
After efficiently logging in with person joe_analyst:
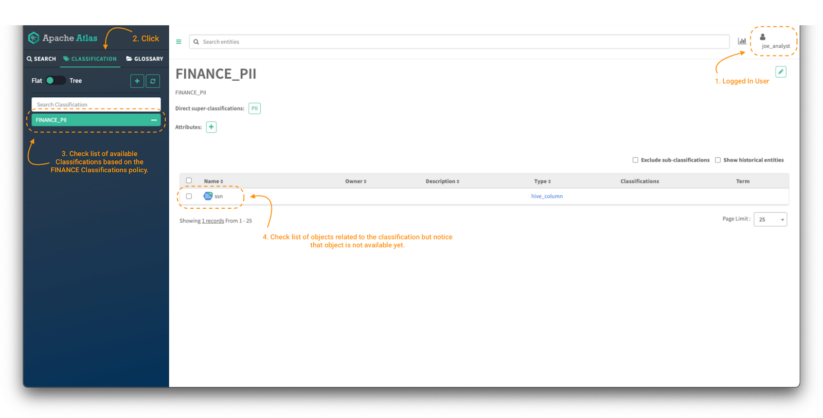
Picture 7 – Atlas classifications for finance information client
To validate that the coverage is utilized and that solely classifications beginning with the phrase FINANCE might be accessed based mostly on the extent of permissions outlined within the coverage, click on on the Classifications tab (notice 2) and examine the listing out there. (notice 3)
Now, to have the ability to entry the content material of the entities (notice 4), it’s required to present entry to the Atlas Entity Kind class and to the particular entities with the corresponding degree of permissions based mostly on our enterprise necessities. The following part will cowl simply that.
2. Authorization for Entity Varieties, Labels and Enterprise Metadata
On this part, we’ll clarify easy methods to shield further sorts of objects that exist in Atlas, that are essential inside an information governance technique; particularly, entities, labels, and enterprise metadata.
Entities in Apache Atlas are a selected occasion of a “kind” of factor: they’re the core metadata object that symbolize information belongings in your platform. For instance, think about you’ve got an information desk in your lakehouse, saved within the Iceberg desk format, referred to as “sales_q3.” This could be mirrored in Apache Atlas by an entity kind referred to as “ceberg desk,” and an entity named “sales_q3,” a specific occasion of that entity kind. There are a lot of entity sorts configured by default within the Cloudera platform, and you’ll outline new ones as properly. Entry to entity sorts, and particular entities, might be managed by means of Ranger insurance policies.
Labels are phrases or phrases (strings of characters) which you can affiliate with an entity and reuse for different entities. They’re a lightweight manner so as to add data to an entity so you could find it simply and share your data in regards to the entity with others.
Enterprise metadata are units of associated key-value pairs, outlined prematurely by admin customers (for instance, information stewards). They’re so named as a result of they’re typically used to seize enterprise particulars that may assist arrange, search, and handle metadata entities. For instance, a steward from the advertising and marketing division can outline a set of attributes for a marketing campaign, and add these attributes to related metadata objects. In distinction, technical particulars about information belongings are normally captured extra straight as attributes on entity situations. These are created and up to date by processes that monitor information units within the information lakehouse or warehouse, and usually are not usually personalized in a given Cloudera setting.
With that context defined, we’ll transfer on to setting insurance policies to manage who can add, replace, or take away varied metadata on entities. We will set fine-grained insurance policies individually for each labels and enterprise metadata, in addition to classifications. These insurance policies are outlined by the info steward, with a purpose to management actions undertaken by information curators and shoppers.
2.1 Knowledge Steward – admin person
First, it’s essential to guarantee that the customers have entry to the entity sorts within the system. It will permit them to filter their search when on the lookout for particular entities.
