ESET Analysis
How ESET Analysis discovered a kill swap that had been used to take down some of the prolific botnets on the market
01 Nov 2023
•
,
3 min. learn

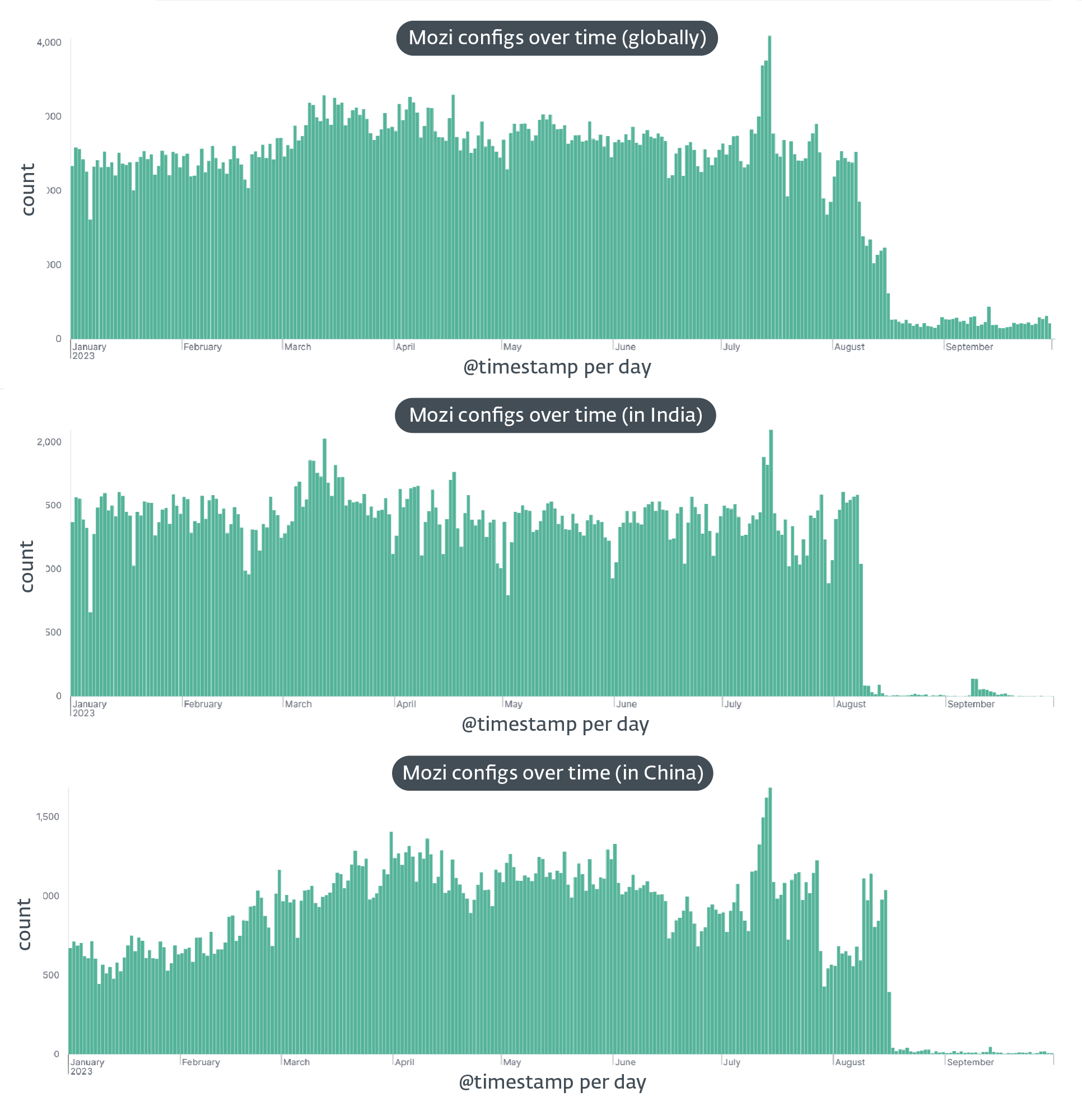
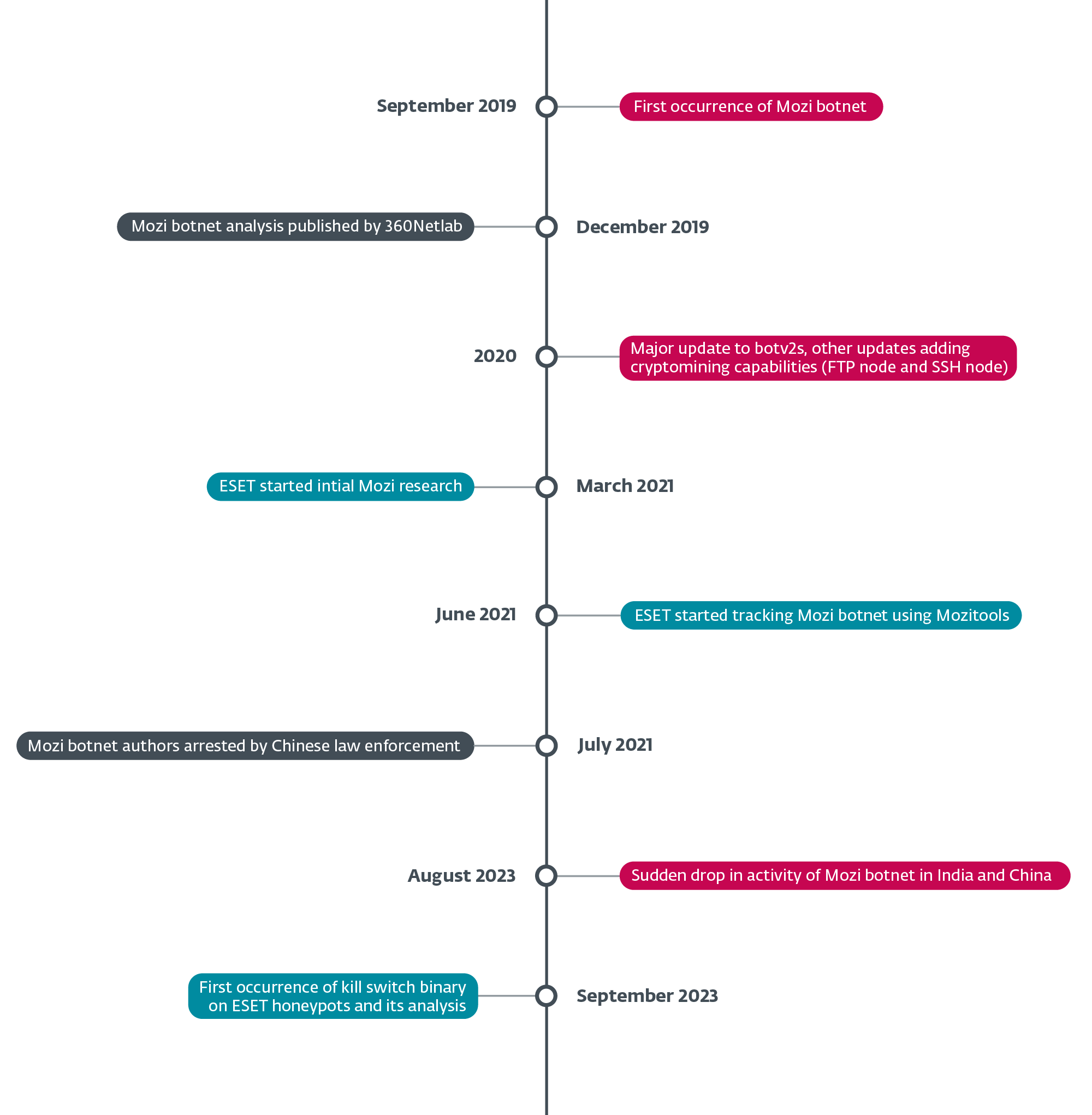
In August 2023, the infamous Mozi botnet, notorious for exploiting vulnerabilities in a whole bunch of hundreds of IoT gadgets every year, skilled a sudden and unanticipated nosedive in exercise. First noticed in India on August 8th, 2023 and every week later in China on August 16th, this mysterious disappearance stripped Mozi bots of most of their performance.
Our investigation into this occasion led us to the invention of a kill swap on September 27th, 2023. We noticed the management payload (configuration file) inside a person datagram protocol (UDP) message that was lacking the standard encapsulation of BitTorrent’s distributed sloppy hash desk (BT-DHT) protocol. The individual behind the takedown despatched the management payload eight occasions, every time instructing the bot to obtain and set up an replace of itself by way of HTTP.
