The Iranian risk actor referred to as MuddyWater has been attributed to a brand new command-and-control (C2) infrastructure referred to as DarkBeatC2, changing into the most recent such instrument in its arsenal after SimpleHarm, MuddyC3, PhonyC2, and MuddyC2Go.
“Whereas often switching to a brand new distant administration instrument or altering their C2 framework, MuddyWater’s strategies stay fixed,” Deep Intuition safety researcher Simon Kenin mentioned in a technical report printed final week.
MuddyWater, additionally referred to as Boggy Serpens, Mango Sandstorm, and TA450, is assessed to be affiliated with Iran’s Ministry of Intelligence and Safety (MOIS). It is recognized to be lively since not less than 2017, orchestrating spear-phishing assaults that result in the deployment of varied reliable Distant Monitoring and Administration (RMM) options on compromised methods.
Prior findings from Microsoft present that the group has ties with one other Iranian risk exercise cluster tracked as Storm-1084 (aka DarkBit), with the latter leveraging the entry to orchestrate damaging wiper assaults in opposition to Israeli entities.
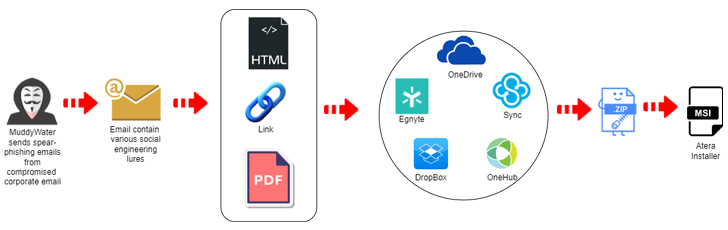
The newest assault marketing campaign, particulars of which have been additionally beforehand revealed by Proofpoint final month, commences with spear-phishing emails despatched from compromised accounts that comprise hyperlinks or attachments hosted on providers like Egnyte to ship the Atera Agent software program.
One of many URLs in query is “kinneretacil.egnyte[.]com,” the place the subdomain “kinneretacil” refers to “kinneret.ac.il,” an academic establishment in Israel and a buyer of Rashim, which, in flip, was breached by Lord Nemesis (aka Nemesis Kitten or TunnelVision) as a part of a provide chain assault focusing on the tutorial sector within the nation.
Lord Nemesis is suspected of being a “faketivist” operation directed in opposition to Israel. It is also value noting that Nemesis Kitten is a non-public contracting firm referred to as Najee Know-how, a subgroup inside Mint Sandstorm that is backed by Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC). The corporate was sanctioned by the U.S. Treasury in September 2022.
“That is vital as a result of if ‘Lord Nemesis’ have been capable of breach Rashim’s e-mail system, they could have breached the e-mail methods of Rashim’s clients utilizing the admin accounts that now we all know they obtained from ‘Rashim,'” Kenin defined.
The online of connections has raised the likelihood that MuddyWater might have used the e-mail account related to Kinneret to distribute the hyperlinks, thereby giving the messages an phantasm of belief and tricking the recipients into clicking them.
“Whereas not conclusive, the timeframe and context of the occasions point out a possible hand-off or collaboration between IRGC and MOIS to inflict as a lot hurt as doable on Israeli organizations and people,” Kenin additional added.
The assaults are additionally notable for counting on a set of domains and IP addresses collectively dubbed DarkBeatC2 which might be chargeable for managing the contaminated endpoints. That is achieved via PowerShell code designed to determine contact with the C2 server upon gaining preliminary entry by way of different means.
In keeping with impartial findings from Palo Alto Networks Unit 42, the risk actor has been noticed abusing the Home windows Registry’s AutodialDLL operate to side-load a malicious DLL and finally arrange connections with a DarkBeatC2 area.
The mechanism, particularly, entails establishing persistence by way of a scheduled job that runs PowerShell to leverage the AutodialDLL registry key and cargo the DLL for C2 framework. The cybersecurity agency mentioned the approach was put to make use of in a cyber assault aimed toward an unnamed Center East goal.
Different strategies adopted by MuddyWater to determine a C2 connection embody the usage of a first-stage payload delivered through the spear-phishing e-mail and leveraging DLL side-loading to execute a malicious library.
A profitable contact permits the contaminated host to obtain PowerShell responses that, for its half, fetches two extra PowerShell scripts from the identical server.
Whereas one of many scripts is designed to learn the contents of a file named “C:ProgramDataSysInt.log” and transmit them to the C2 server through an HTTP POST request, the second script periodically polls the server to acquire further payloads and writes the outcomes of the execution to “SysInt.log.” The precise nature of the next-stage payload is at the moment unknown.
“This framework is much like the earlier C2 frameworks utilized by MuddyWater,” Kenin mentioned. “PowerShell stays their ‘bread and butter.'”
Curious Serpens Targets Protection Sector with FalseFont Backdoor
The disclosure comes as Unit 42 unpacked the inside workings of a backdoor referred to as FalseFont that is utilized by an Iranian risk actor referred to as Peach Sandstorm (aka APT33, Curious Serpens, Elfin, and Refined Kitten) in assaults focusing on the aerospace and protection sectors.
“The risk actors mimic reliable human sources software program, utilizing a pretend job recruitment course of to trick victims into putting in the backdoor,” safety researchers Tom Fakterman, Daniel Frank, and Jerome Tujague mentioned, describing FalseFont as “extremely focused.”
As soon as put in, it presents a login interface impersonating an aerospace firm and captures the credentials in addition to the tutorial and employment historical past entered by the sufferer to a threat-actor managed C2 server in JSON format.
The implant, in addition to its graphical consumer interface (GUI) element for consumer inputs, additionally stealthily prompts a second element within the background that establishes persistence on the system, gathers system metadata, and executes instructions and processes despatched from the C2 server.
Different options of FalseFont embody the power to obtain and add recordsdata, steal credentials, seize screenshots, terminate particular processes, run PowerShell instructions, and self-update the malware.