So as to take action, we have to create a coverage:
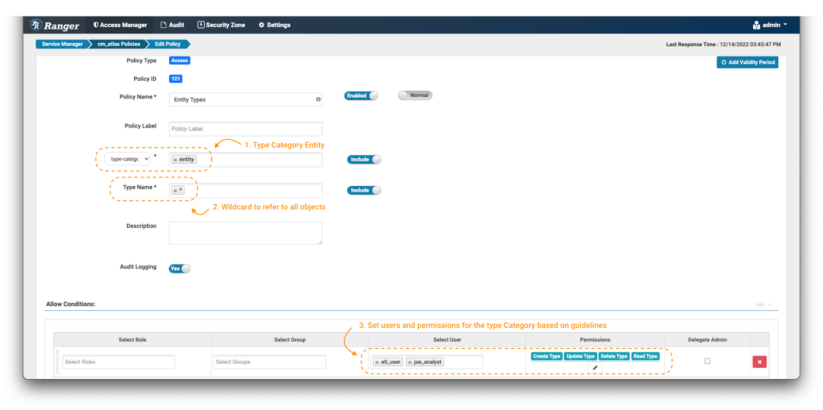
Picture 8 – Atlas entity kind insurance policies
Within the create coverage web page, outline the identify and labels as described earlier than. Then, choose the type-category “entity”(notice 1). Use the wildcard notation (*) (notice 2) to indicate all entity sorts, and grant all out there permissions to etl_user and joe_analyst.(notice 3)
It will allow these customers to see all of the entity sorts within the system.
The following step is to permit information client joe_analyst to solely have learn entry on the entities which have the finance classification tags. It will restrict the objects that he’ll have the ability to see on the platform.
To do that, we have to observe the identical course of to create insurance policies as proven within the earlier part, however with some modifications on the coverage particulars:
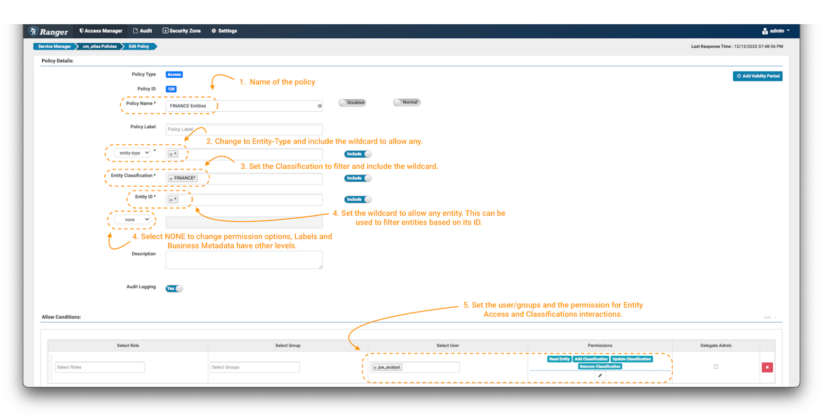
Picture 9 – Instance Atlas finance entity insurance policies
- As all the time, identify (and label) the coverage to allow simple administration later.
- The primary essential change is that the coverage is utilized on an “entity-type” and never in a “type-category.” Choose “entity-type” within the drop-down menu (notice 2) and kind the wildcard to use it to all of the entity sorts.
- Some further fields will seem within the type. Within the entity classification area you possibly can specify tags that exist on the entities you wish to management. In our case, we wish to solely permit objects which can be tagged with phrases that begin with “finance.” Use the expression FINANCE*. (notice 3)
- Subsequent, filter the entities to be managed by means of the entity ID area. On this train, we’ll use the wildcard (*) (notice 4) and for the extra fields we’ll choose “none.” This button will replace the listing of permissions that may be enforced within the situations panel. (notice 4)
- As an information client, we would like the joe_analyst person to have the ability to see the entities. To implement this, choose the Learn Entity permission. (notice 5)
- Add a brand new situation for the info curator etl_user however this time embrace permissions to switch the tags appropriately, by including the Add Classification, Replace Classification & Take away Classification permissions to the particular person.
On this manner, entry to particular entities might be managed utilizing further metadata objects like classification tags. Atlas supplies another metadata objects that can be utilized not solely to complement the entities registered within the platform, but additionally to implement a governance technique over these objects, controlling who can entry and modify them. That is the case for the labels and the enterprise metadata.