The kill swap demonstrated a number of functionalities, together with:
- killing the mother or father course of, i.e., the unique Mozi malware,
- disabling some system companies resembling sshd and dropbear,
- changing the unique Mozi file with itself,
- executing some router/machine configuration instructions,
- disabling entry to varied ports (iptables -j DROP), and
- establishing the identical foothold because the changed unique Mozi file
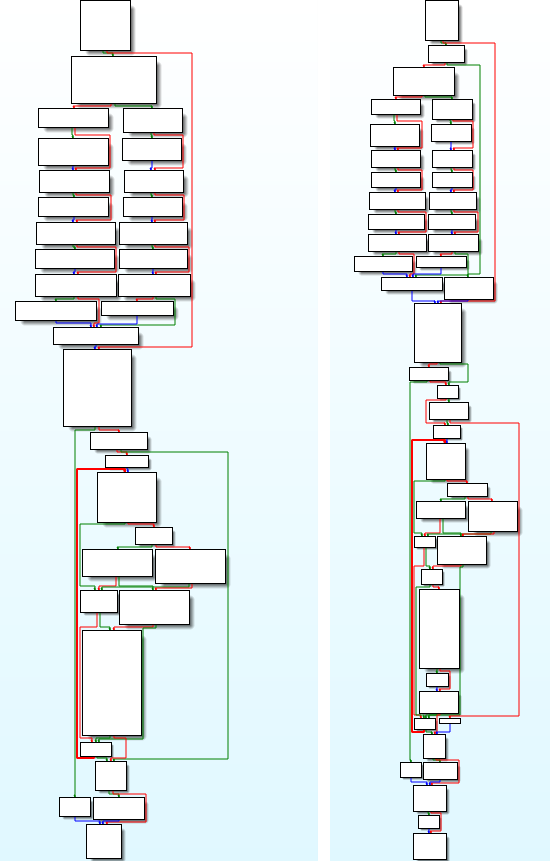
We recognized two variations of the management payload, with the most recent one functioning as an envelope containing the primary one with minor modifications, resembling including a operate to ping a distant server, most likely meant for statistical functions.
Regardless of the drastic discount in performance, Mozi bots have maintained persistence, indicating a deliberate and calculated takedown. Our evaluation of the kill swap reveals a powerful connection between the botnet’s unique supply code and lately used binaries, and in addition using the right non-public keys to signal the management payload (see Determine 2).

This leads us to the speculation suggesting two potential originators of this takedown: the Mozi botnet creators, or Chinese language regulation enforcement forcing the cooperation of the creators. The sequential focusing on of bots in India after which in China means that the takedown was carried out intentionally, with one nation focused first and the opposite every week later.
The demise of some of the prolific IoT botnets is an interesting case of cyberforensics, offering us with intriguing technical data on how such botnets within the wild are created, operated, and dismantled. We’re persevering with to analyze this case and can publish an in depth evaluation within the coming months. However for now, the query stays: Who killed Mozi?
For any inquiries about our analysis revealed on WeLiveSecurity, please contact us at threatintel@eset.com.
ESET Analysis affords non-public APT intelligence reviews and information feeds. For any inquiries about this service, go to the ESET Menace Intelligence web page.
IoCs
Recordsdata
|
SHA-1 |
Filename |
Detection |
Description |
|
758BA1AB22DD37F0F9D6FD09419BFEF44F810345 |
mozi.m |
Linux/Mozi.A |
Authentic Mozi bot. |
|
9DEF707F156DD4B0147FF3F5D1065AA7D9F058AA |
ud.7 |
Linux/Mozi.C |
Mozi bot kill swap. |
Community
|
IP |
Area |
Internet hosting supplier |
First seen |
Particulars |
|
157.119.75[.]16 |
N/A |
AS135373 EFLYPRO-AS-AP EFLY NETWORK LIMITED |
2023-09-20 |
Kill swap internet hosting server |
MITRE ATT&CK methods
This desk was constructed utilizing model 13 of the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
|
Tactic |
ID |
Title |
Description |
|
Useful resource Growth |
Purchase Infrastructure: Digital Personal Server |
The Mozi kill swap operators rented a server at eflycloud.com to host the replace information. The Mozi kill swap operators rented a number of servers that ship payloads on BT-DHT networks. |
|
|
Preliminary Entry |
Exploit Public-Dealing with Utility |
The Mozi kill swap operators despatched an replace command to Mozi shoppers on a BT-DHT community. |
|
|
Persistence |
Boot or Logon Initialization Scripts: RC Scripts |
The kill swap creates a number of scripts, resembling /and so forth/rc.d/rc.native, to ascertain persistence. |
|
|
Exfiltration |
Exfiltration Over Different Protocol: Exfiltration Over Unencrypted Non-C2 Protocol |
The kill swap sends an ICMP ping to the operator maybe for the aim of monitoring. |
|
|
Affect |
Service Cease |
The kill swap stops the SSH service and blocks entry to it with iptables. |