If you wish to implement some management over who can add or take away labels:
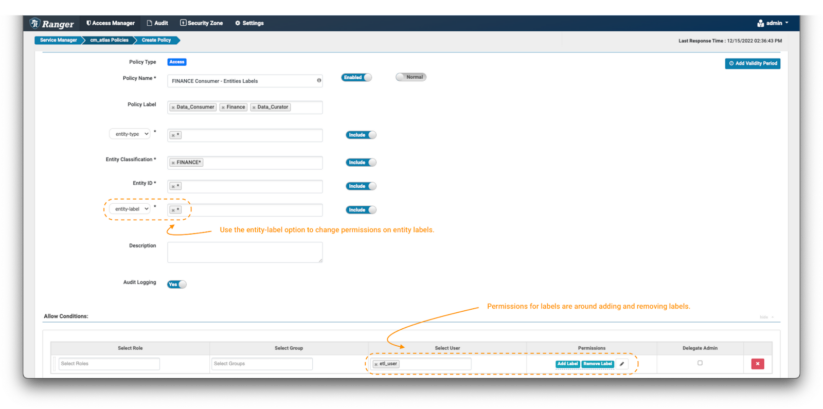
Picture 10 – Instance Atlas finance label coverage
- The one distinction between setting a coverage for labels versus the earlier examples is setting the extra fields filter to “entity-label” as proven within the picture and fill with the values of labels that wish to be managed. On this case, we use the wildcard (*) to allow operations on any label on entities tagged with FINANCE* classifications.
- When the entity-label is chosen from the drop-down, the permissions listing can be up to date. Choose Add Label & Take away Label permission to grant the info curator the choice so as to add and take away labels from entities.
The identical precept might be utilized to manage the permissions over enterprise metadata:

Picture 11 – Instance Atlas finance enterprise metadata coverage
- On this case, one should set the extra fields filter to “entity-business-metadata” as proven within the picture and fill with the values of enterprise metadata attributes that wish to be protected. On this instance, we use the wildcard (*) to allow operations on all enterprise metadata attributes on entities tagged with FINANCE* classifications.
- While you allow the entity-business-metadata drop-down, the permissions listing can be up to date. Choose Replace Enterprise Metadata permission to grant the info curator the choice to switch the enterprise metadata attributes of monetary entities.
As a part of the tremendous grained entry management offered by Apache Ranger over Apache Atlas objects, one can create insurance policies that use an entity ID to specify the precise objects to be managed. Within the examples above we have now typically used the wildcard (*) to confer with “all entities;” under, we’ll present a extra focused use-case.
On this state of affairs, we wish to create a coverage pertaining to information tables that are a part of a selected mission, named “World Vast Financial institution.” As an ordinary, the mission house owners required that every one the tables are saved in a database referred to as “worldwidebank.”
To satisfy this requirement, we will use one of many entity sorts pre-configured in Cloudera’s distributions of Apache Atlas, particularly “hive_table”. For this entity kind, identifiers all the time start with the identify of the database to which the desk belongs. We will leverage that, utilizing Ranger expressions to filter all of the entities that belong to the “World Vast Financial institution” mission.
To create a coverage to guard the worldwidebank entities:
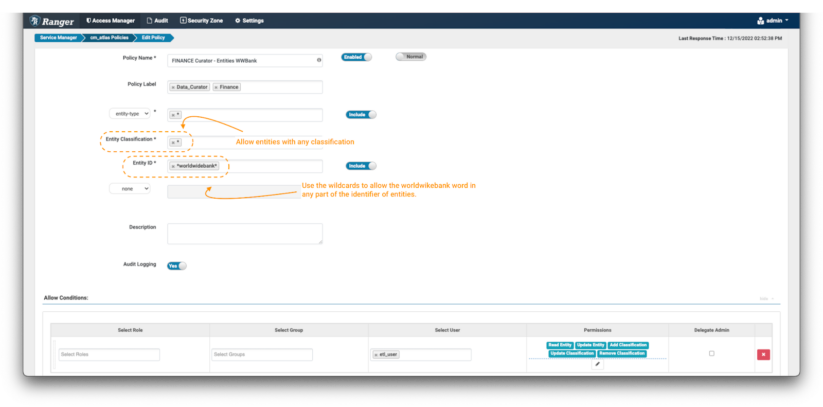
Picture 12 – Instance Atlas Worldwide Financial institution entity coverage
- Create a brand new coverage, however this time don’t specify any entity classification, use the wildcard “*” expression.
- Within the entity ID area use the expression: *worldwidebank*
- Within the Situations, choose the permissions Learn Entity, Replace Entity, Add Classification, Replace Classification & Take away Classification to the info curator etl_user to have the ability to see the main points of those entities and enrich/modify and tag them as wanted.
2.2 Knowledge Curator – etl_user person
As a way to permit finance information client joe_analyst to make use of and entry the worldwidebank mission entities, the info curator etl_user should tag the entities with the permitted classifications and add the required labels and enterprise metadata attributes.
Login to Atlas and observe the method to tag the suitable entities:
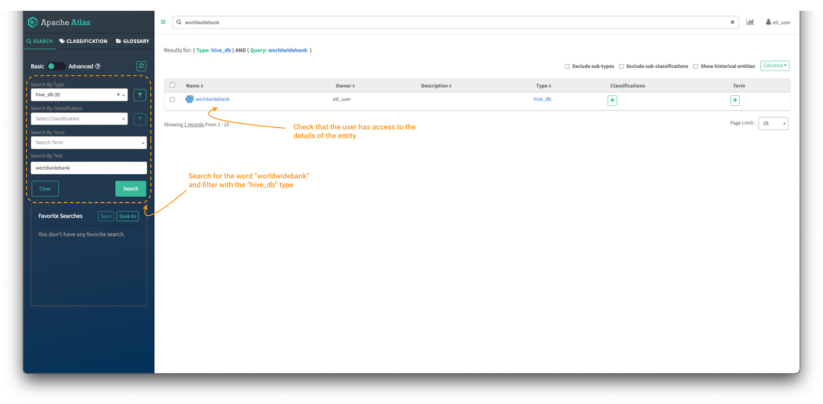
Picture 13 – Knowledge curator entity search
- First, seek for the worldwidebank belongings utilizing the search bar. You too can use the “search by kind” filter on the left panel to restrict the search to the “hive_db” entity kind.
- As information curator, it is best to have the ability to see the entity and be allowed to entry the main points of the worldwidebank database entity. It ought to have a clickable hyperlink to the entity object
- Click on on the entity object to see its particulars.
After clicking the entity identify, the entity particulars web page is proven:
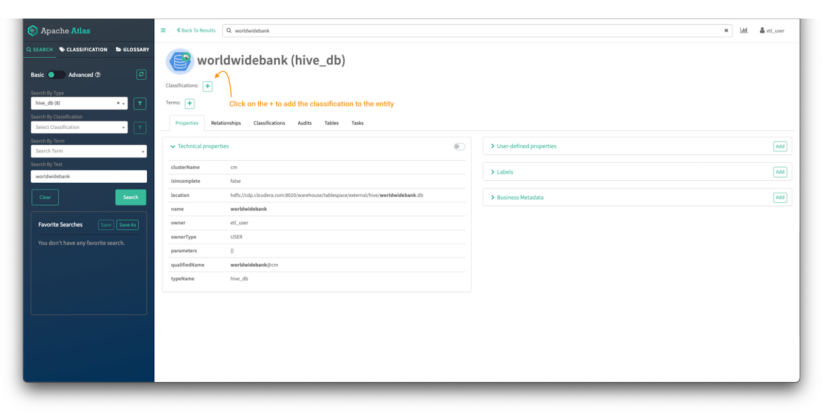
Picture 14 – Worldwide Financial institution database entity element
Within the high of the display, you possibly can see the classifications assigned to the entity. On this case there aren’t any tags assigned. We’ll assign one by clicking on the “+” signal.
Within the “Add Classification” display:
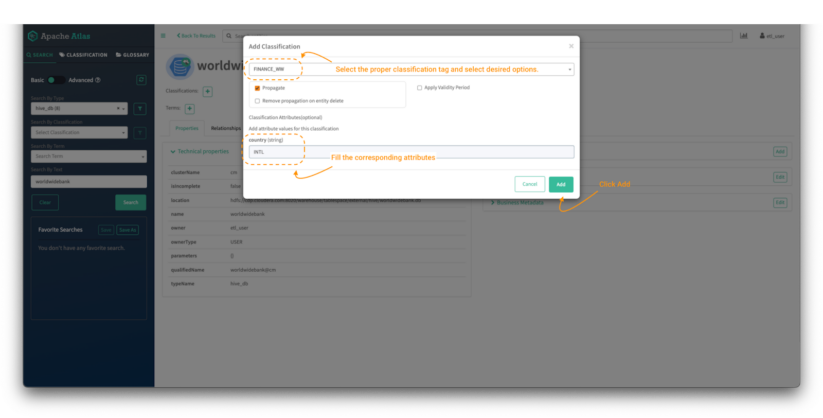
Picture 15 – Worldwide Financial institution database tag course of
- Seek for the FINANCE_WW tag and choose it.
- Then fill the suitable attributes if the classification tag has any. (Non-obligatory in Picture 5, within the 1.2 Knowledge Curator – etl_user person part above.)
- Click on on “add.”
That can tag an entity with the chosen classification.
Now, enrich the worldwidebank hive_db entity with a brand new label and a brand new enterprise metadata attribute referred to as “Venture.”
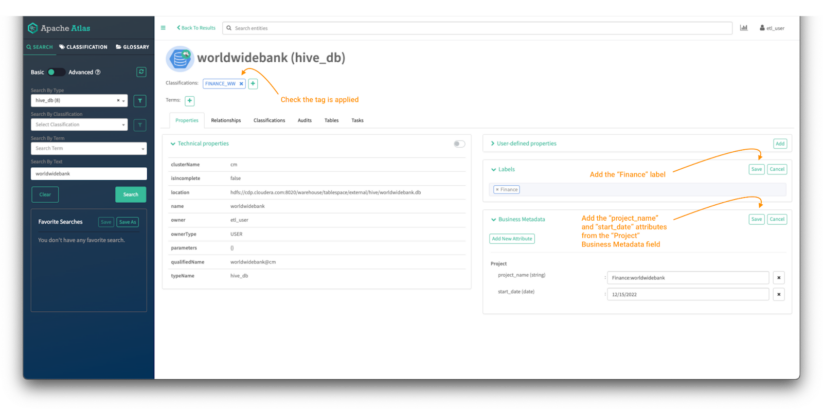
Picture 16 – Worldwide Financial institution database tag course of
Now, enrich the worldwidebank hive_db entity with a brand new label and a brand new enterprise metadata attribute referred to as “Venture.”
- So as to add a label, click on “Add” on the labels menu.
- Kind the label within the house and click on “save.”
- So as to add a enterprise metadata attribute, click on “Add” on the enterprise metadata menu.
- Click on on “Add New Attribute” if it’s not assigned or “edit” if it already exists.
- Choose the attribute you wish to add and fill the main points and hit “save.”
NOTE: The creation of the enterprise metadata attributes will not be included within the weblog however the steps might be adopted right here.
With the “worldwidebank” Hive object tagged with the “FINANCE_WW” classification, the info client ought to have the ability to have entry to it and see the main points. Additionally, it is very important validate that the info client additionally has entry to all the opposite entities tagged with any classification that begins with “finance.”
2.3 Knowledge Client – joe_analyst person
To validate that the insurance policies are utilized accurately, login into Atlas:
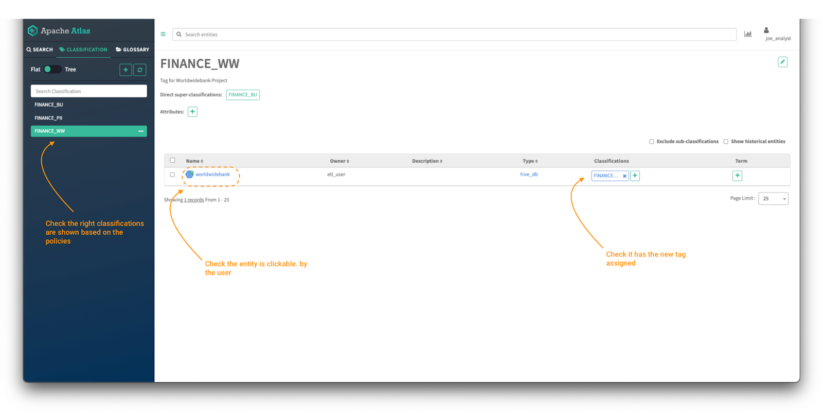
Picture 17 – Finance information belongings
Click on on the classifications tab and validate:
- The listing of tags which can be seen based mostly on the insurance policies created within the earlier steps. All of the insurance policies should begin with the phrase “finance.”
- Click on on the FINANCE_WW tag and validate the entry to the “worldwidebank” hive_db object.
After clicking on the “worldwidebank” object:
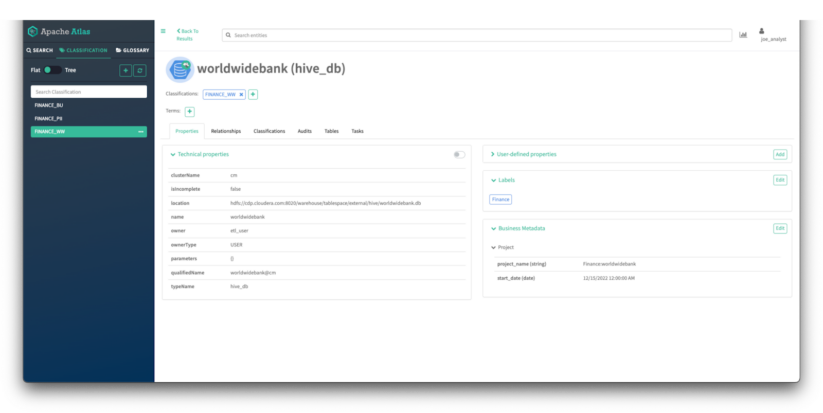
Picture 18 – WorldWideBank database asset particulars
You may see all the main points of the asset that the place enriched by the finance information curator in earlier steps:
- It is best to see all of the technical properties of the asset.
- It is best to have the ability to see the tags utilized to the asset
- It is best to see the labels utilized to the asset.
- It is best to see the enterprise metadata attributes assigned to the asset.
3. Authorization for Glossary and Glossary Phrases
On this part, we’ll clarify how an information steward can create insurance policies to permit fine-grained entry controls over glossaries and glossary phrases. This permits information stewards to manage who can entry, enrich or modify glossary phrases to guard the content material from unauthorized entry or errors.
A glossary supplies applicable vocabularies for enterprise customers and it permits the phrases (phrases) to be associated to one another and categorized in order that they are often understood in several contexts. These phrases might be then utilized to entities like databases, tables, and columns. This helps summary the technical jargon related to the repositories and permits the person to find and work with information within the vocabulary that’s extra acquainted to them.
Glossaries and phrases may also be tagged with classifications. The good thing about that is that, when glossary phrases are utilized to entities, any classifications on the phrases are handed on to the entities as properly. From an information governance course of perspective, because of this enterprise customers can enrich entities utilizing their very own terminology, as captured in glossary phrases, and that may mechanically apply classifications as properly, that are a extra “technical” mechanism, utilized in defining entry controls, as we have now seen.

First, we’ll present how as an information steward you possibly can create a coverage that grants learn entry to glossary objects with particular phrases within the identify and validate that the info client is allowed to entry the particular content material.
3.1 Knowledge Steward – admin person
To create a coverage to manage entry to glossaries and phrases, you possibly can:
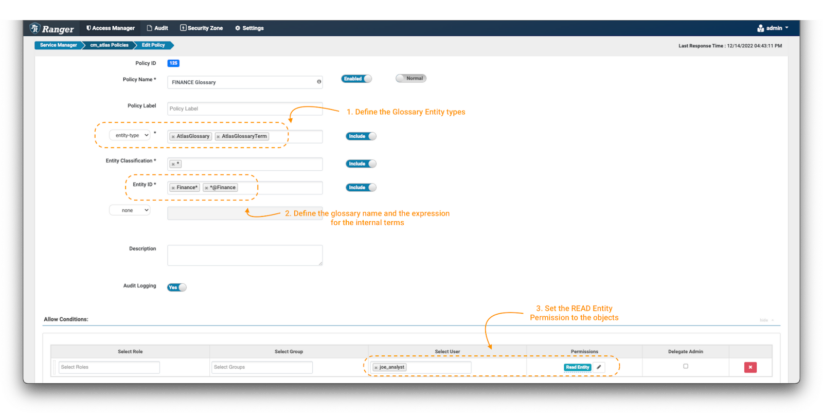
Picture 19 – Glossary management coverage
- Create a brand new coverage, however this time use the “entity-type” AtlasGlossary and AtlasGlossaryTerm. (notice 1)
- Within the entity classifications area, use the wildcard expression: *
- The entity ID is the place you possibly can outline which glossaries and phrases you wish to shield. In Atlas, all of the phrases of a glossary embrace a reference to it with an “@” on the finish of its identify (ex. time period@glossary). To guard the “Finance” glossary itself, use Finance*; and to guard is phrases, use *@Finance (notice 2).
- Within the Situations, choose the permissions Learn Entity to the info client joe_analyst to have the ability to see the glossary and its phrases. (notice 3)
3.2 Knowledge Client – joe_analyst person
To validate that solely “Finance” glossary objects might be accessed:
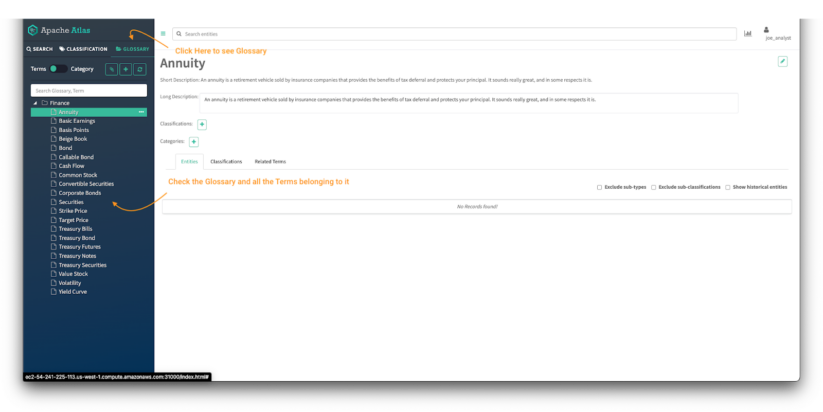
Picture 20 – Finance Atlas glossary
- Click on on the glossary tab within the Atlas panel.
- Examine the glossaries out there within the Atlas UI and the entry to the main points of the phrases of the glossary.
Conclusion
This text has proven how a corporation can implement a tremendous grained entry management technique over the info governance elements of the Cloudera platform, leveraging each Apache Atlas and Apache Ranger, the basic and integral elements of SDX. Though most organizations have a mature strategy to information entry, management of metadata is usually much less properly outlined, if thought-about in any respect. The insights and mechanisms shared on this article can assist implement a extra full strategy to information in addition to metadata governance. The strategy is essential within the context of a compliance technique the place information governance elements play a essential function.
You may be taught extra about SDX right here; or, we’d like to hear from you to debate your particular information governance wants.


